Acute appendicitis (AA) is the most frequent cause of emergency abdominal surgery in our setting, representing around 60% of all acute abdominal diseases requiring surgery.1 In western countries, a very uncommon cause of AA is amebic infection, although its incidence is growing due to immigration.
We present the case of a 38-year-old male patient who had emigrated from Burkina Faso and had been living in our country for 9 years. He came to our emergency department complaining of abdominal symptoms that had developed over the previous 24h; they had initiated in the umbilical region and had been located in recent hours in the right iliac fossa (RIF). The patient presented with a fever of 38.4°C, with no diarrhea or any other symptoms. On physical examination, there was pain upon palpation of the RIF with abdominal guarding and signs of peritoneal irritation. Emergency blood tests showed hemoglobin 14mg/dl, 17460 leukocytes (85% neutrophils) and 94% prothrombin activity. Abdominal ultrasound revealed findings compatible with retrocecal AA. Emergency surgery was performed laparoscopically, and purulent AA was found with purulent peritonitis in the RIF. A laparoscopic appendectomy was performed. The patient had a favorable postoperative and was discharged on the 2nd day post-op.
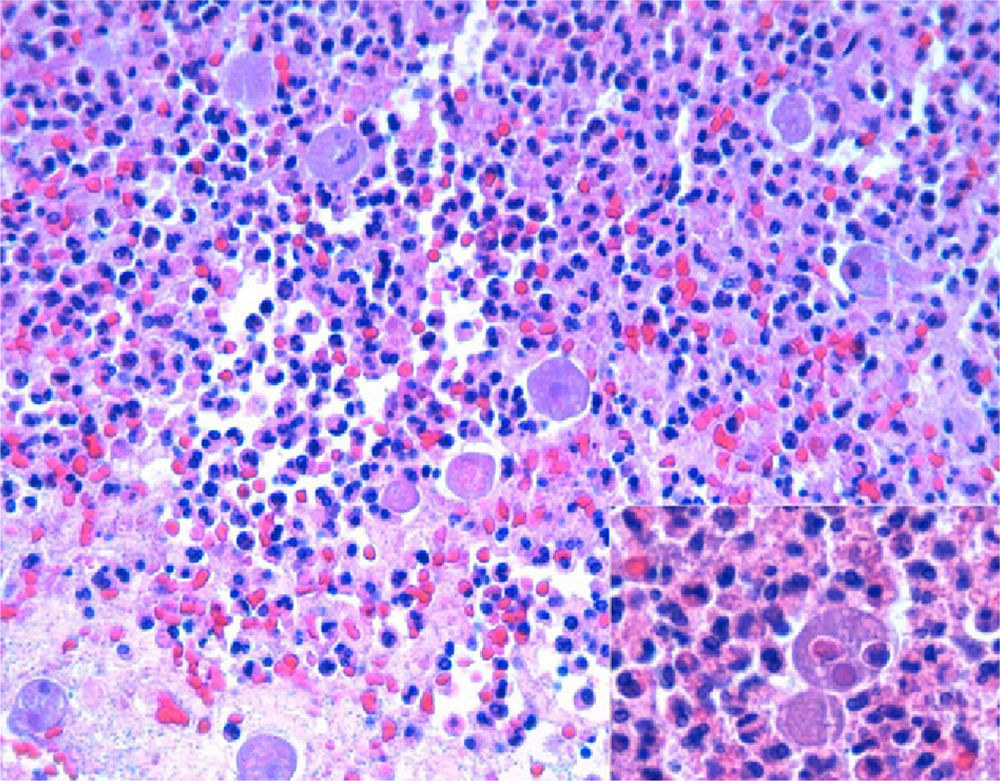
The pathology study reported a cecal appendix with intense acute inflammatory infiltrates and areas of gangrene and periappendicitis. At a greater magnification, numerous Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites were observed, interspersed with fibrin-inflammatory material in the appendix lumen (hematoxylin–eosin stain, Fig. 1). Subsequently, specific staining was done with the PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) technique, demonstrating the presence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in the inflammatory tissue substituting the appendicular mucosa (Fig. 2). When the diagnosis of amebic AA was made, antiparasitic treatment was initiated with metronidazole.
Parasitic appendicitis is a very rare entity in western countries. There are few published reports about this pathology in the literature, and are limited to communications of clinical cases that have appeared due to growing immigration in our society. Other reviews from under-developed countries describe a frequency of parasitic appendicitis between 2.3% and 3.9% of the total number of surgically treated AA.2,3 Precarious living conditions, poor hygiene and the ingestion of parasites as cysts that later transform into trophozoites are the most important predisposing causes in these countries.
The presence of these trophozoites produces edema of the appendix mucosa, with obstruction of the lumen and later appendix infection.4 The clinical symptoms of amebic appendicitis does not normally differ from the usual AA symptoms (pain in RIF with local peritonism and fever), although it may be associated with dysentery, which is characterized by bloody diarrhea with abundant mucus, abdominal pain and fever. The post-op evolution of patients with amebic appendicitis is similar to other patients except for the greater percentage of intestinal fistulas (2.3% vs 0.07%).3 The treatment of choice for these patients, as in any classic appendicitis, is surgery followed by appropriate antibacterial coverage (generally Metronidazole) and complete patient work-up in specialized units with stool analysis.
In conclusion, acute appendicitis due to amebae is exceptionally rare in our society, although increased immigration in our setting could entail its growing prevalence. Therefore, proper patient medical histories are increasingly important, especially in patients with risk factors. The two fundamental pillars of this disease are surgery and correct antiparasitic treatment.
Please cite this article as: Abellán I, et al. Apendicitis aguda amebiásica. Cir Esp. 2013;91:201–2