To identify drug-related problems using the STOPP/START criteria of patients over 64 years polymedicated with 12 or more drugs.
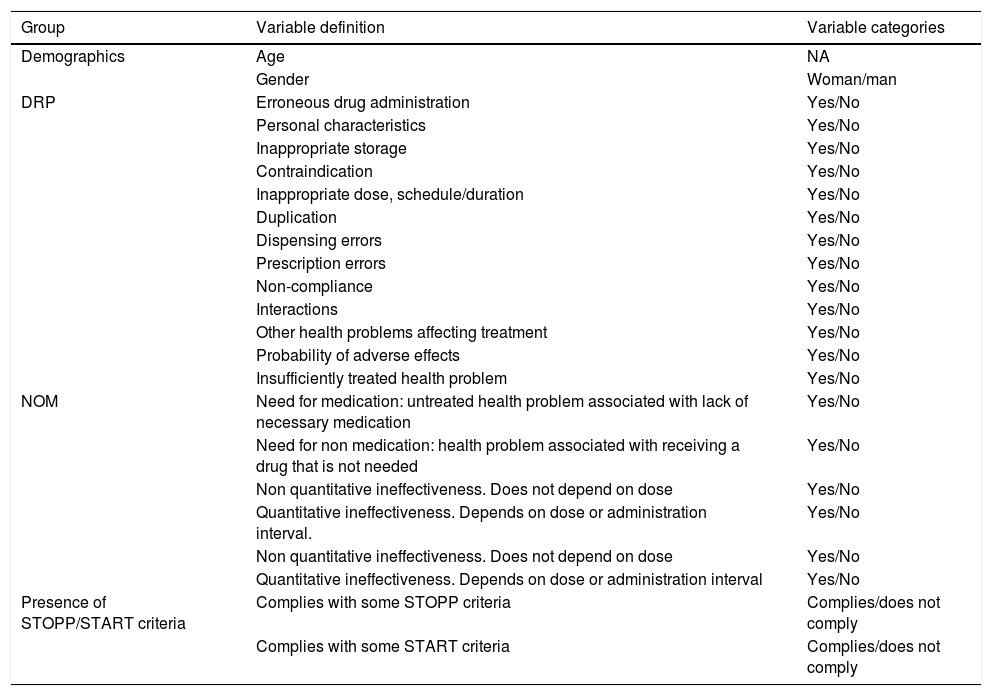
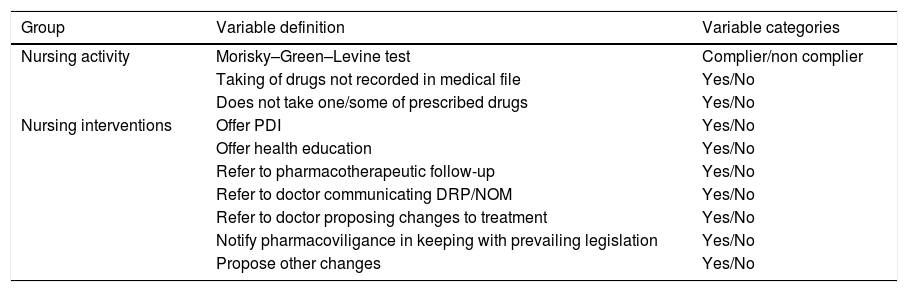
MethodDescriptive cross-sectional. We analysed 172 cases randomly selected from the register of 1500 polymedicated patients of the Quality Improvement Programme for Chronic and Polymedicated Patients of the Galician Health Service for the area of Santiago in 2017. Drug-related problems and the negative results associated with medication were recorded. Treatment compliance was assessed by the Morisky–Green–Levine test. Nursing interventions were recorded based on the Programme's nursing report. Bivariate analysis of the data was performed and the association between the variables was estimated by calculating the odds ratio (OR).
