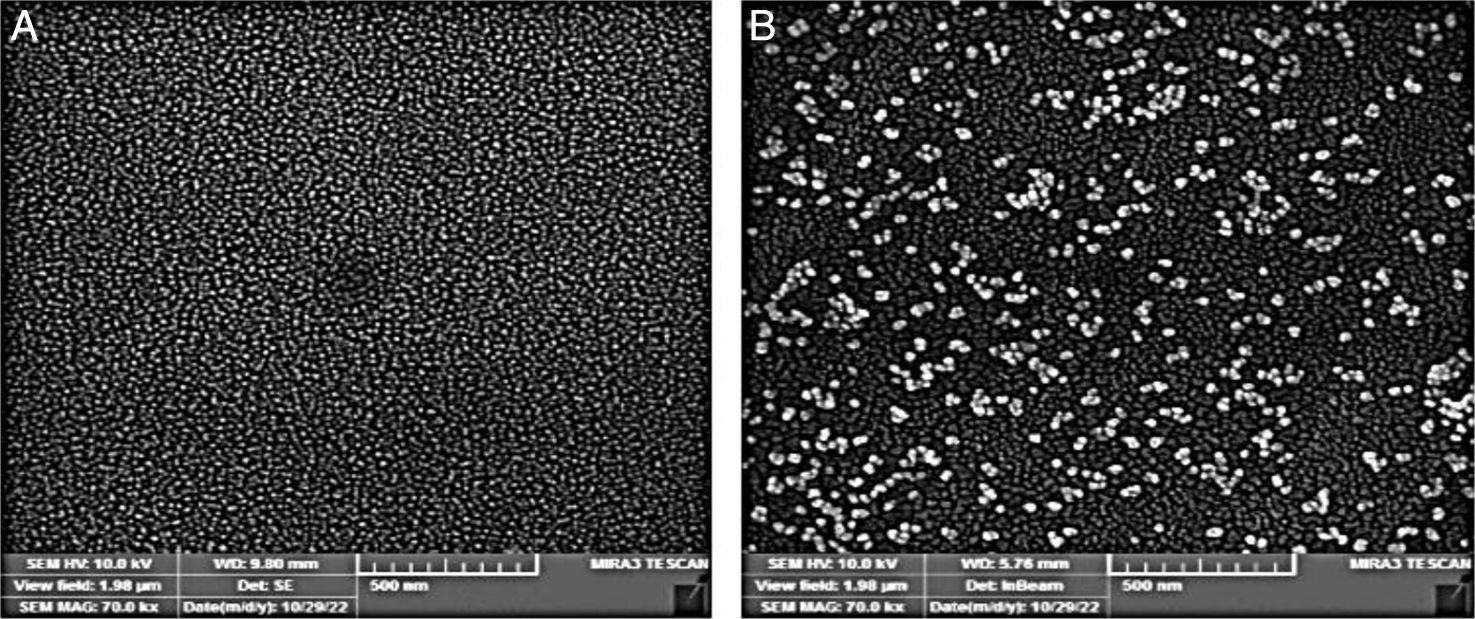
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are chemically inert, have low toxicity, and are easy to modify and functionalize for the detection of many pathogens. They have excellent immune modulatory and adjuvant properties. The aim of this study was to improve the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) by adding GNPs in tests based on interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) measurement.
MethodsGNPs were coated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) recombinant proteins including TB10.4, CFP-10, ESAT-6, and TB7.7. Then, they exposed the whole blood of subjects with active tuberculosis (aTB), LTBI, and healthy controls (HC). Subsequently, IFN-γ produced in GNP tubes (QFT-NG) was measured and compared with IFN-γ produced in tubes without GNPs [QFT-A: (CFP-10, ESAT-6, TB7.7, TB10.4), QFT-B: (CFP-10, ESAT-6, TB7.7)].
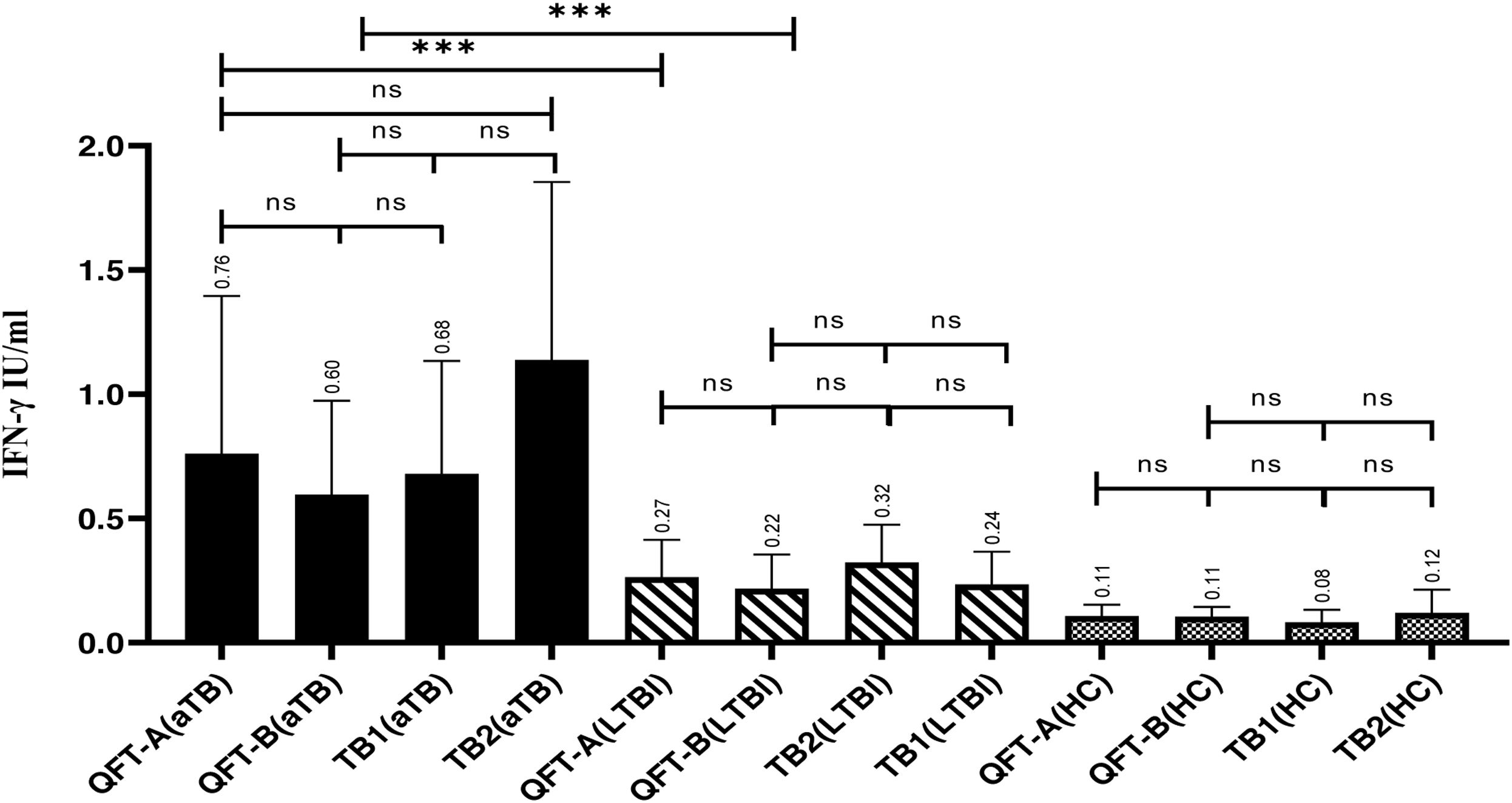
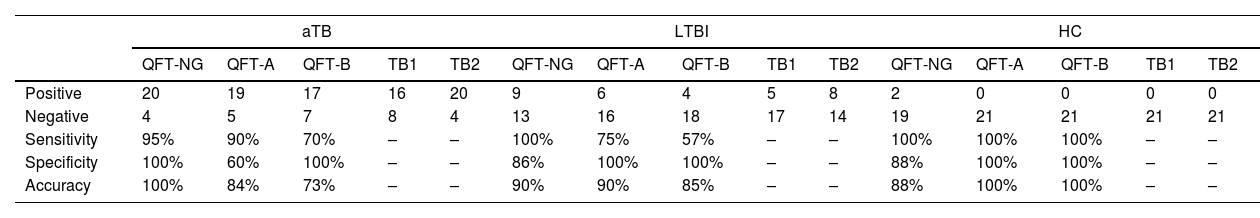
ResultsThe results showed that the IFN-γ production in the GNPs tubes was significantly higher than in tubes without GNPs in aTB, LTBI, and HC subjects. In aTB patients, the mean difference (MD) between the QFT-NG and QFT-A tubes was 0.44, with a P-value of 0.04, and a 95% CI: 0.07–0.88. Furthermore, in LTBI individuals, the QFT-NG and QFT-A tubes exhibited an MD=0.21, P-value=0.03, 95% CI: 0.15–0.4. In the aTB and LTBI subjects were detected in the QFT-NG tubes with a sensitivity of 95%, 100% and specificity 100%, 86%, respectively.
ConclusionThe use of GNPs coated with Mtb recombinant proteins can aid in detecting LTBI subjects by increasing IFN-γ levels.
Las nanopartículas de oro (NPO) son químicamente inertes, tienen baja toxicidad y son fáciles de modificar y funcionalizar para la detección de muchos patógenos. Tienen excelentes propiedades inmunomoduladoras y adyuvantes. El objetivo de este estudio fue mejorar el diagnóstico de tuberculosis añadiendo NPO en pruebas basadas en la medición de interferón gamma.
MétodosLas NPO se recubrieron con proteínas recombinantes de Mycobacterium tuberculosis, incluidas TB10.4, CFP-10, ESAT-6 y TB7.7. Luego, expusieron la sangre total de sujetos con tuberculosis activa (TBa), infección tuberculosa latente (ITBL) y controles sanos (CS). Posteriormente, se midió el IFN-γ producido en tubos con NPO (QFT-NG) y se comparó con el IFN-γ producido en tubos sin NPO (QFT-A, QFT-B).
ResultadosLos resultados mostraron que la producción de IFN-γ en los tubos con NPO fue significativamente mayor que en los tubos sin NPO en sujetos con TBa, ITBL y CS. En pacientes con TBa, la diferencia media (DM) entre los tubos QFT-NG y QFT-A fue de 0,44, con un valor de p de 0,04 y un IC del 95% de 0,07 a 0,88. Además, en personas con ITBL, los tubos QFT-NG y QFT-A mostraron un DM=0,21, un valor de p=0,03 y un IC del 95% de 0,15-0,4. Los sujetos con TBa y ITBL se detectaron en los tubos QFT-NG con una sensibilidad del 95% y del 100% y una especificidad del 100% y del 86%, respectivamente.
ConclusiónEl uso de NPO recubiertos con proteínas recombinantes de M. tuberculosis puede ayudar a detectar sujetos con ITBL y TBa al aumentar los niveles de IFN-γ.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí