To look at the relationship between food consumption patterns and household income in pregnant and lactating women, in Malili District, East Luwu Regency, South Sulawesi.
MethodThis study was an analytical survey, using a cross-sectional approach with 128 respondents consisting of 42 pregnant women and 86 lactating mothers. Data collection using questionnaires with interview techniques. Data analysis using bivariate analysis using the chi-square test and fisher exact test.
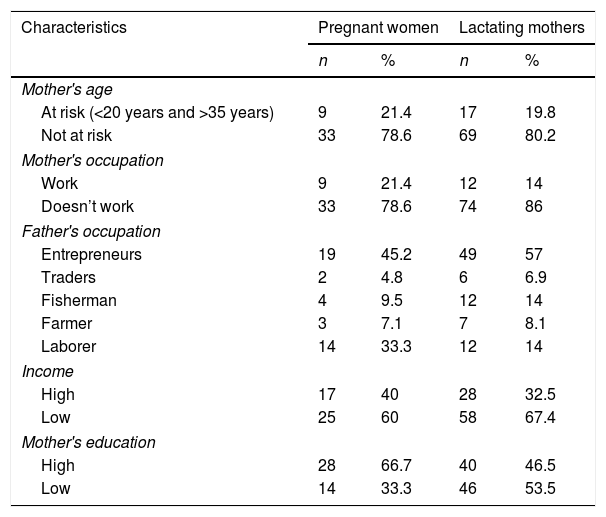
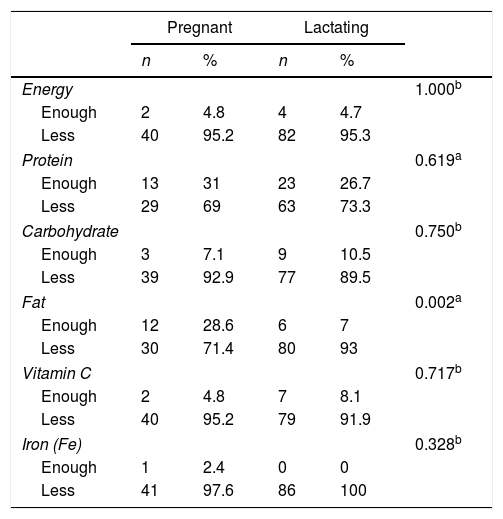
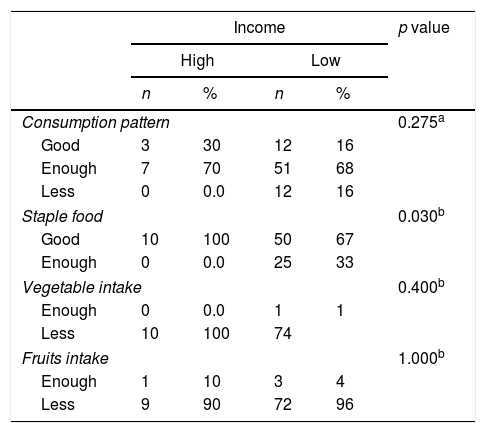
ResultsOf the total respondents there were high-risk age <20 years and >35 years 20%, low education 47%, housewives 84%, and low income 45%, high income 55%. The results showed that nutritional intake obtained a value of p=0.002 (p<0.05) which showed that there were differences in fat intake in pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers, whereas in energy, protein, carbohydrate, vitamin C, and FE intake there were no differences. In the consumption pattern, fruit intake, vegetable intake has no relationship with household income but the chi-square test on staple foods obtained a value of p=0.03 (p<0.05) which indicates that there is a relationship between food consumption and income.
ConclusionThere is a relationship between staple food consumption and household income in pregnant and lactating women.