Lamellar keratoplasties have had a great impact in the management of corneal edema due to endothelial dysfunction. Minimally invasive transplant techniques such as Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK) have helped to reduce the morbidity involved in performing penetrating keratoplasty in this type of patient. Even so, these are complex techniques that are not free of complications and require a long line of surgical learning and an even more demanding experience in postoperative management.
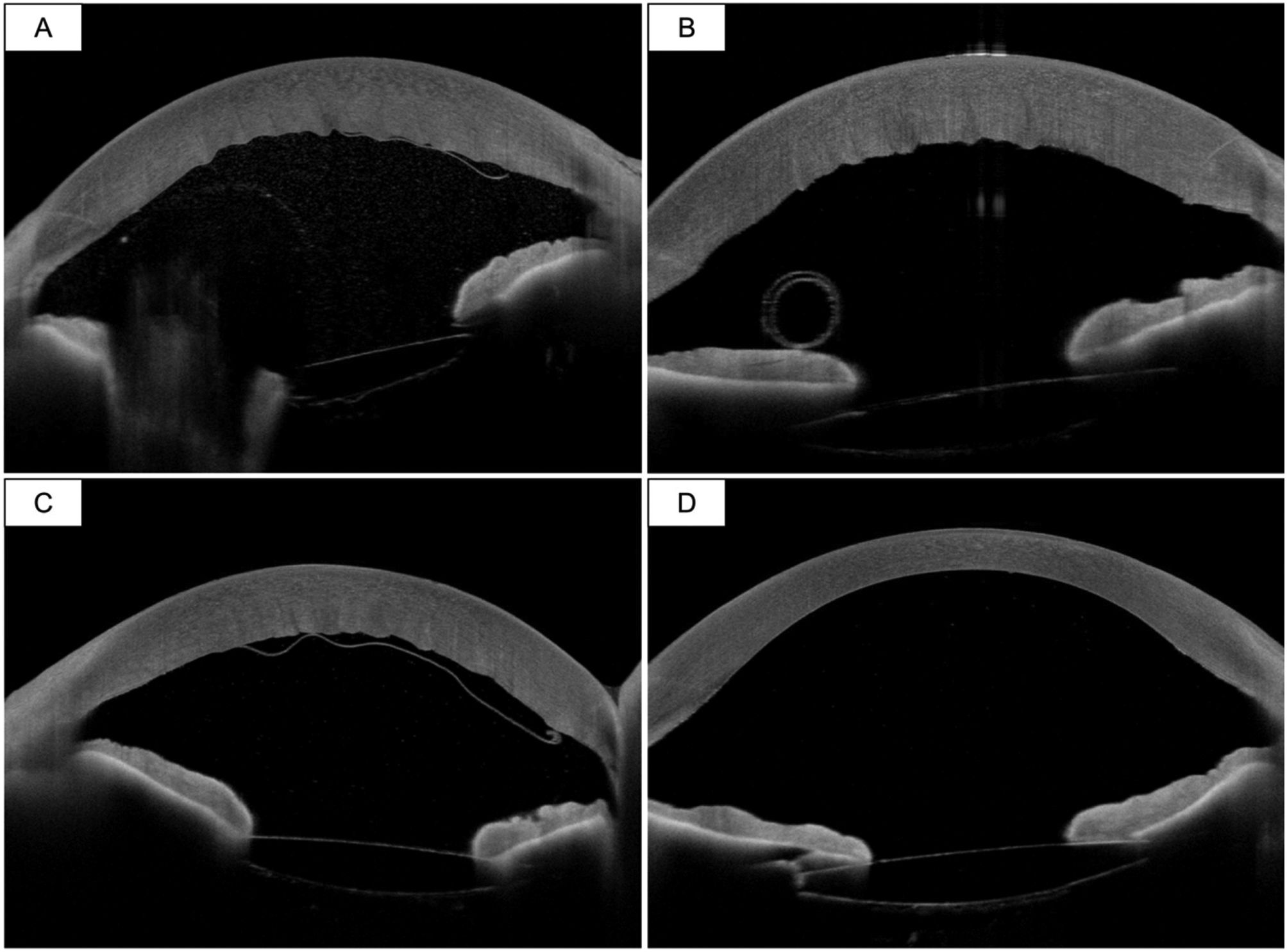
Clinical caseAn 89-year-old woman suffering from Fuchs endothelial dystrophy and undergoing combined cataract and DMEK surgery presented stromal edema predominantly inferior and sectoral detachment of the graft 24 h after the intervention. After re-bubbling in consultations and 4 days later, the graft was observed rolled and free in the anterior chamber.
