Veno-venous extracorporeal oxygenation for respiratory support has emerged as a rescue alternative for patients with hypoxemia. However, in some patients with more severe lung injury, extracorporeal support fails to restore arterial oxygenation. Based on four clinical vignettes, the aims of this article were to describe the pathophysiology of this concerning problem and to discuss possibilities for hypoxemia resolution.
METHODS:Considering the main reasons and rationale for hypoxemia during veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, some possible bedside solutions must be considered: 1) optimization of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation blood flow; 2) identification of recirculation and cannula repositioning if necessary; 3) optimization of residual lung function and consideration of blood transfusion; 4) diagnosis of oxygenator dysfunction and consideration of its replacement; and finally 5) optimization of the ratio of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation blood flow to cardiac output, based on the reduction of cardiac output.
CONCLUSION:Therefore, based on the pathophysiology of hypoxemia during veno-venous extracorporeal oxygenation support, we propose a stepwise approach to help guide specific interventions.
Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) has been widely used to support patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (1-5). In some patients, however, extracorporeal support fails to restore arterial oxygenation (6-8). Knowledge of the multiple mechanisms possibly underlying this failure to oxygenate is essential for troubleshooting this concerning clinical situation (6,9). In this manuscript, we use four clinical vignettes to explore the potential mechanisms of severe hypoxemia during VV-ECMO and to suggest possible bedside solutions.
CALCULATIONSFor the calculations, we used the standard formulas: (9,10)
- •
ECMO recirculation ratio (%) = (SatdO2 – ScvO2) × 100 / (SatrO2 – ScvO2);
- •
Pulmonary shunt (%) = (CcO2 – CvO2) × 100 / (CcO2 – CaO2);
- •
CaO2 (mL O2 / 100 mL blood) = 1.36 × Hb × Arterial SatO2 + 0.0031 × PaO2;
- •
CvO2 (mL O2 / 100 mL blood) = 1.36 × Hb × ScvO2 + 0.0031 × PvO2; and
- •
CcO2 (mL O2 / 100 mL blood) = 1.36 × Hb × 1 + 0.0031 × <1?show=[to]?>(Ventilator FiO2 × 690).
SatdO2 – oxygen saturation at the drainage cannula; ScvO2 – oxygen saturation at the superior vena cava; SatrO2 – oxygen saturation at the return cannula; CxO2 – content of oxygen in arterial (a), venous (v), or pulmonary capillary (c) blood sample.
CLINICAL VIGNETTESSevere hypoxemia was diagnosed when PaO2 persisted at less than 50 mm Hg in two arterial blood samples at least 60 minutes apart with ongoing VV-ECMO support. Blood samples were collected while the patient slowly performed three to four inspirations, to average the cyclic variations of PaO2 during the respiratory cycle, which is common in patients with severe ARDS (11). All ECMO-supported patients were cannulated using a veno-venous configuration. Patients 1, 3, and 4 were cannulated using the femoro–jugular approach, in which a single, large, multiperforated drainage cannula was inserted into the femoral vein and was advanced to the cavo-atrial junction. The return cannula was a single-stage catheter inserted into the right internal jugular vein and advanced to the superior vena cava. A femoro-femoral approach was used on patient 2, in which both the drainage and return cannulae were inserted through femoral veins. The first was positioned in the superior cavo-atrial junction, and the second, in the inferior vena cava.
The clinical characteristics of the patients are shown in Table1. In Table2, the characteristics of the patients at the time of the diagnosis of severe hypoxemia are described. Cardiac output was estimated by transthoracic echocardiography using the velocity time integral technique. The ECMO device consisted of a centrifugal magnetic pump with a polymethylpentene oxygenation membrane (Rotaflow/Jostra Quadrox - D, Maquet Cardiopulmonary AG, Hirrlingen, Germany).
Characteristics of patients.
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General characteristics | ||||
| Age – yr | 14 | 18 | 17 | 30 |
| Sex | F | F | M | F |
| Weight – kg | 48 | 48 | 84 | 60 |
| SAPS 3 at ECMO beginning | 105 | 89 | 74 | 95 |
| Etiological diagnosis of ARDS | SLE+alveolar hemorrhage | Lobar pneumonia+ cystic fibrosis | Aspirationpneumonitis | Pneumocystosis+ AIDS |
| ECMO retrieval | By ambulance | No retrieval | By ambulance | By ambulance |
| P/F ratio at ECMO beginning – mm Hg | 36 | 43 | 47 | 55 |
| PaCO2 at ECMO beginning – mm Hg | 36 | 117 | 47 | 55 |
| ECMO support characteristics | ||||
| Configuration | Veno-venous | Veno-venous | Veno-venous | Veno-venous |
| Days on ECMO support | 6 | 18 | 11 | 32 |
| Anticoagulation | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ECMO weaning and withdrawal | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| ICU support while on ECMO | ||||
| Vasopressors | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Inotropes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Renal replacement therapy | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Mechanical ventilation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Other hypoxemia rescue therapy | No | Alveolar recruitment | Nitric oxide | Nitric oxide |
| 90-day outcomes | ||||
| Survival | Yes | No | No | No |
| Dialysis dependency | No | ———- | ———- | ———- |
| Oxygen dependency | No | ———- | ———- | ———- |
ECMO - extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus.
AIDS - acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
ICU - intensive care unit.
Clinical characteristics at the time of severe hypoxemia diagnosis.
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMO support | ||||
| ECMO day of hypoxemia occurrence *) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ECMO blood flow – mL/min | 5080 | 6000 | 6500 | 5300 |
| Sweep gas flow – L/min | 2 | 5 | 10 | 7 |
| FiO2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Drainage cannula diameter – French | 20 | 22 | 21 | 22 |
| Atrial cannula diameter – French | 20 | 22 | 21 | 22 |
| Drainage cannula SatO2 - % | 58 | 85 | 61 | 64 |
| Drainage cannula PO2 – mm Hg | 30 | 46 | 32 | 35 |
| Return cannula SatO2 - % | 100 | 100 | 99 | 100 |
| Return cannula PO2 – mm Hg | 180 | 402 | 220 | 163 |
| Blood flow/cardiac output ratio | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.50 |
| Recirculation - % | 26.3 | 62.5 | 7.3 | 20.0 |
| Mechanical ventilation | ||||
| Ventilatory mode | PSV | PCV | PCV | PCV |
| FiO2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| PEEP – cm H2O | 15 | 15 | 10 | 13 |
| Plateau pressure – cm H2O | 20 | 25 | 20 | 18 |
| Tidal volume – mL | 150 | 90 | 50 | 90 |
| Respiratory rate – breaths/min | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Patients characteristics | ||||
| Arterial pH | 7.421 | 7.435 | 7.500 | 7.370 |
| PaCO2 – mm Hg | 42 | 41 | 36 | 47 |
| PvCO2 – mm Hg | 52 | 51 | 61 | 59 |
| PaO2 – mm Hg | 46 | 45 | 45 | 37 |
| PvO2 – mm Hg | 23 | 29 | 35 | 30 |
| Arterial Sat O2 - % | 82 | 88 | 80 | 84 |
| Venous Sat O2 - % | 43 | 60 | 58 | 55 |
| Hemoglobin – g/dL | 7.4 | 7.5 | 8.2 | 8.0 |
| Pulmonary shunt - % | 36.6 | 44.9 | 62.9 | 47.8 |
| Lactate – mmol/L | 1.38 | 1.12 | 2.6 | 2.1 |
| Lung injury score | 3.75 | 3.50 | 4.00 | 3.75 |
| Temperature - °C | 37.2 | 38.0 | 39.0 | 37.6 |
| Total SOFA | 14 | 17 | 18 | 12 |
| Hemodynamics | ||||
| Cardiac output – L/min | 8.9 | 9.8 | 11.5 | 10.6 |
| Heart rate – beats/min | 129 | 130 | 128 | 117 |
| Mean arterial blood pressure – mm Hg | 109 | 75 | 65 | 105 |
| Central venous pressure – mm Hg | 10 | 7 | 5 | 8 |
| Inotropes in use | None | None | None | None |
| Vasopressors in use | None | Norepinephrine | Norepinephrine | None |
| Sedation and analgesia | ||||
| Analgesia in use | Fentanyl | Fentanyl | Fentanyl | None |
| Sedation in use | None | Propofol | Propofol | None |
| RASS | 0 | -1 | -5 | 0 |
* This was the first day of severe hypoxemia
RASS - Richmond agitation sedation scale.
