The use of systemic corticosteroids during Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced infectious mononucleosis is a controversial but widespread practice. We aimed to investigate the frequency of complications in adolescents and adults with infectious mononucleosis in relation to the use of corticosteroids.
MethodsWe reviewed the clinical records of 396 patients admitted to the hospital with infectious mononucleosis (52.0% male; median age, 19 years; range, 15–87 years), with a focus on both short-term (infectious and non-infectious) and long-term (hematological malignancies) complications in relation to corticosteroid use.
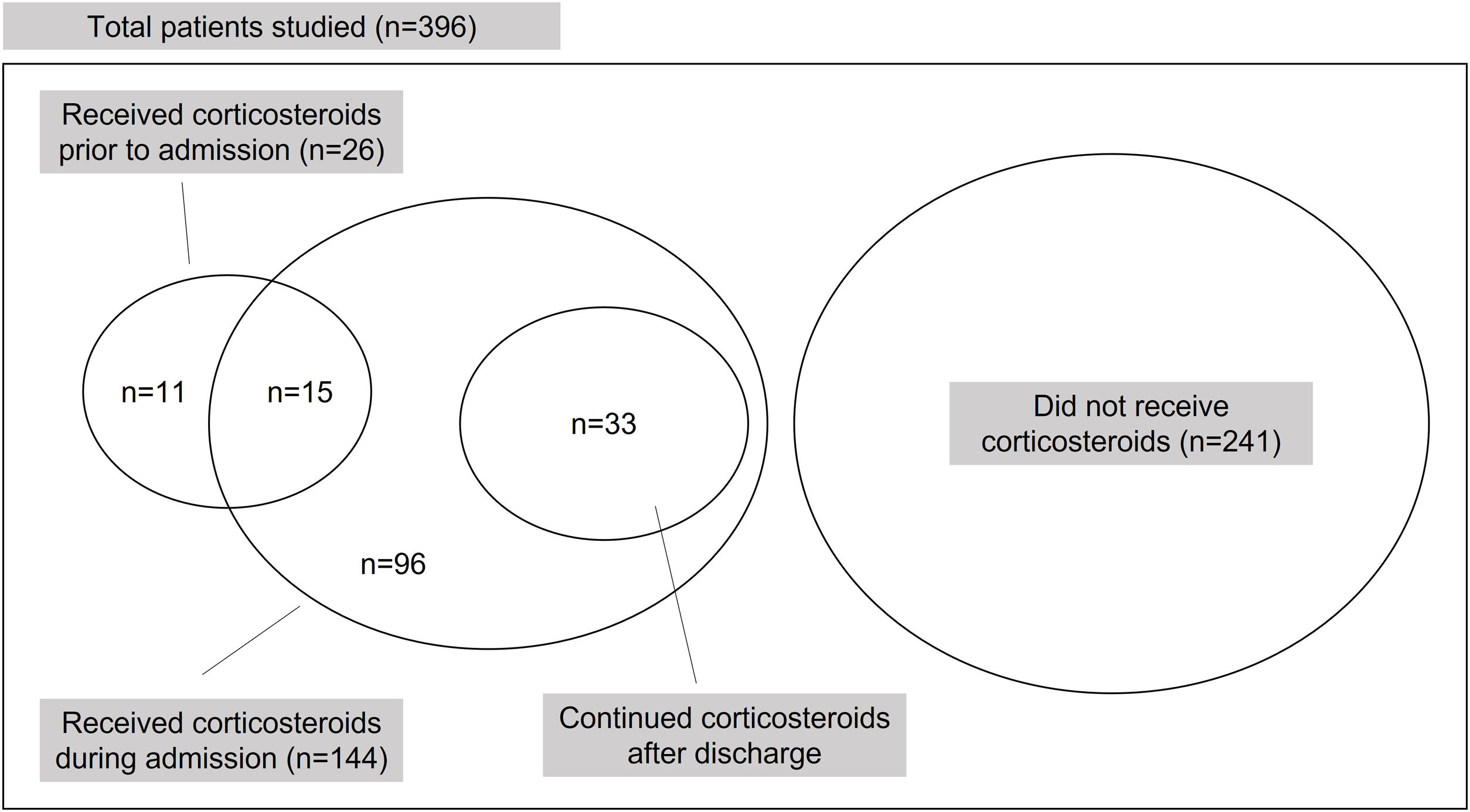
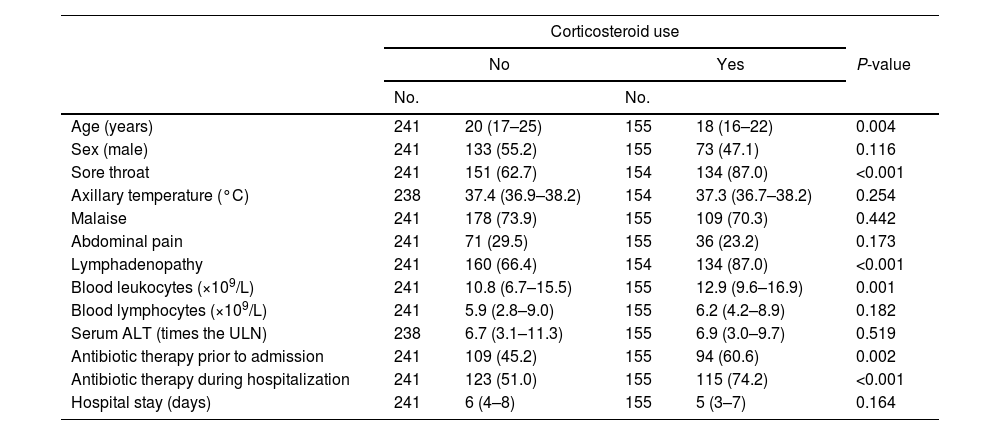
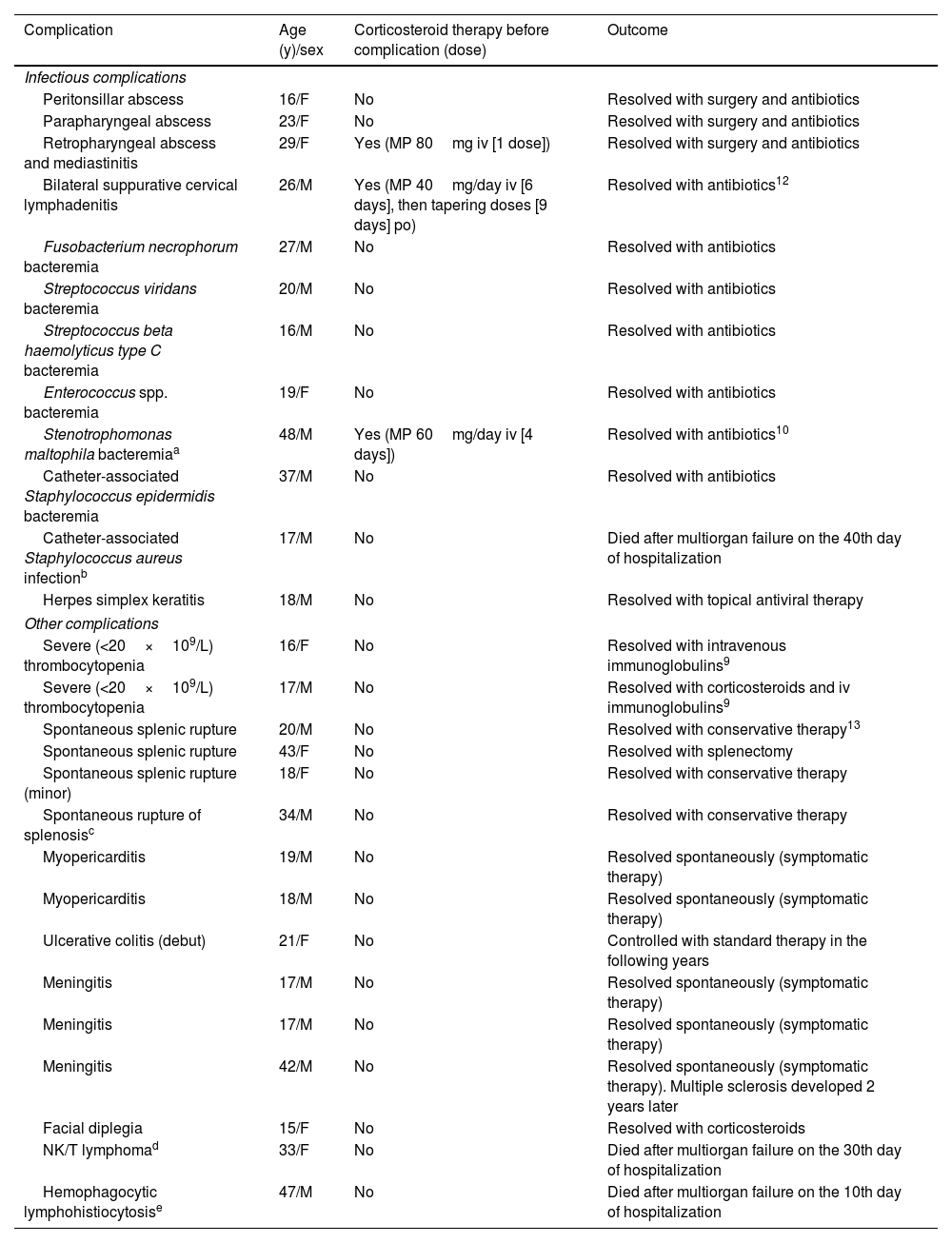
ResultsA total of 155 (38.6%) patients received corticosteroids at some point during infectious mononucleosis. Corticosteroid use was significantly (P≤0.002) associated with sore throat, lymphadenopathy, leukocytosis, and with antibiotics use (mainly indicated after suspicion of tonsillar bacterial superinfection). Overall, 139/155 (89.7%) patients who were treated with corticosteroids also received antibiotics either before or during hospitalization, compared with 168/241 (69.7%) patients who did not. The frequency of short-term severe complications, either infectious (peritonsillar–parapharyngeal abscess or bacteremia) or non-infectious (splenic rupture, severe thrombocytopenia, myopericarditis, or lymphocytic meningitis) were similar in patients receiving and not receiving corticosteroids. After a median of 15 years of follow-up, only one Hodgkin's lymphoma was diagnosed, in a patient who was not treated with corticosteroids during infectious mononucleosis.
ConclusionsThe use of systemic corticosteroids during EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis is generally safe, at least with concomitant antibiotic therapy. However, this should not encourage the use of corticosteroids in this context, given that their efficacy has yet to be demonstrated.
El uso de corticoides durante la mononucleosis infecciosa es una práctica controvertida, pero habitual. El objetivo del estudio fue investigar la frecuencia de complicaciones del empleo de corticoides en adolescentes y adultos con mononucleosis.
MétodosSe revisaron las historias de 396 pacientes ingresados en el hospital por mononucleosis (52,0% varones; edad 15-87 años), las complicaciones a corto plazo (infecciosas y no infecciosas) y a largo plazo (neoplasias hematológicas) y su posible relación con el uso de corticoides.
ResultadosUn total de 155 (38,6%) pacientes recibieron corticoides en algún momento de la enfermedad. El uso de corticoides se asoció (p≤0,002) con la presencia de odinofagia, adenopatías, leucocitosis y con el empleo de antibióticos por sospecha de sobreinfección bacteriana. En conjunto, 139/155 (89,7%) pacientes tratados con corticoides recibieron también antibióticos antes o durante el ingreso, comparado con 168/241 (69,7%) pacientes que no fueron tratados con corticoides. La frecuencia de complicaciones graves a corto plazo, fueran infecciosas (absceso periamigdalino/parafaríngeo o bacteriemia) o no infecciosas (rotura esplénica, trombopenia grave, miopericarditis o meningitis linfocitaria) fue similar en los pacientes que recibieron corticoides y en los que no los recibieron. Tras una mediana de 15 años solo se diagnosticó un linfoma de Hodgkin en un paciente no tratado con corticoides durante la mononucleosis.
ConclusionesEl uso de corticoides sistémicos durante la mononucleosis infecciosa es seguro, al menos con el uso concomitante de antibióticos. Sin embargo, esto no debe ser una justificación para su uso en la mononucleosis, pues su eficacia está por demostrar.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí