Analizar el impacto de una intervención educacional sobre la calidad de la dieta mediterránea (DM), la actividad física y el estado ponderal en adolescentes.
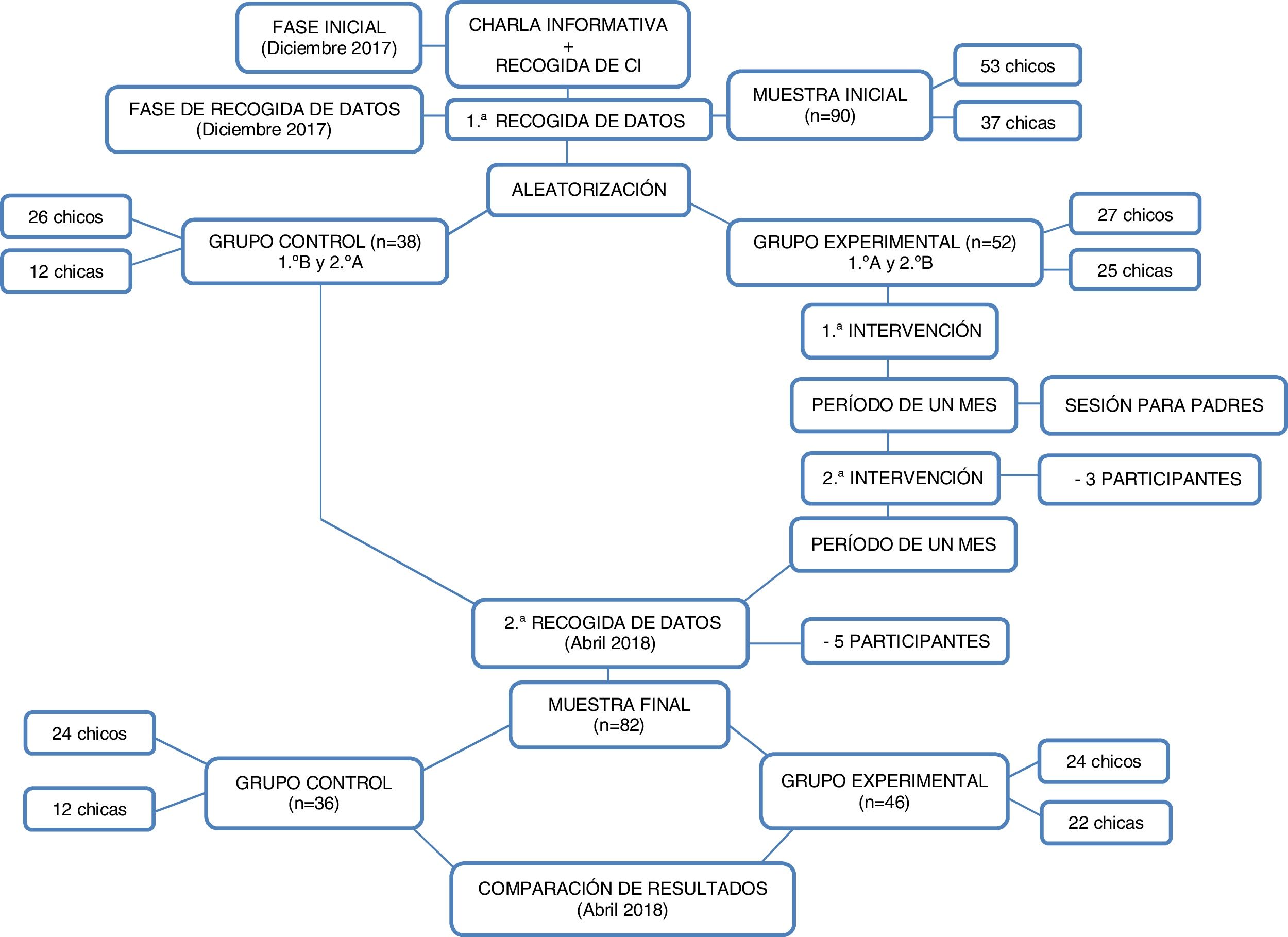
MétodoEnsayo clínico aleatorizado y controlado con intervención educacional multimodal (grupo control [n=36] y grupo experimental [n=46]). Recogida de datos, al inicio y al final del estudio, en población adolescente de la ciudad de Cáceres. En ambos grupos se determinaron medidas antropométricas y datos sociodemográficos. Se evaluó la calidad de la DM mediante el test KIDMED, el grado de actividad física a través del cuestionario PAQ-A y el estado ponderal con las tablas de crecimiento de la Fundación Faustino Orbegozo Eizaguirre.
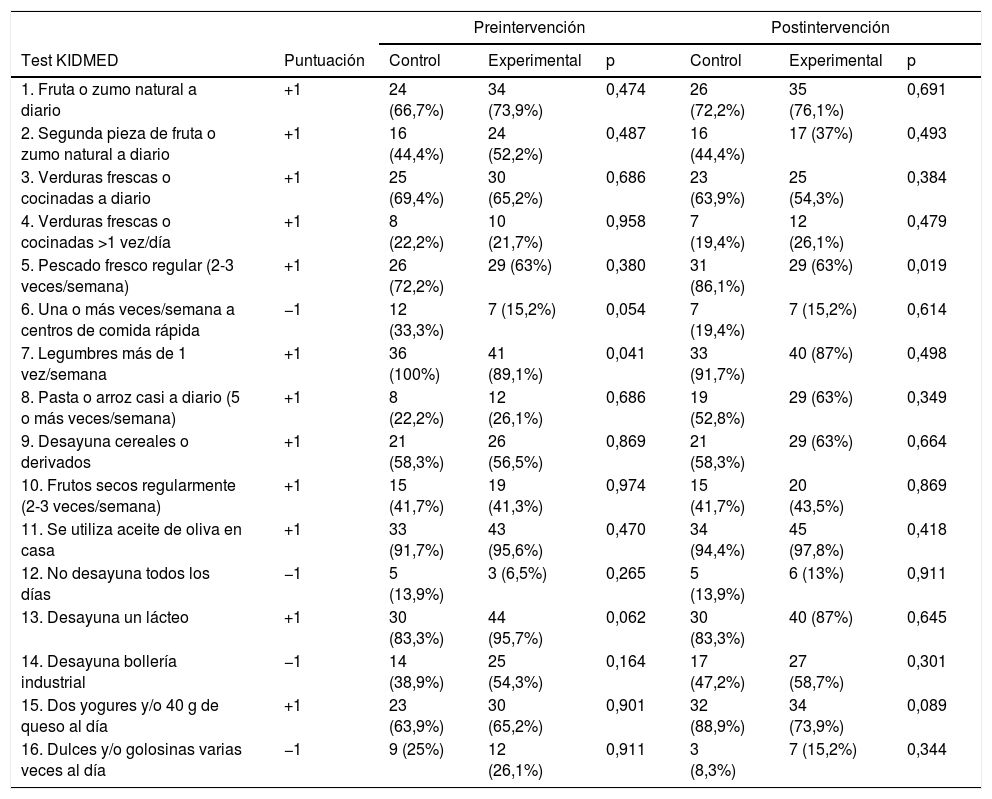
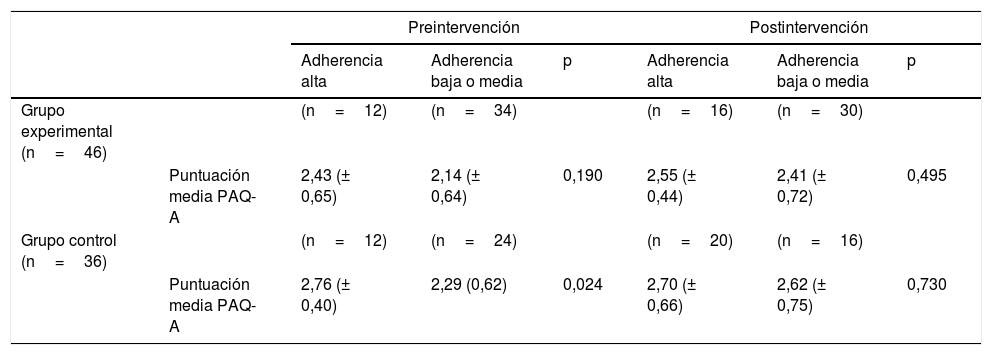
ResultadosObtuvimos un aumento significativo en el grupo experimental en el cuestionario PAQ-A que valora la actividad física (p=0,029). No se observaron diferencias significativas entre grupos en el estado ponderal (p=0,916). Al comparar la calidad de la DM (calidad alta vs moderada o baja) con la actividad física (pcontrol=0,730; pexperimental=0,495) y con el estado ponderal (pcontrol=0,838; pexperimental=0,372), no se observaron diferencias significativas.
ConclusionesLa intervención educacional no mejoró la calidad de la DM ni la actividad física, aunque la mayoría de nuestra muestra presentaba normopeso y actividad física aceptable. Debemos continuar mejorando el patrón alimentario saludable de nuestros adolescentes para garantizar un estado de salud adecuado en el futuro.
To analyse the impact of an educational intervention on the quality of the Mediterranean diet, physical activity and weight status in adolescents.
MethodRandomised clinical trial (RCT), controlled with a multimodal educational intervention (control group [n=36] and experimental group [n=46]). Data collection at the beginning and end of the study, in teenagers from Cáceres, Spain. In both groups anthropometric measurements and sociodemographic data were determined. The quality of the Mediterranean diet was assessed through the KIDMED test, the degree of physical activity through the PAQ-A questionnaire and weight status with the growth charts of the Faustino Orbegozo Eizaguirre Foundation.
ResultsWe obtained a significant increase in the experimental group in the PAQ-A questionnaire that assesses physical activity (P=.029). No significant differences were observed between groups in the weight status (P=.916). When comparing the quality of the Mediterranean diet (high vs moderate or low quality) with physical activity (Pcontrol=.730; experimental P=.495) and with weight status (Pcontrol=.838; experimental P=.372), No significant differences are observed.
ConclusionsThe educational intervention did not improve the quality of the Mediterranean diet or physical activity, although most of our sample had normal weight and acceptable physical activity. We must continue to improve the healthy eating pattern of our adolescents, to ensure an adequate state of health in the future.