Classically, during VV-ECMO, the extracorporeal transmembrane oxygen transfer depends primarily on ECMO blood flow, and the transfer of carbon dioxide depends on sweep gas flow (10,12). Arterial blood oxygenation results from a more complex interplay among recirculation, ECMO blood flow, oxygenator function, patient cardiac output (CO), and pulmonary shunting (9).
For didactic reasons, the VV-ECMO support can be modeled by two oxygenators in series: the extracorporeal membrane and the native lungs (Figure1 - Panel A) (9). Through the first oxygenator (VV-ECMO apparatus), blood drawn from the vena cava is pumped at a set flow rate, leaving a fraction of the venous return, i.e., of the CO (13), to proceed to the heart deoxygenated. Therefore, any elevation of the CO, unaccompanied by equal elevations in the ECMO blood flow, will result in a higher fraction of the CO returning deoxygenated to the right heart and to the native lungs (Figure1 - Panel B). In this situation, the intuitive reaction would be to increase the VV-ECMO blood flow to improve oxygenation. This increase could, however, precipitate recirculation between the return and drainage cannulae, mitigating any possible benefits (9). In addition, high blood flows can cause hemolysis and collapse of the inferior vena cava over the drainage cannula, suddenly reducing blood flow and thus aggravating hypoxemia. Some authors have recognized an ECMO blood flow to cardiac output ratio greater than 0.6 as an index for ECMO efficiency (12).
VV-ECMO–supported patient model. Panel A shows a regular patient, in whom the ECMO blood flow (3.5 L/min)/cardiac output (5.0 L/min) ratio was equal to 0.7. In this condition, it is expected that only 1.5 L/min (30% of the venous return) will pass through the vena cava without oxygenation. Panel B exemplifies a hyperdynamic patient, in whom the ECMO blood flow (3.5 L/min)/cardiac output (10.0 L/min) ratio was equal to 0.35. In this example, 6.5 L/min (65% of the venous return) will pass through the vena cava without oxygenation. In the former example, if the patient has a severe lung injury with a high pulmonary shunt, he or she will most likely develop severe hypoxemia. SatdO2 – oxygen saturation at the drainage cannula. ScvO2 – oxygen saturation at the vena cava. SatrO2 – oxygen saturation at the return cannula. According to Mesai et al. (9):
ECMO effective blood flow = (1 – recirculation ratio) × ECMO blood flow.The second oxygenator in the model (native lungs, Figure1 – Panel A) will further improve blood oxygenation according to its residual function, which is inversely proportional to the pulmonary shunt (9). The pulmonary shunt can be modulated by decreasing the alveolar collapse, e.g., with the use of higher levels of end-expiratory pressure. The pulmonary shunt also depends on the CO, and it has been shown that reducing CO in healthy lungs slightly improves pulmonary shunting (14), an effect that is even more pronounced in injured lungs during hypoxemic respiratory failure (15). By the same token, the use of inotropic drugs can worsen pulmonary shunting (16). Oxygenation of mixed venous blood has been positively correlated with CO (17) and is an important modulator of the pulmonary shunt (14,15,18). In ICU patients, however, the response of the pulmonary shunt to venous hypoxemia is erratic, depending on systemic factors related to the underlying disease (19).
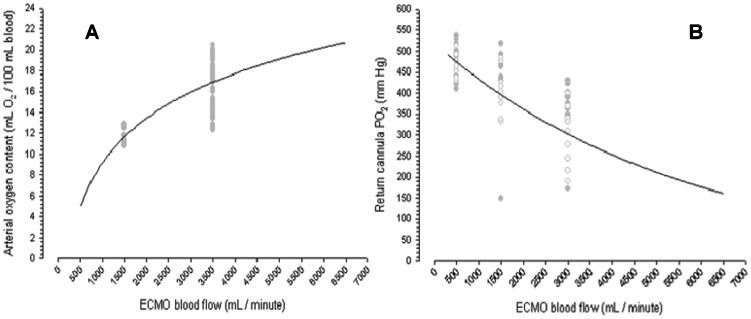
Blood recirculation from the return cannula to the drainage cannula can reduce the efficacy of the ECMO support because the membrane will oxygenate already oxygenated blood (10), while the systemic venous blood will return to the heart without proper oxygenation. Finally, oxygenator dysfunction can also contribute to persistent hypoxemia. The presence of blood clots or water drops inside the membrane reduces the exchange surface and consequently the oxygenator's efficiency. This complication can be diagnosed by the direct visualization of thrombi inside the membrane or by the presence of low post-oxygenation PO2 (Figure2B) and high PCO2.
Panel A shows the systemic arterial content of oxygen as a function of ECMO blood flow, and Panel B shows the expected PO2 in the return cannula as a function of ECMO blood flow. Both panels were created based on a polymethylpentene oxygenator with normal function. In this graph, the original data from the swine experimental study of Park et al. were used (10). The data used presented a wide range of pre-membrane pH, drainage cannula SatO2, and drainage cannula PO2. The data were collected during a baseline clinical situation, without organ dysfunctions and after 12 hours of peritonitis and severe lung injury induction.
In summary, there are four main mechanisms of hypoxemia during VV-ECMO: a high recirculation ratio, a high pulmonary shunt, a low cardiac output to ECMO blood flow ratio (<0.6), and oxygenator dysfunction. These mechanisms can occur alone or, more frequently, in combination. Figure1 shows the equation for the prediction of arterial oxygen saturation, using all of the concepts discussed above (9).
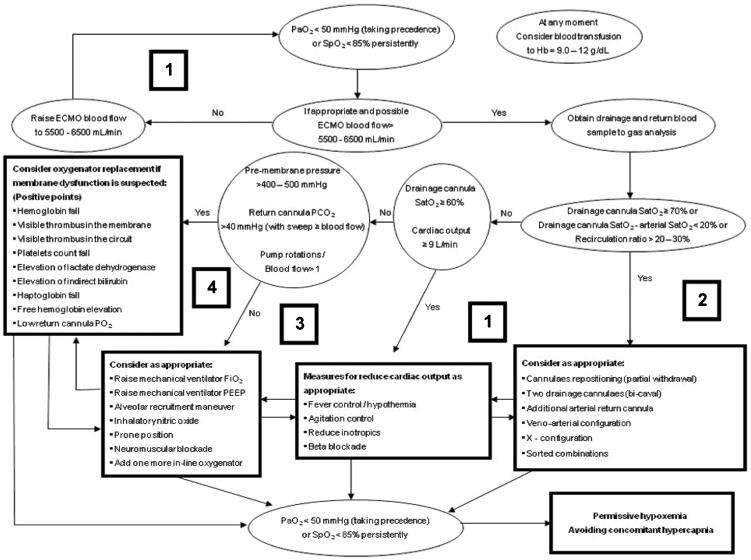
Practical approach for hypoxemia during VV-ECMO supportThe rationale for VV-ECMO support is to maintain arterial oxygenation compatible with life and to prevent further lung injury by allowing for the use of protective ventilatory settings. Accordingly, a low driving pressure (10 cm H2O), a high PEEP (10 - 15 cm H2O), a low respiratory rate (10 breaths/minute), and a low FiO2 (0.3) have been successfully combined with VV-ECMO support with good outcomes (2). To maintain this protective ventilation, an arterial saturation ≥85% or a PaO2≥50 mm Hg has been considered sufficient while maintaining low alveolar ventilation (8,20). However, certain patients with refractory hypoxemia do not achieve this minimal safe oxygenation under protective ventilation settings. For these patients, we suggest a sequential approach (Figure3), aiming for an arterial SatO2≥85% in patients with a normal or near normal PaCO2.
