Strains can be classified in terms of biofilm production from quantitative absorbance values collectively by dividing strains into tertile ranks or individually by calculating the optical density for the negative control. However, these methods have not been compared in a large sample of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Therefore, our objective was to analyze the agreement between both methods in terms of biomass production and metabolic activity of their biofilm.
MethodsWe classified 233 S. aureus strains by biomass production and metabolic activity using the crystal violet and XTT assays, respectively. Strains were classified as low, moderate, or high biofilm producers according to tertile or optical density.
ResultsWe found no agreement between both methods (p<0.001 and p=0.028, respectively).
ConclusionsWe consider strains’ biofilm classification by optical density to be a more reliable method, as it depends on the individual absorbance of each strain.
Las cepas se pueden clasificar en términos de producción de biopelícula a partir de valores cuantitativos de absorbancia dividiendo de forma colectiva las cepas en rangos por terciles o individualmente calculando la densidad óptica para el control negativo. Sin embargo, estos métodos no se han comparado en una gran muestra de cepas de Staphylococcus aureus. Por lo tanto, nuestro objetivo fue analizar la concordancia entre ambos métodos en términos de producción de biomasa y actividad metabólica de la biopelícula.
MétodosSe clasificaron 233 cepas de S. aureus por producción de biomasa y actividad metabólica utilizando los ensayos de cristal violeta y de XTT, respectivamente. Las cepas se clasificaron como altamente, moderadamente o bajamente productoras de biopelícula según terciles o densidad óptica.
ResultadosNo encontramos concordancias entre ambos métodos (p<0,001 y p=0,028, respectivamente).
ConclusionesConsideramos que la clasificación del biofilm de cepas por densidad óptica es un método más fiable, ya que depende de la absorción individual de cada cepa.
Bacterial biofilms are microbial communities that adhere to a surface or an interface and become embedded in an extracellular matrix. Biofilms constitute a significant problem in clinical settings and are responsible for more than 65% of human infections and treatment failures.1,2Staphylococcus aureus is a major causative agent of this kind of infection and has been described as a high biofilm-former, mainly in device-related bloodstream infections.3
Various approaches have been used for the in vitro study of biofilm production.2,4 The most common are those based on static models that measure absorbance in the crystal violet (CV) assay and the tetrazolium salt reduction assay (XTT) because of their simplicity and low cost.5,6
However, quantitative absorbance values can be converted into qualitative degrees of biofilm production using two different methods. In one, the absorbance values of several strains are organized collectively in ascending order and divided into tertiles, each representing a different degree of biofilm production (low, moderate, and high). In the other, the optical density (OD) of each individual strain is calculated and degrees of biofilm production are established according to the OD of the negative control. To our knowledge, these methods have not been compared across a broad range of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Therefore, our objective was to analyze the concordance between both methods of classifying S. aureus strains in terms of biomass production and the metabolic activity of their biofilm.
MethodsWe selected 233 S. aureus strains isolated from patients with bacteremia and tested them using the CV and XTT assays based on a previous study by our group.7 Biofilm was formed as described by Peeters et al., with some modifications.2 Briefly, a loopful of overnight culture of S. aureus was inoculated in 20ml of TSB, which was then incubated overnight with shaking at 30°C in an orbital shaker. After three centrifuge-resuspension cycles with PBS, the pellet was re-suspended in 10ml of TSB. This suspension was adjusted to 0.5 McFarland turbidity using a turbidimeter, and 100μl was inoculated in the 96-well plate and incubated at 37°C for 24h. Planktonic cells were removed by three washes of 100μl of PBS and dried at room temperature before developing CV and XTT assays. Each strain was tested in triplicate, and TSB was used as a negative control. The absorbance was measured at 550nm (CV assay)/492nm (XTT assay) in a spectrophotometer (Biochrom EZ Read 400). Absorbance values for the CV assay were only available in 116 of the 233 strains due to some data loss caused by a computer issue. The cut-offs (based on tertiles) used to classify the strains according to biomass production by CV and metabolic activity by XTT were, respectively, as follows: low, <0.530/<0.214; moderate, 0.530–1.291/0.214–0.416; and high, ≥1.292/≥0.417. Optical density (OD) absorbance values of the strains obtained by CV and XTT were used to classify semi-quantitatively biofilm production according to the method described in Stepanovic et al.8 Specifically, the cut-off OD (ODc) was defined as three standard deviations above the mean OD of the negative control and strains were classified as follows: OD≤2×ODc=weak biofilm producer; 2×ODc<OD <4×ODc=moderate biofilm producer; and OD≥4×ODc=high biofilm producer, respectively.9
Qualitative variables were expressed as percentages of the number of strains classified in the same group. The agreement between both methods of classification was analyzed using Cohen's kappa coefficient. The kappa statistic values vary from 0 to 1, where 0=agreement equivalent to chance, 0.20=slight agreement, 0.21–0.40=fair agreement, 0.41–0.60=moderate agreement, 0.61–0.80=substantial agreement, 0.81–0.99=near perfect agreement, and 1=perfect agreement. The analysis was performed using SPSS software 21.0.
ResultsAccording to biomass production, 51.7%, 31.9%, and 16.4% were strains classified, respectively, as high, moderate, and low biomass producers using the tertile method. However, for the OD method, 87.1%, 8.6%, and 4.3% were classified as high, moderate, and low biomass producers. In the case of metabolic activity, 31.8%, 38.2%, and 30.1% of strains were classified by the tertile method as having high, moderate, and low metabolic activity. In contrast, 84.1%, 12.4%, and 3.4% were classified as high, moderate, and low metabolic activity by the OD method.
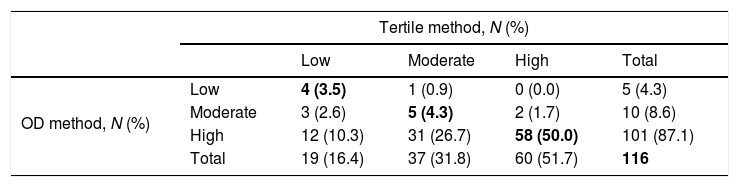
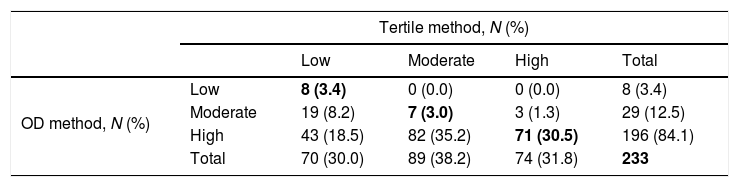
The concordance for biomass production for low, moderate, and high groups was 3.5%, 4.3%, and 50.0%. The concordance for metabolic activity for low, moderate, and high groups was 3.4%, 3.0%, and 30.5%.
The global agreement, defined as the percentage of strains in the same category by both methods—biomass production and metabolic activity—was 57.8% and 36.9% (κ=0.180, p<0.01; and κ=0.065, p=0.028, respectively) (Tables 1 and 2).
Concordance between tertile and OD methods for classification of S. aureus strains in terms of biomass production by the CV method.
| Tertile method, N (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Moderate | High | Total | ||
| OD method, N (%) | Low | 4 (3.5) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (4.3) |
| Moderate | 3 (2.6) | 5 (4.3) | 2 (1.7) | 10 (8.6) | |
| High | 12 (10.3) | 31 (26.7) | 58 (50.0) | 101 (87.1) | |
| Total | 19 (16.4) | 37 (31.8) | 60 (51.7) | 116 | |
OD, optical density; CV, crystal violet assay.
Concordance between tertile and OD methods for classification of S. aureus strains in terms of metabolic activity by the XTT assay.
| Tertile method, N (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Moderate | High | Total | ||
| OD method, N (%) | Low | 8 (3.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (3.4) |
| Moderate | 19 (8.2) | 7 (3.0) | 3 (1.3) | 29 (12.5) | |
| High | 43 (18.5) | 82 (35.2) | 71 (30.5) | 196 (84.1) | |
| Total | 70 (30.0) | 89 (38.2) | 74 (31.8) | 233 | |
OD, optical density; XTT, tetrazolium salt assay.
We found no agreement between the tertile and OD methods for classification of S. aureus strains in terms of biomass production or metabolic activity.
DiscussionS. aureus is one of the most virulent microorganisms causing device-associated nosocomial infections. This virulence is due to the ability of S. aureus to form biofilm.1
Over the years, several in vitro models have been developed to study biofilm formation. The static 96-well plate model is the most frequently used because of its low cost and simplicity.8,10 However, despite the study carried out by Stepanovic et al., which showed that the classification by OD values was the most widely used for biofilm formation in bacterial biofilms,8 classification of biofilm formation into qualitative degrees remains controversial, as individual laboratories use the most suitable one for their research.11–12
Different conclusions have been reached in clinical studies assessing the impact of biofilm production using degrees of biofilm production according to patient outcome.
Muñoz et al., reported that biofilm was not a predictor of mortality or unfavorable prognosis in adults with candidemia when biofilm production was classified by tertile.13,14 Rajendran et al., in contrast, reported that candidemia and biofilm production were significantly associated with C. albicans mortality in 15.6% of their study population (217 patients).15 Therefore, the different results from various studies may be due to the fact that the authors have classified the strains using different parameters for biofilm production. Moreover, Guembe et al., found that biofilm production in 485 patients with S. aureus bacteremia was not associated with poor outcome. The results may have been different if the OD method had been used to classify strains in terms of biofilm production.7,13–15
The main limitation of the study is that concordance between methods to classify S. aureus biofilm production was only tested using CV and XTT, and data can not be extrapolated to other biofilm production methods, such as MBEC assay or CDC Bioreactor.
ConclusionFor this reason, we compared the two main methods for biofilm classification and found no concordance between biomass production and metabolic activity, thus demonstrating the importance of establishing a unique standard method that can be widely used to compare results between laboratories.
We consider that calculating the OD of each strain individually and comparing it against the OD of the negative control (OD method) seems the most reliable method for biofilm classification, as it can be used independently of the number of strains.
Availability of data and materialsThe original datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributionsMCL, BA, CC-S and MG contributed in the conception and design of the study and had full access to all of the study data. MCL, BA, AS and RC made substantial contributions to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. PM, MCL, BA and MG contributed substantially to the study design, data analysis and interpretation, and the writing of the manuscript. MG contributed to the conception and design of the study and data analysis and interpretation and was involved in drafting the manuscript and critically reviewing it for important intellectual content. She takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approvalThe study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Gregorio Marañón.
Consent for publicationNot applicable.
Financial supportM. Guembe is supported by the Miguel Servet Program (ISCIII-MICINN, MS13/00268) of the health Research Fund (FIS, PI18/00045) of the Carlos III Health Institute (ISCIII), Madrid, Spain. MC. Latorre is supported by the Consejería de Educación, Juventud y Deporte de la Comunidad de Madrid y Fondo Social Europeo (PEJD-2017-PRE/BMD-3596). Beatriz Alonso was supported by the Consejería de Educación, Juventud y Deporte de la Comunidad de Madrid y Fondo Social Europeo (PEJ15/BIO/AI-0406). The study was partially financed by grants from the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) “A way of making Europe”.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
We thank Thomas O’Boyle for his help in the preparation of the manuscript.