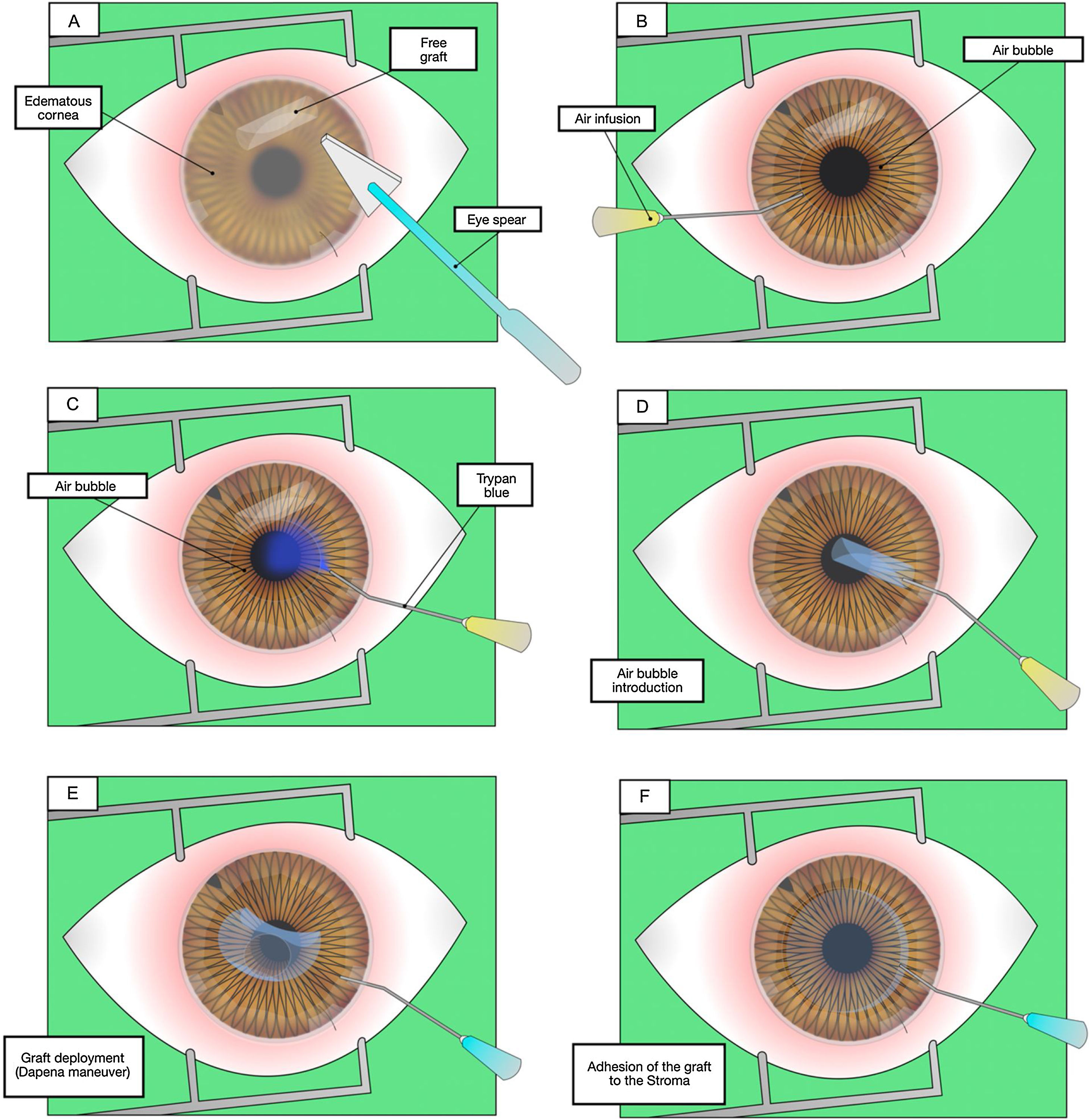
She underwent re-DMEK with preservation of the original graft after 24 h, with de-epithelialization to optimize visualization. The graft was stained with trypan blue and the posterior stroma was protected with air. The graft was reimplanted under intraocular maneuvers and with an air bubble.
24 h after surgery, the adhered graft was observed, with a great decrease in stromal edema. One month later, the patient had a clear cornea, persistent complete graft adhesion, and visual acuity of 0.9.
ConclusionThe discovery of free roll in the anterior chamber after DMEK surgery constitutes the most complex form of graft detachment. Corneal edema as well as the arrangement of the different intraocular structures are conditions to be considered for the surgical resolution of this complication. In many cases, surgical repositioning of the graft is feasible, which means saving costs without the need to use new donor corneal tissues.
Las queratoplastias lamelares han supuesto un gran impacto en el manejo del edema corneal por disfunción endotelial. Las técnicas de trasplante mínimamente invasivo como la Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK) han permitido reducir la morbilidad que suponía la realización de una queratoplastia penetrante en este tipo de pacientes. Aun así, se trata de técnicas complejas que no están exentas de complicaciones y que requieren una larga línea de aprendizaje quirúrgico y una aún más exigente experiencia en el manejo postoperatorio.
Caso clínicoUna mujer de 89 años afecta de distrofia endotelial de Fuchs e intervenida de cirugía combinada de catarata y DMEK presentó a las 24 h de la intervención un edema estromal de predominio inferior y un despegamiento sectorial del injerto. Tras un re-bubbling en consultas y 4 días más tarde, se observó el injerto enrollado y libre en cámara anterior.
Se intervino de re-DMEK con preservación del injerto original tras 24 h, con desepitelización para optimizar la visualización. Se tiñó el injerto con azul tripán y se protegió el estroma posterior con aire. Se reimplantó el injerto bajo maniobras intraoculares y con burbuja de aire.
A las 24 h de la cirugía se observó el injerto adherido, con una gran disminución del edema estromal. Un mes después, la paciente presentaba una córnea transparente, una persistente adhesión completa del injerto y una agudeza visual de 0.9.
ConclusiónEl hallazgo del free roll en cámara anterior tras cirugía de DMEK constituye la forma más compleja de despegamiento del injerto. El edema corneal así como la disposición de las diferentes estructuras intraoculares son condicionantes a tener en cuenta para la resolución quirúrgica de esta complicación. En muchos casos el reposicionamiento quirúrgico del injerto es factible, hecho que implica ahorrar costes sin necesidad de utilizar nuevos tejidos corneales donantes.
La OCT de segmento anterior resulta una herramienta imprescindible para conocer la situación del injerto y poder planificar de manera óptima la cirugía.