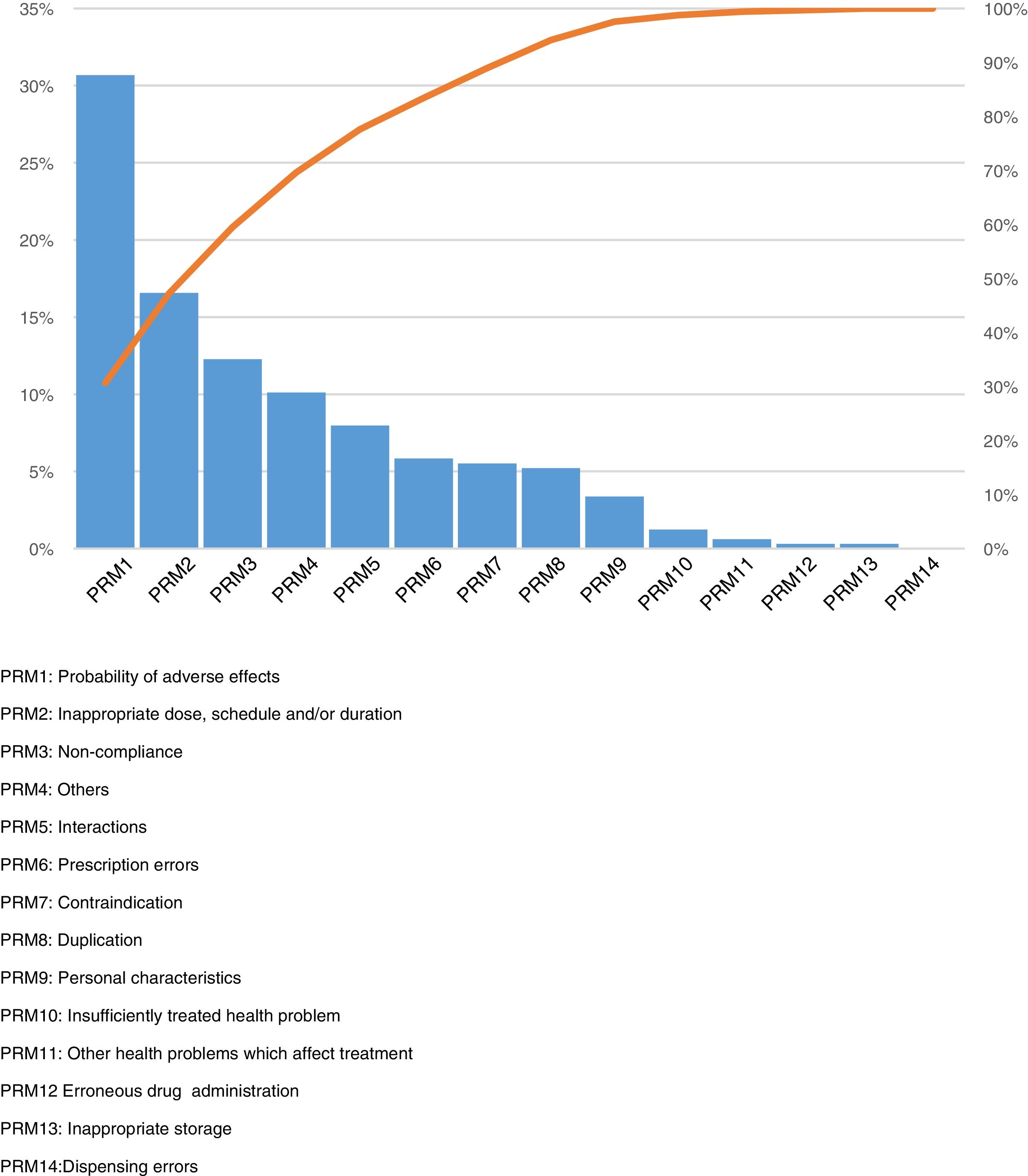
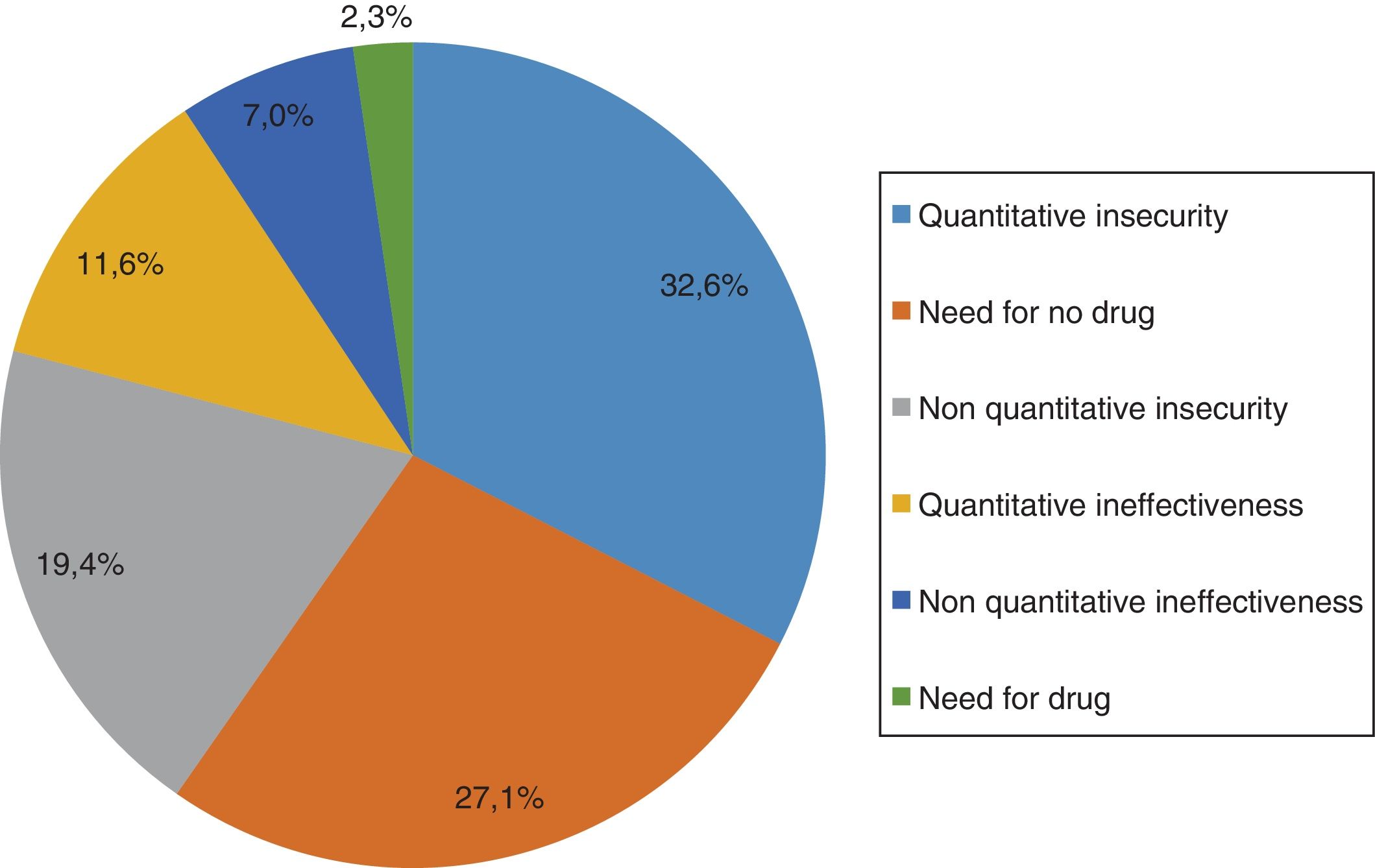
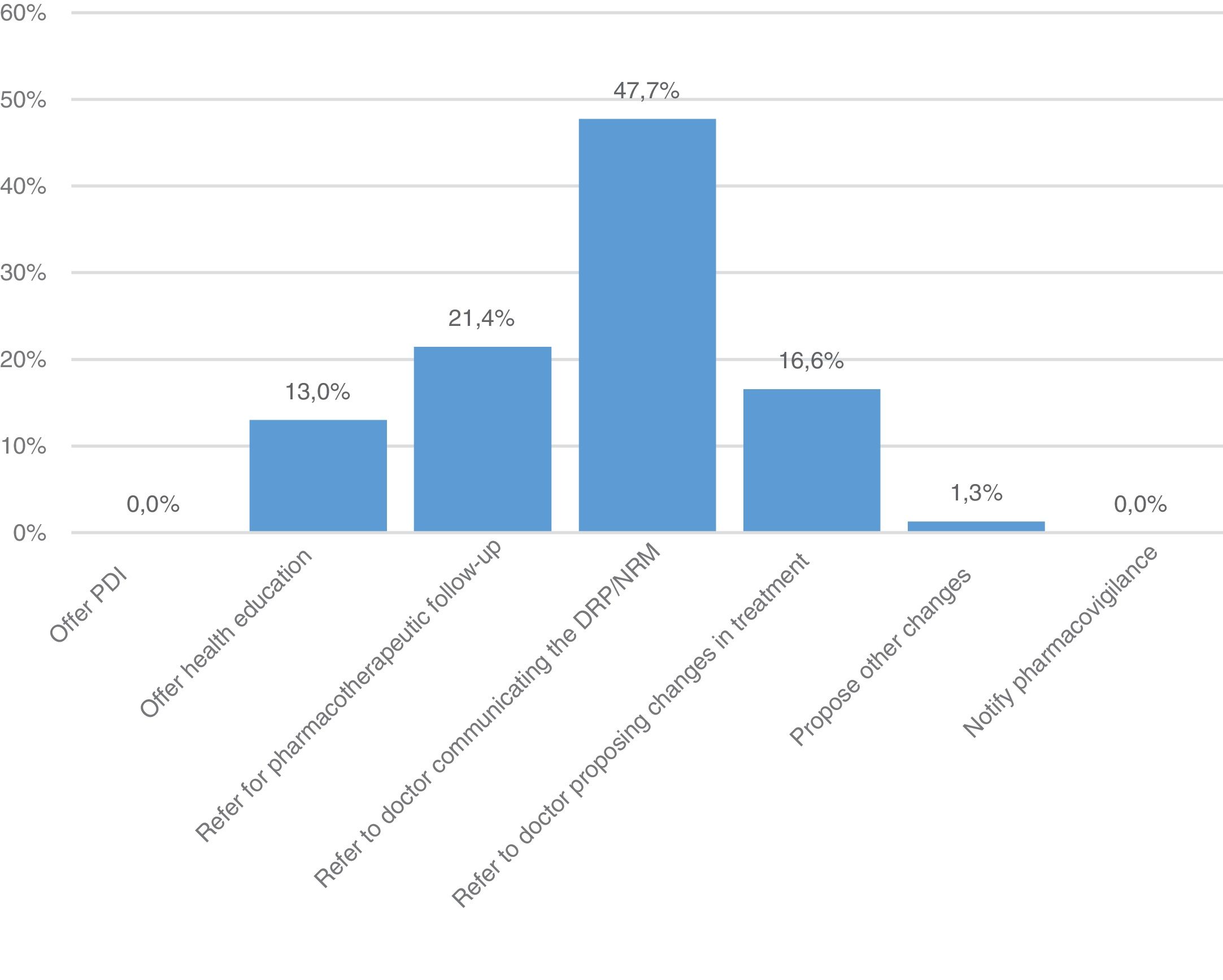
ResultsThe 56.4% of the patients were women. The mean age was 77.34±10.11 years. The most common problem was the likelihood of presenting adverse effects, observed in 64.1% of the patients. Women were more likely to have this problem than men (OR: 1.37; 95% CI: 1.06–1.78). Eighteen percent of the patients were considered non-compliant with the prescribed treatment, according to the Morisky–Green–Levine test. Of the patients, 25.6% had received health education interventions.
ConclusionsNurses must periodically re-evaluate patient medication to check adherence to treatment and determine whether it is causing any type of adverse effect, as well as incorporate health education interventions in this field into their activity.
