This study aims to identify the effects of coaching methods in reducing HbA1c to improve glycemic control.
MethodsThe search for articles in this study was obtained from several databases, namely: PubMed, Cochrane, EBSCO, and Google Scholar. The article criteria were examined in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, adult patients (18–60 years), the Randomized Control Trial, a study that measured HbA1c, carried out in the last ten years and reported in English.
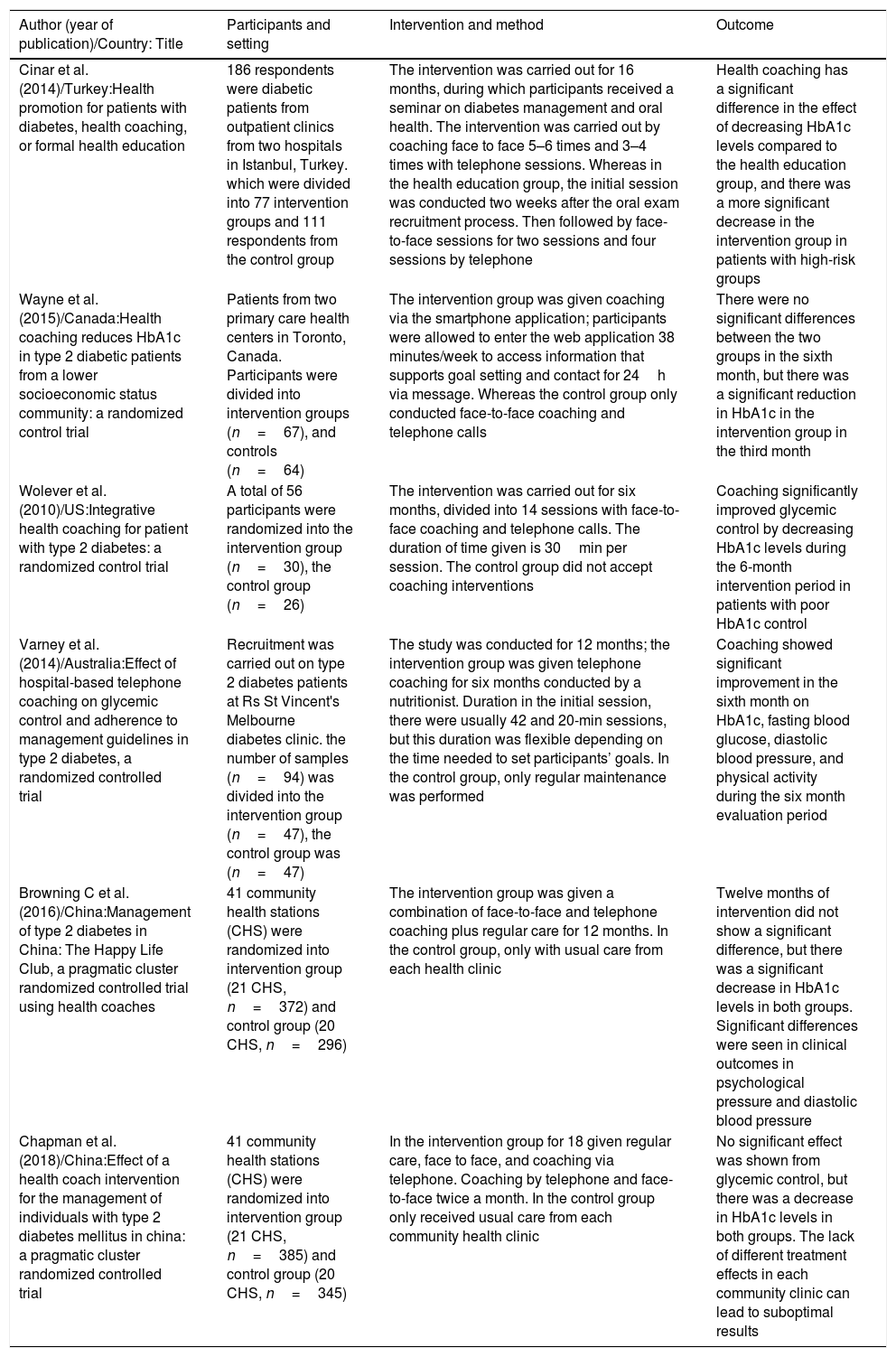
ResultsSix studies were selected in this study – those studies showing significant positive results for a decrease in HbA1c after coaching intervention.
ConclusionThe coaching method is promising to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It can be seen in the study that face-to-face coaching combined with a telephone, can be recommended.