4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
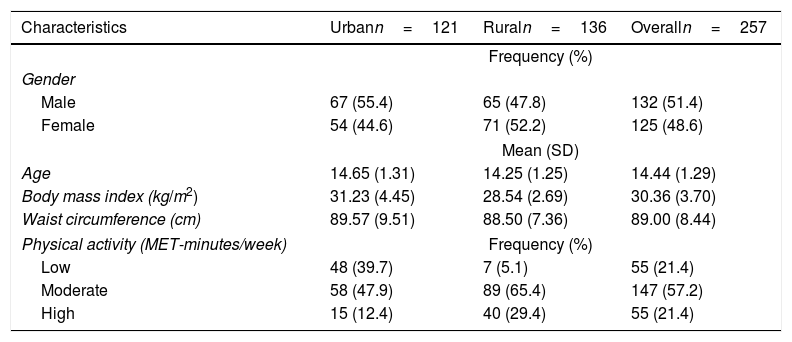
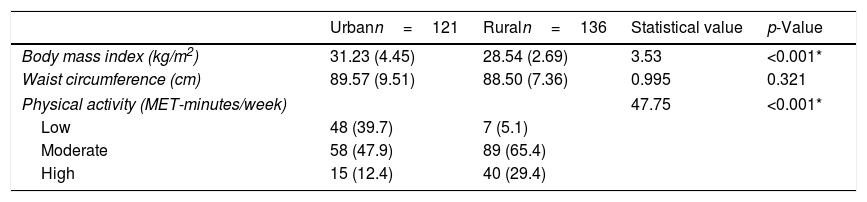
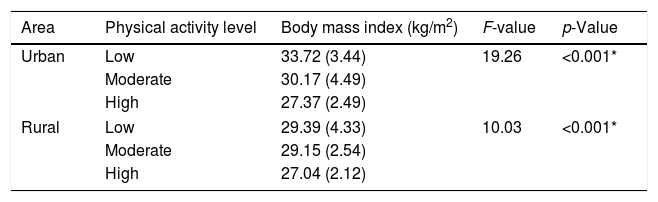
More infoThis study was conducted to examine the association between physical activity (PA) and body weight status among adolescents in rural and urban areas. This cross-sectional study involved 257 adolescents aged 13–19 years, randomly selected from secondary schools around Kelantan, Malaysia. Body weight and height were measured and body mass index (BMI) was calculated. The students completed the International Physical Activity Questionnaire – Short Form, to assess their physical activity. Ethical clearance was obtained from respected bodies. Adolescents in the urban area had significantly higher BMI (p-value<0.001) and lower physical activity (p-value<0.001) than adolescents in the rural area. A significant association also found between BMI and PA in both urban and rural areas. In conclusion, more physically active adolescents had lower BMI than who are less physically active. Being physically active could lower the body weight and BMI, hence improve musculoskeletal health, and could reduce co-morbidity.