Eikenella corrodens (EC) is part of the normal microbiota of the oropharynx and a recognised opportunistic pathogen. It is mainly involved in head and neck infections, but it has also been identified as a cause of pleuropulmonary and intraabdominal infections. Its identification could be difficult due to its fastidious growth requirements, especially in the context of polymicrobial infection and is probably underreported.
MethodsWe carried out a retrospective 5-year review of clinical charts and laboratory database.
ResultsWe describe the clinical and microbiological characteristics of 9 deep-seated infections caused by EC, diagnosed in locations different from the head and neck.
ConclusionEC deep-seated infections are often found in patients with comorbid conditions and a history of interventional procedures. Due to the characteristic torpid evolution of EC abscesses, imaging to assess the necessity of debridement and avoid early cessation of antibiotics is necessary.
Eikenella corrodens (EC) es parte de la microbiota habitual orofaríngea y un conocido patógeno oportunista. Está involucrado principalmente en infecciones de cabeza y cuello, pero también causa de infecciones pleuropulmonares e intraabdominales. Su identificación podría ser difícil debido a sus exigentes requisitos de crecimiento, especialmente en el contexto de la infección polimicrobiana y probablemente sea un microorganismo infradiagnosticado.
MétodosRealizamos una revisión retrospectiva de 5 años de las historias clínicas y la base de datos del laboratorio.
ResultadosDescribimos las características clínicas y microbiológicas de 9 casos de infecciones en localizaciones profundas causadas por EC, diagnosticadas en localizaciones diferentes de la cabeza y el cuello.
ConclusionesLas infecciones profundas por EC aparecen con frecuencia en pacientes con comorbilidades y antecedentes de procedimientos invasivos. Dada la evolución tórpida característica de los abscesos causados por EC, emplear técnicas de imagen para valorar la necesidad de desbridamiento y evitar la retirada prematura de los antimicrobianos.
Eikenella corrodens (EC) belongs to the family Neisseriaceae. It is a small, non-motile, non-spore-forming, facultatively anaerobic gramnegative rod. It grows slowly on blood or chocolate agar at 37°C. Colonies are greyish, sometimes surrounded by a greenish discoloration on the blood agar, and produce a bleach-like odour. About 50% of the strains pit or corrode the agar, and this characteristic gave the microorganism its name.1 Nowadays, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry is a rapid and accurate tool for the identification of E. corrodens.2
E. corrodens is a component of the normal microbiota of the oropharynx and is a common cause of periodontitis and opportunistic infections of the head and neck. It is also a typical pathogen of human bite wounds or clenched-fist injuries. Deep-seated infections such as pleuropulmonary and abdominal infections have been described. Pleuropulmonary infections are seen in patients with medical history of aspirative pneumonia and alcoholism, and abdominal infections are often preceded by surgery.3 Intravenous drug users are at risk of bacteraemia and endocarditis. Osteomyelitis can occur following a puncture wound with objects such as forks, toothpicks and fish bones, or after a human bite or clenched-fist injury. Thyroid abscesses and central nervous system infections have been described in children.4
Deep-seated infections caused by this micoorganism are unusual and its identification may raise some doubts regarding antibiotic choice and length of treatment. Despite appropriate antimicrobial therapy, E. corrodens infections tend to relapse if treatment is withhold too early and drainage may be necessary to achieve cure. We describe 9 cases of deep-seated infections located in anatomical regions different from the head and neck diagnosed at our hospital between 2010 and 2015. We decided to review these cases in order to describe the clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of this infection these infections.
Material and methodsE. corrodens isolates cultured from abscesses or usually sterile sites were identified preforming a restrospective review of the laboratory database and clinical and surgical records of these patients, during the years 2010–2015. Identification of E. corrodens was performed using conventional culture techniques and biochemical tests, and mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS; Bruker Daltonics, Leipzig, Germany). Susceptibility testing was performed with MIC gradient strips (Etest, BioMerieux, France) and interpreted according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) criteria.
ResultsE. corrodens was isolated from 39 clinical samples during the study period: 21 head and neck abscesses, 9 superficial wounds, and 9 deep-seated abscesses or usually sterile sites or fluids. These last nine cases were selected for the study.
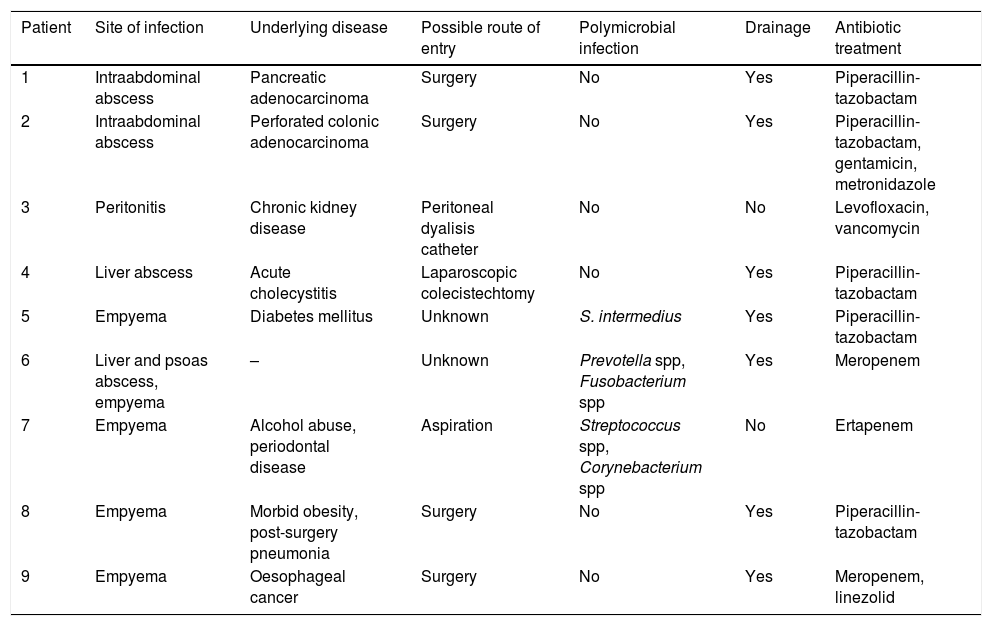
Case reportsPatient #1: 72-year-old man who presented with asymptomatic jaundice and was diagnosed of adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head and underwent cephalic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Postoperatively, the patient was febrile and had elevated sepsis markers. An abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan showed a single suprahepatic collection that was drained percutaneously and grew E. corrodens in pure culture.
Patient #2: 66-year-old man, admitted for urgent surgery due to acute abdomen secondary to a perforated tumoral mass on the transverse colon. Two weeks after surgery the patient was febrile and the CT scan showed a subphrenic collection, which was drained through a percutaneous catheter. E. corrodens was isolated in pure culture.
Patient #3: 49-year-old man on peritoneal dialysis for 2 years, who noted suppuration around the insertion point of the catheter. The catheter was removed and samples of the discharge and peritoneal fluid were submitted for culture, and pure growth of E. corrodens was obtained.
Patient #4: 68-year old man who presented to the emergency room two weeks after laparoscopic cholecystectomy because of persistent fever and right upper quadrant pain. The CT scan showed a 10cm liver abscess. The sample obtained from the drainage of the abscess grew a pure culture of E. corrodens. Blood cultures were also positive for this organism.
Patient #5: 83-year-old diabetic woman who complained of productive cough and right-sided chest pain. CT scan revealed a pleural effusion occupying the whole hemithorax, which was drained through a chest tube. The sample thus obtained was purulent and grew E. corrodens and Staphylococcus intermedius.
Patient #6: 49-year-old woman with no relevant medical history, who consulted for chest pain and cough in the last 72h. She referred that 2 months ago she noted suppuration through the right inguinal region that ceased spontaneously. Physical examination revealed hypoventilation in the right lung. A thoracoabdominal CT scan showed a pleural effusion occupying two thirds of the lung, a pararenal fluid collection affecting the psoas muscle, and a liver abscess. The empyema and the psoas abscess were drained, whereas the liver abscess was monitored through imaging and resolved with antibiotic therapy alone. E. corrodens was found in both pleural fluid and psoas abscess samples. In addition, Prevotella spp. was isolated form the pleural fluid and Fusobacterium spp. from the psoas abscess sample.
Patient #7: 47-year-old alcoholic man who complained of fever and purulent sputum. Poor oral hygiene was noted during physical examination. CT scan imaging revealed a lung cavitation with an air-fluid level in the left upper lobe. Drainage was performed through transthoracic puncture and grew E. corrodens, Corynebacterium spp., and Streptococcus spp.
Patient #8: 54-year-old woman with a history of recent bariatric surgery and postoperative nosocomial pneumonia, presenting a month after discharge with dyspnoea and chest pain. Massive left empyema was diagnosed through CT scan and drainage. E. corrodens was identified in the sample.
Patient #9: 66-year-old man presenting a worsening of the respiratory function and a bilious fluid drain from the chest tube on the postoperative phase of esophagectomy used to treat a locally advanced oesophageal cancer. The CT scan showed bilateral pleural effusion and the fluid sent for culture grew E. corrodens.
The mean age was 61 years (±12.25 SD). Six of the 9 patients were male. E. corrodens grew in pure culture in 6 cases, whereas in 3 cases the infection was polymicrobial. E. corrodens isolates were susceptible to penicillin (85.7%), ampicillin (85.7%), amoxicillin-clavulanate (85.7%), cefotaxime (100%), imipenem (100%), ciprofloxacin (100%), tetracycline (100%), cotrimoxazole (77.7%) and rifampicin (75%).
All patients were treated with antibiotics for at least 4 weeks, except the patient on peritoneal dialysis (patient #2), who recovered after 2 weeks of treatment. All infections resolved after antibiotics and draining if needed (see Table 1).
Clinical characteristics and treatment of deep-seated Eikenella corrodens infections.
| Patient | Site of infection | Underlying disease | Possible route of entry | Polymicrobial infection | Drainage | Antibiotic treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intraabdominal abscess | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Surgery | No | Yes | Piperacillin-tazobactam |
| 2 | Intraabdominal abscess | Perforated colonic adenocarcinoma | Surgery | No | Yes | Piperacillin-tazobactam, gentamicin, metronidazole |
| 3 | Peritonitis | Chronic kidney disease | Peritoneal dyalisis catheter | No | No | Levofloxacin, vancomycin |
| 4 | Liver abscess | Acute cholecystitis | Laparoscopic colecistechtomy | No | Yes | Piperacillin-tazobactam |
| 5 | Empyema | Diabetes mellitus | Unknown | S. intermedius | Yes | Piperacillin-tazobactam |
| 6 | Liver and psoas abscess, empyema | – | Unknown | Prevotella spp, Fusobacterium spp | Yes | Meropenem |
| 7 | Empyema | Alcohol abuse, periodontal disease | Aspiration | Streptococcus spp, Corynebacterium spp | No | Ertapenem |
| 8 | Empyema | Morbid obesity, post-surgery pneumonia | Surgery | No | Yes | Piperacillin-tazobactam |
| 9 | Empyema | Oesophageal cancer | Surgery | No | Yes | Meropenem, linezolid |
E. corrodens is an opportunistic pathogen that shows a propensity towards the formation of abscesses in any location. Infections tend to be indolent and benign, but invasive infections and relapse have been described. This slow-growing, fastidious bacterium is often involved in polymicrobial infections and thus might be underdiagnosed because it is outgrown by coinfecting microorganisms in conventional culture media.
It has been described that E. corrodens shows exponential growth in the presence of different strains of Streptotoccus spp.5 Polymicrobial infections are in fact frequent and in some series account for up to 65% of cases,3,6 with Streptococcus spp. and anaerobes being the species usually involved.
In the present study we have found that a break in mucocutaneous barriers (invasive procedures, surgery, peritoneal catheter) can lead to bacteraemia and deep-seated E. corrodens infections. Five of the patients in this series had undergone such a procedure. In a small series, several E. corrodens abdominal abscesses secondary to surgery have been reported.7 Microaspiration could be a mechanism of respiratory infections.
Most E. corrodens isolates are susceptible to penicillin, ampicillin, second- and third-generation cephalosporins, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, and tetracyclines. All strains are resistant to clindamycin and metronidazole. Some strains are β-lactamase producers, and the β-lactamase is inhibited by clavulanic acid and sulbactam. The production of β-lactamase and the resistance to streptomycin and sulphonamides has been associated with a plasmid,8 and with a transposon.9 A non-inducible β-lactamase encoded by the chromosome has also been described in this organism.10 The 9 cases presented here were successfully treated with β-lactams or levofloxacin and 7 patients required surgical drainage. Incision and drainage of the abscesses and debridement of necrotic tissue have been found essential to achieve proper healing.6E. corrodens infections are prone to cause relapses even with appropriate therapy, so avoiding early cessation of antibiotic and assessing the necessity of new imaging are recommended in order to assess the development of collections when response to treatment is poor are recommended.4
In conclusion, deep-seated infections in which E. corrodens is involved are often present in patients with comorbid conditions and subjected to invasive procedures that may serve as the route of entry for the pathogen. Despite being a bacterium susceptible to several antibiotics, patients are often treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics for a long period of time, even in the absence of no coinfecting microorganisms where cultured. This may be explained by the clinical suspicion of a polymicrobial infection or due to the characteristic torpid evolution of abscesses caused by E. corrodens, which tend to relapse if antibiotic therapy is stopped too early. Proper imaging to assess the evolution of the collections is important to monitor the response to therapy.
FundingThe present investigation has not received specific subsidies from agencies of the public sector, commercial sector or non-profit entities.
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.