Analizar el impacto que el trasplante hepático ha tenido en el paciente como condicionante de su estado de salud.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio prospectivo, cuya muestra la formaron aquellos pacientes trasplantados hepáticos en el Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón desde noviembre 2019 hasta agosto 2021. Se utilizaron la escala hospitalaria de ansiedad y depresión, el Modelo para enfermedad hepática en estadio terminal sodio, el índice de fragilidad hepática y el cuestionario efectos del trasplante. Se utilizaron la prueba t de Student para las variables continuas y la prueba de chi-cuadrado para las categóricas. Para aquellas muestras no paramétricas se utilizaron el signo de Wilcoxon, U de Mann-Whitney y Kruskal-Wallis.
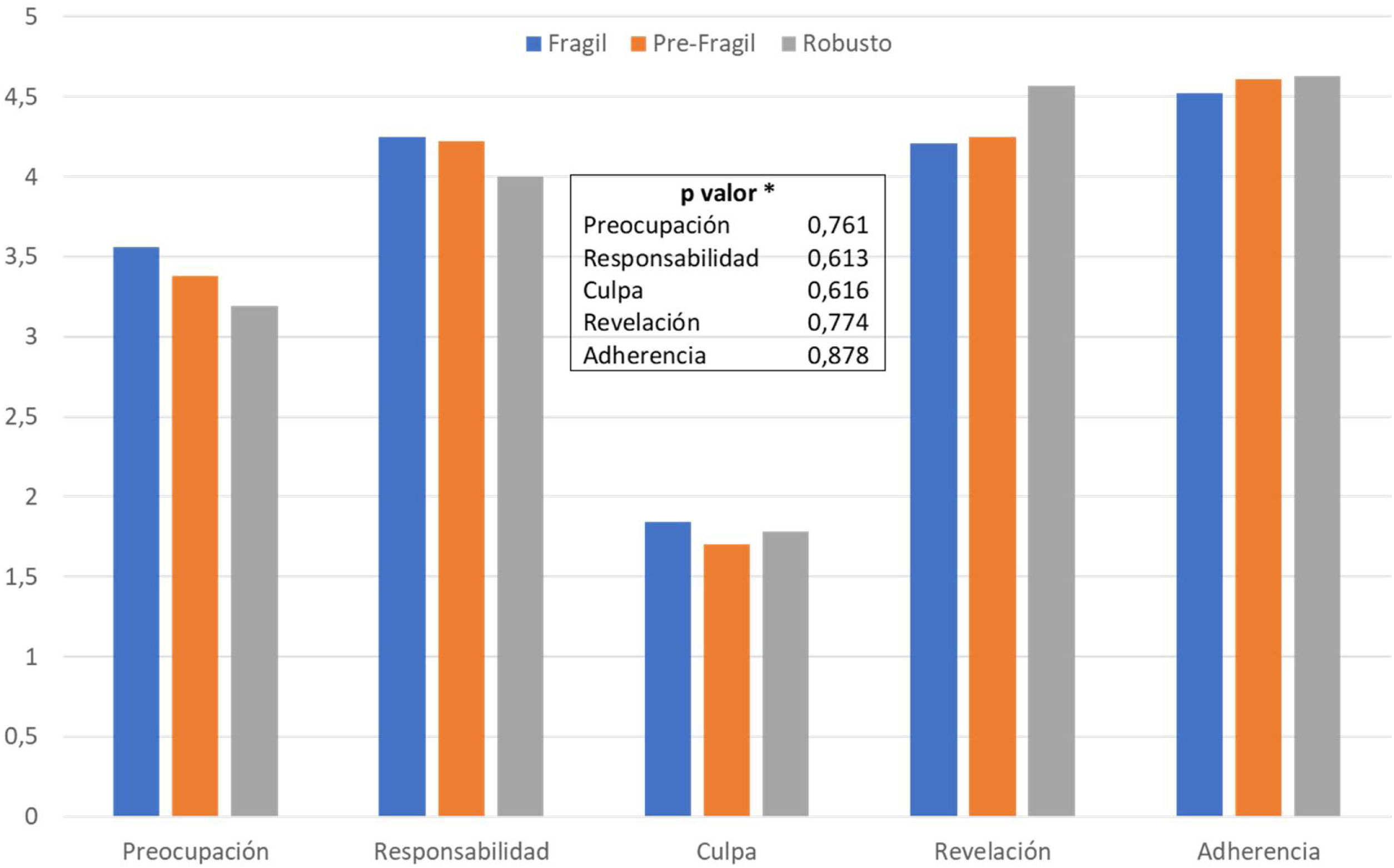
ResultadosLa muestra la conformaron 60 pacientes con una media de edad de 55,68 años, siendo el 70% hombres. La puntuación media de ansiedad y depresión de los pacientes mejoró significativamente tras el trasplante hepático. El impacto de la salud física resultó en que aquellos pacientes con un mayor índice del Modelo para enfermedad hepática en estadio terminal sodio se correlacionaron con un mayor sentimiento de culpa tras el trasplante. Además, una mayor adherencia al tratamiento inmunosupresor se correlacionó directamente con una mayor revelación e inversamente con la culpa, tras el trasplante.
ConclusiónEl trasplante hepático es un proceso que impacta en la salud de los pacientes. Aquellos pacientes que llegan al trasplante con una situación física más deteriorada presentan una mayor culpa tras el trasplante. Dicho impacto se correlaciona inversamente con la adherencia al tratamiento inmunosupresor. Las enfermeras deben intervenir en dichos pacientes para reducir el impacto en la adherencia al tratamiento.
To analyse the impact that liver transplantation has had on the patient as a condition of their health.
MethodA prospective study was carried out, the sample of which was made up of liver transplant patients at the Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital from November 2019 to August 2021. The hospital anxiety and depression scale, the Model for End-stage liver disease sodium and liver fragility index and the Transplant Effects Questionnaire Spanish were used. The data were analysed using descriptive statistics. The Student's t test was used for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. For non-parametric samples, the Wilcoxon, Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis's sign were used.
ResultsThe sample was made up of 60 patients with a mean age of 55.68 years, 70% being men. The mean anxiety and depression scores of the patients improved significantly after liver transplantation. The impact of physical health resulted that those patients with a higher Model for End-stage liver disease sodium were correlated with a greater feeling of guilt after transplantation. Furthermore, greater adherence to immunosuppressive treatment was directly correlated with greater disclosure and inversely with guilt, after transplantation.
ConclusionLiver transplantation is a process that impacts the health of patients. Those patients who arrive at the transplant with a more deteriorated physical situation present a greater guilt after the transplant. This impact is inversely correlated with adherence to immunosuppressive treatment. Nurses should intervene in such patients to reduce the impact on adherence to treatment.