Two common ailments in contemporary Western society are gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and morbid obesity (MO)1. Despite the many parallels between their epidemiology and presumed etiology, the correlation between the 2 processes remains incomplete1. There is an association between central obesity and the prevalence of GERD, as studies have shown that the gastric pressure, gastroesophageal pressure gradient and incidence of hiatal hernia are high in these patients2. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is considered the gold standard surgical treatment for patients with MO and GERD1–4. The latter occurs in 70% of patients who are candidates for bariatric surgery, and its resolution is estimated at between 85% and 90%4, regardless of the weight loss obtained5.
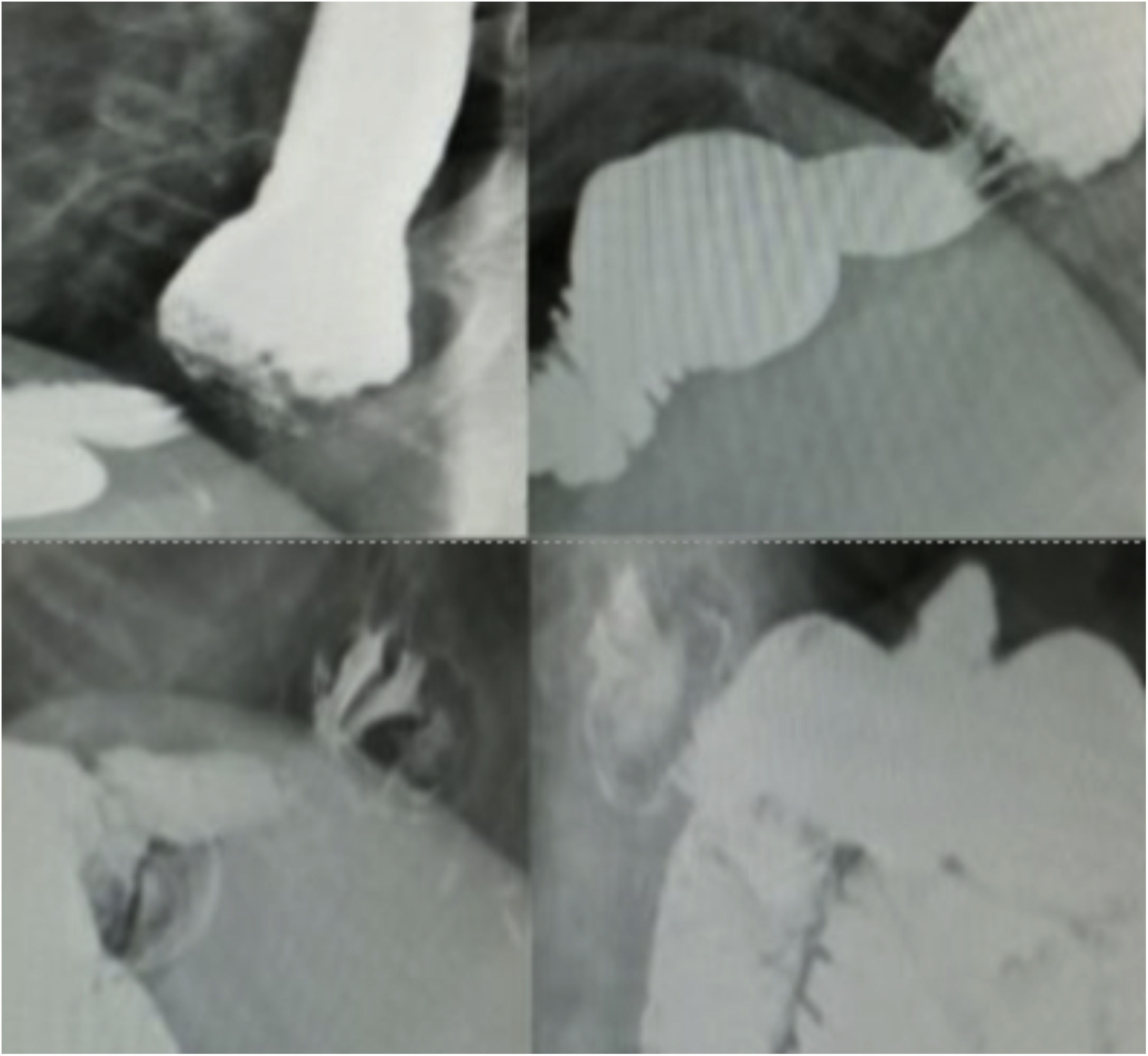
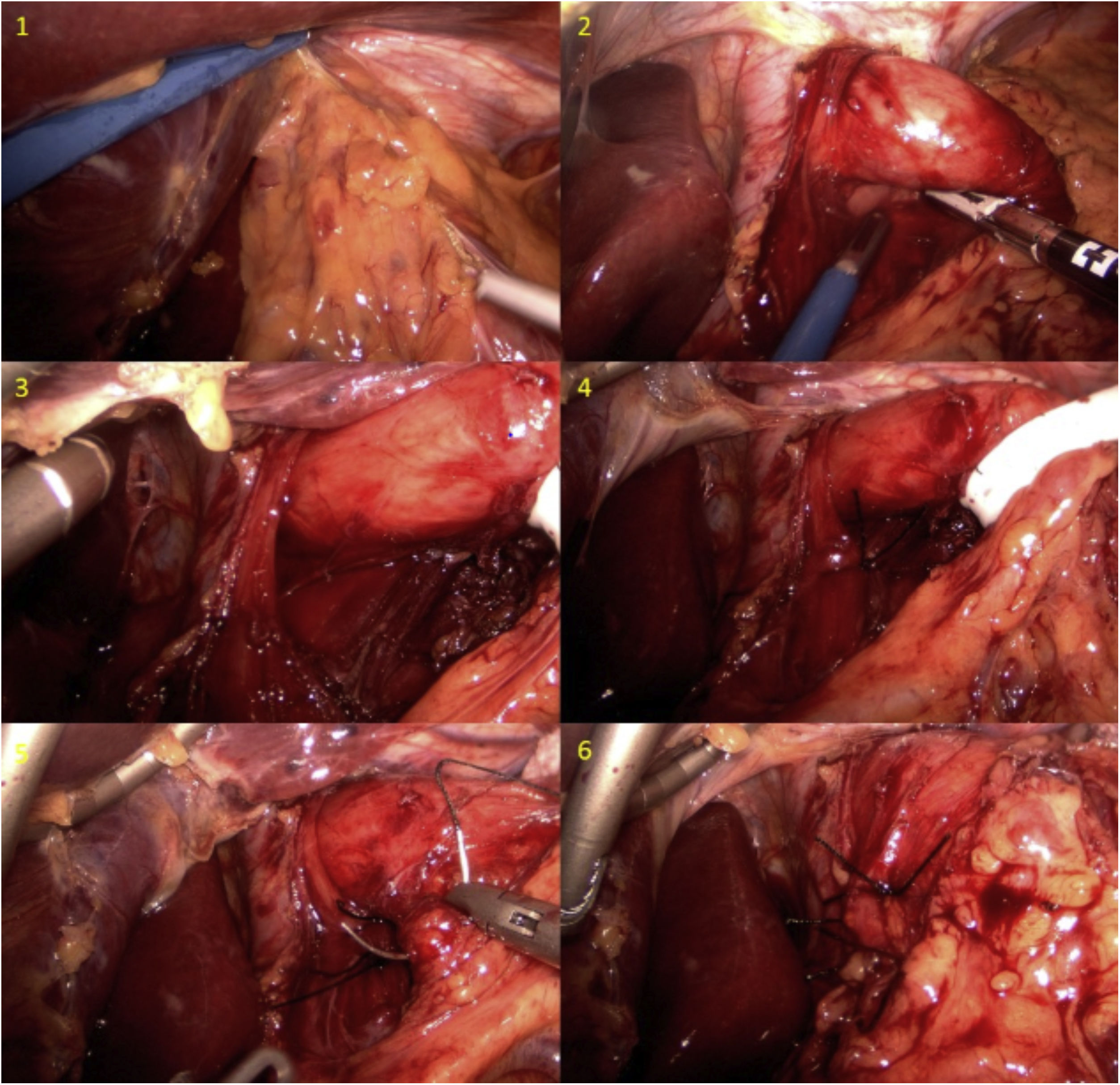
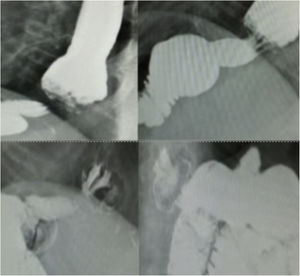
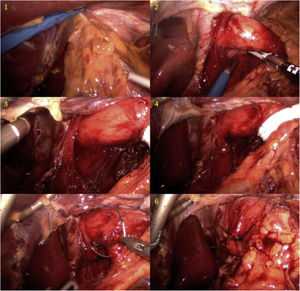
We present an unusual clinical case of a patient with coexisting MO and GERD, whose GERD symptoms worsened despite RYGB. A 50-year-old female patient had a personal history of hiatal hernia accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux (Los Angeles grade B peptic esophagitis) and a body mass index (BMI) of 44.6 kg/m2. In 2011, she had undergone simplified gastric bypass. The patient’s outpatient follow-up was good, with acceptable weight-loss results: 24 months after surgery, BMI was 28 kg/m2 and the percentage of excess BMI lost was 75.76%. However, her GERD did not improve and even worsened, despite treatment with high-dose proton pump inhibitors. She developed grade C peptic esophagitis (observed on digestive endoscopy) and a hiatal hernia due to sliding of the gastric stump (observed on barium swallow study) (Fig. 1). Esophageal pH monitoring revealed mixed pathological acid reflux with very severe intensity (DeMeester score: 60.1 points), and manometry was anodyne. Based on her previous history and complementary studies, we decided to perform laparoscopic Hill’s gastropexy (Fig. 2). We released the adhesions of the omentum to the esophagogastric junction. After dissection of both crura and exposure of the esophagus, both were closed with two 2/0 silk sutures. Subsequently, we affixed the lesser curvature to the preaortic fascia using 2/0 silk sutures. The postoperative period was uneventful, and the patient was discharged from the hospital with subsequent outpatient follow-up. Currently, 24 months after surgery, the patient remains asymptomatic, showing no signs of reflux during the follow-up barium swallow study or pH monitoring (DeMeester score 13.8 points). In addition, no esophagitis lesions were found during follow-up endoscopy.
RYGB is currently the most frequently advocated bariatric technique for patients with MO who are candidates for bariatric surgery with GERD1–4. Few cases have been described of patients presenting worsened GERD symptoms after this technique6. When this occurs, the surgical possibilities are limited to infrequently used techniques. Based on the classic description by Hill7 and on other studies comparing different antireflux techniques8, our group has incorporated Hill’s gastropexy in patients with MO and GERD after RYGB. Hill’s gastropexy does not seek to create a valvular mechanism, but rather ensures that the lower esophageal sphincter remains below the diaphragm by affixing the lesser curvature to the preaortic fascia8. The laparoscopic Hill repair has demonstrated excellent long-term durability, and 85% of results are ‘good’ to ‘excellent’, with a median follow-up of 19 years and a reoperation rate of less than 10%9. Recently, Sanchez Pernaute et al.10 have shown good results with this technique in patients with MO and GERD who were candidates for laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Despite being a technique that has fallen into disuse today, it is a technical resource to consider when the gold standard techniques cannot be carried out, as it is a simple technique that is not associated with increased postoperative complications.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Estébanez-Ferrero B, Torres-Fernández R, Ferrer-Márquez M, Sánchez-Fuentes P, Vidaña-Márquez E. Manejo laparoscópico del reflujo gastroesofágico tras bypass gástrico en Y de Roux mediante gastropexia de Hill. Cir Esp. 2022;100:182–184.