The approach presented in Figure3 is based on the following ideas: 1) optimizing the ECMO blood flow to cardiac output ratio (initially manipulating the ECMO blood flow), 2) identifying recirculation and repositioning of the cannulae accordingly, 3) optimizing residual lung function, 4) diagnosing oxygenator dysfunction and considering its replacement, and 5) optimizing the ECMO blood flow to cardiac output ratio based on the reduction in cardiac output (avoiding fever or providing active patient cooling, decreasing oxygen consumption if necessary with neuromuscular blockers, and possibly reducing cardiac output with the use of beta-blockers after careful consideration of the potential clinical deterioration due to cardiovascular depression) (6,8). Blood transfusions to optimize the DO2 can be considered at any time.
Permissive hypoxemia is an option, according to the patient's clinical situation, when other interventions have failed. Severe ARDS patients without VV-ECMO support develop long-term neuropsychological impairment associated with hypoxemia in the acute phase of the disease (21). However, in VV-ECMO–supported severely injured patients, an arterial SatO2 as low as 70% has been allowed in awake and participative patients with normal arterial PCO2 (7), with a high survival rate (76%) and without significant long-term sequelae in health-related quality of life (7,22). Maintaining a normal PCO2 seems to be mandatory in permissive severe hypoxemia because the association of low PO2 with high PCO2 can potentially cause severe brain injury (23).
The clinical vignettesPatient 1 – She was awake and collaborative, with a high recirculation ratio and a low ECMO blood flow to cardiac output. The ventilator FiO2 was 0.3. In this patient, the ECMO blood flow was raised to 6000 mL/min when the SpO2 reached 85%.
Patient 2 – This patient was cannulated with a femoro-femoral approach, with a high recirculation ratio and an adequate ECMO blood flow to cardiac output ratio. Due to difficulty in repositioning the cannulae, we chose to perform alveolar recruitment. A slight improvement in oxygenation was obtained, keeping the arterial SatO2 between 85 and 89%.
Patient 3 – The patient was febrile and hyperdynamic. There was no recirculation, and the ECMO blood flow to cardiac output was low (ratio = 0.56). This patient received active interventions to control the fever, which slowly improved the hypoxemia.
Patient 4 – This patient had a low ratio of ECMO blood flow to cardiac output and a low recirculation ratio. The ECMO blood flow was raised, thereby bringing the hypoxemia to an acceptable level.
Severe hypoxemia can occur during VV-ECMO respiratory support, and it is crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms. Knowledge of the pathophysiology of hypoxemia is important to guide specific interventions. A stepwise approach, as proposed here, can often be used to address this concerning clinical situation. When other alternatives have failed, permissive severe hypoxemia is acceptable. In this group of patients, maintaining normocapnia is essential to attenuate the risk of associated sequelae.
APPENDIXThe ECMO group comprises: Luciano Cesar Pontes Azevedo, Marcelo Park, André Luiz de Oliveira Martins, Eduardo Leite Vieira Costa, Guilherme Paula Pinto Schettino, Marcelo Brito Passos Amato, Carlos Roberto Ribeiro Carvalho, Mauro Tucci, Alexandre Toledo Maciel, Eliane Silva, Leandro Utino Taniguchi, Edzângela Vasconcelos, Raquel Nardi, Michele de Nardi, Wellington da Silva, Cláudio Machtans, and Adriana Sayuri Hirota.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONSNunes LB, Mendes PV, Barbosa EV, Hirota AS, and Park M were responsible for the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. Nunes LB, Mendes PV, and Park M wrote the manuscript. Costa EL, Azevedo LC, and Schettino GP critically reviewed the manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.