Identificar los problemas relacionados con la medicación mediante los criterios STOPP/START en pacientes polimedicados mayores de 64 años con 12 o más fármacos.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo transversal. Se analizaron 172 casos seleccionados aleatoriamente del registro de 1.500 pacientes polimedicados del Programa de Mejora de la Calidad en el Paciente Crónico y Polimedicado del Servicio Gallego de Salud para el área de Santiago en el 2017. Se registraron los problemas relacionados con los medicamentos y los resultados negativos asociados a la medicación. El incumplimiento terapéutico se evaluó mediante el test de Morisky-Green-Levine. Las intervenciones enfermeras se registraron a partir del informe enfermero del programa. Se realizó análisis bivariante de los datos y la asociación entre las variables se estimó mediante el cálculo de la odds ratio.
ResultadoEl 56,4% de las pacientes eran mujeres. La media de edad fue de 77,34±10,11 años. El problema más habitual fue la probabilidad de presentar efectos adversos, observándose en el 64,1% de los pacientes. Las mujeres presentaron mayor probabilidad de presentar este problema que los varones (OR: 1,37; IC 95%: 1,06-1,78). Un 18% de los pacientes se consideraron no cumplidores del tratamiento prescrito, según el test de Morisky-Green-Levine. Un 25,6% de los pacientes recibieron intervenciones de educación sanitaria.
ConclusionesLa enfermera debe reevaluar periódicamente la medicación de los pacientes para comprobar adherencia al tratamiento y conocer si están provocando algún tipo de efecto adverso, así como incorporar a su actividad intervenciones de educación para la salud en este campo.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora