Evaluar la influencia de una intervención educativa sobre el conocimiento, la detección y el manejo de la violencia de pareja íntima (VPI) por parte de matronas.
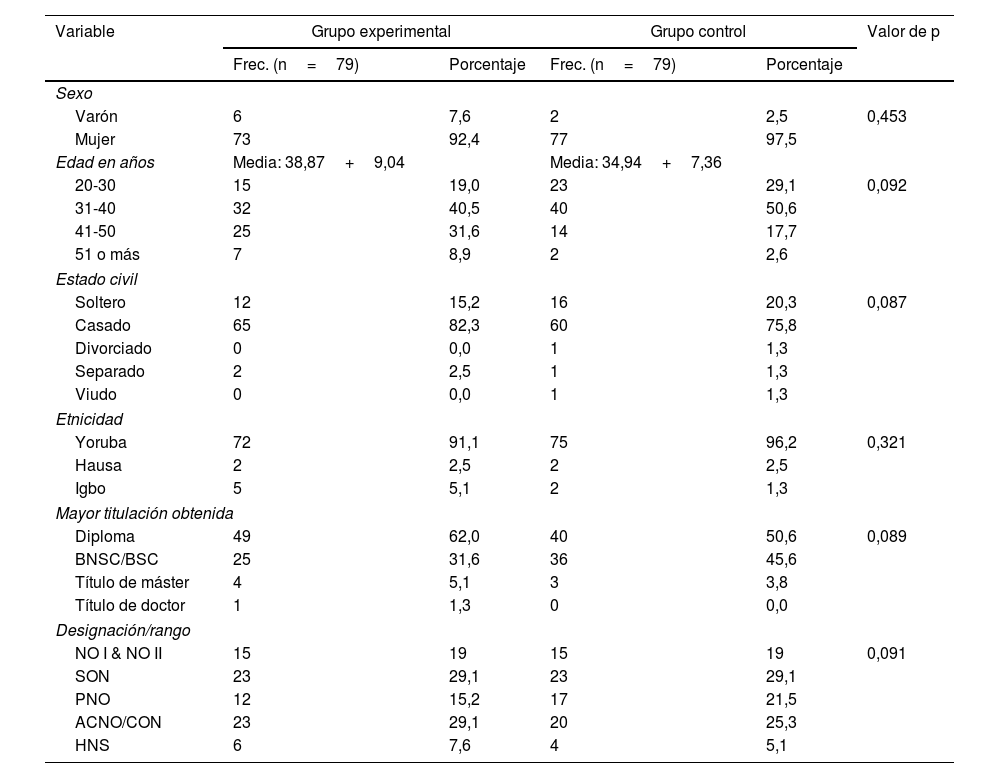
MétodoEstudio quasi-experimental donde participaron 158 matronas procedentes de 2 distritos en el estado de Ekiti (Nigeria). La muestra se dividió en grupos: experimental y de control (79 matronas por grupo). Los datos se recogieron mediante un cuestionario y una lista de verificación de observación. Se realizó un programa de capacitación educativa adaptado sobre detección y manejo de la VPI en el grupo experimental. Se realizó una medición antes de la intervención, inmediatamente después y 6 semanas después. Los datos se analizaron utilizando estadística descriptivas e inferenciales (Chi-cuadrado y regresión logística binaria) con un nivel de significancia establecido en p<0,05.
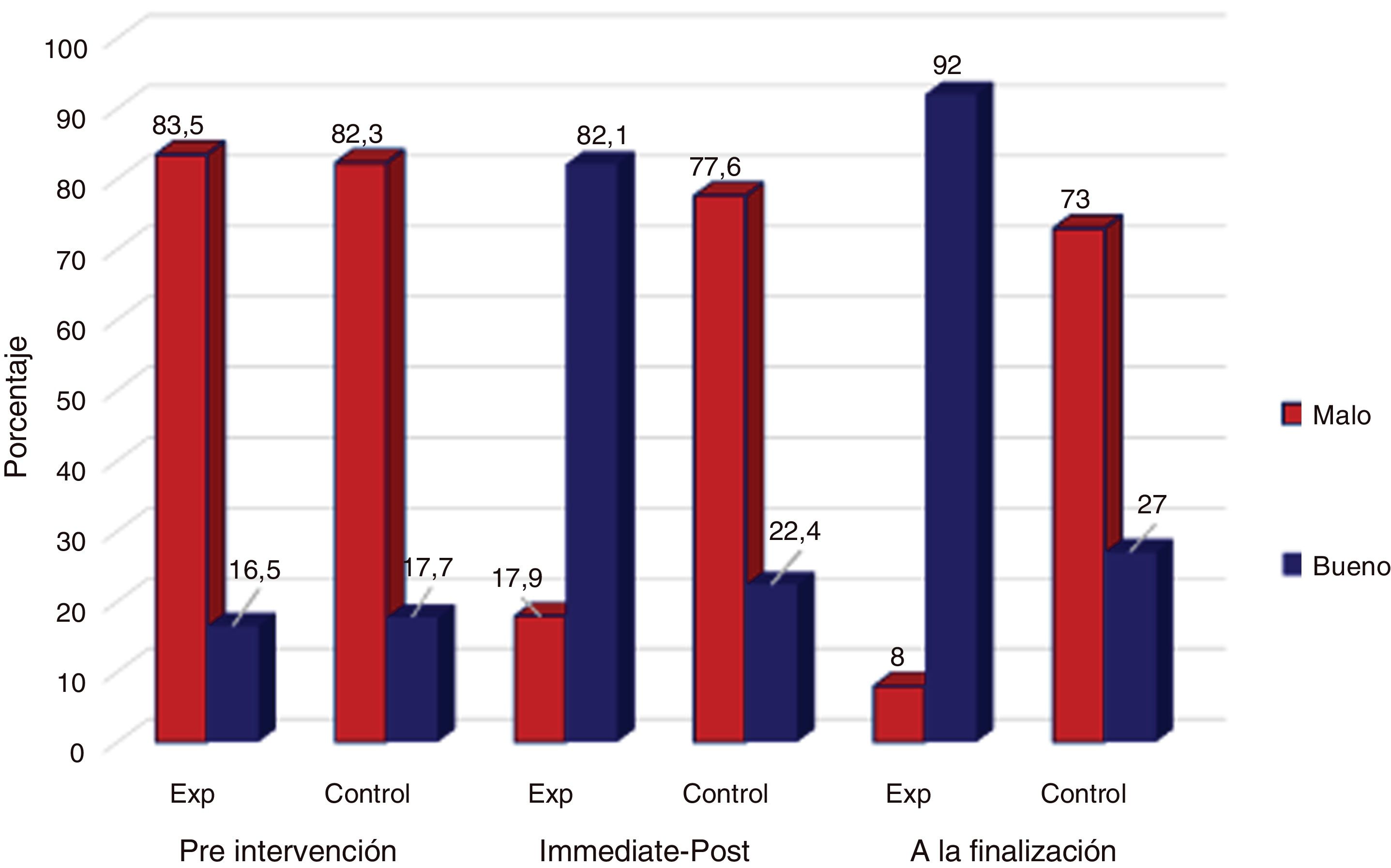
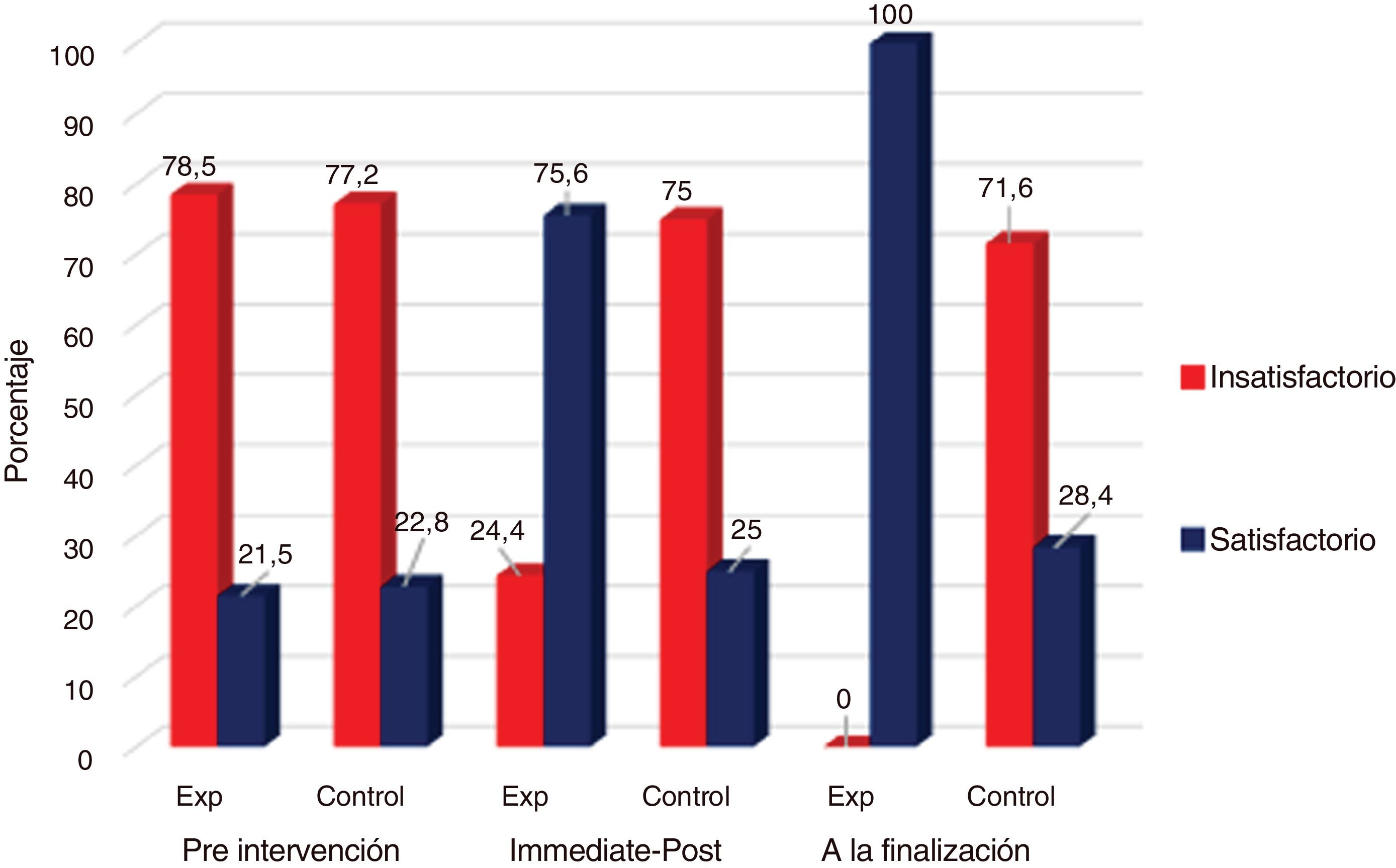
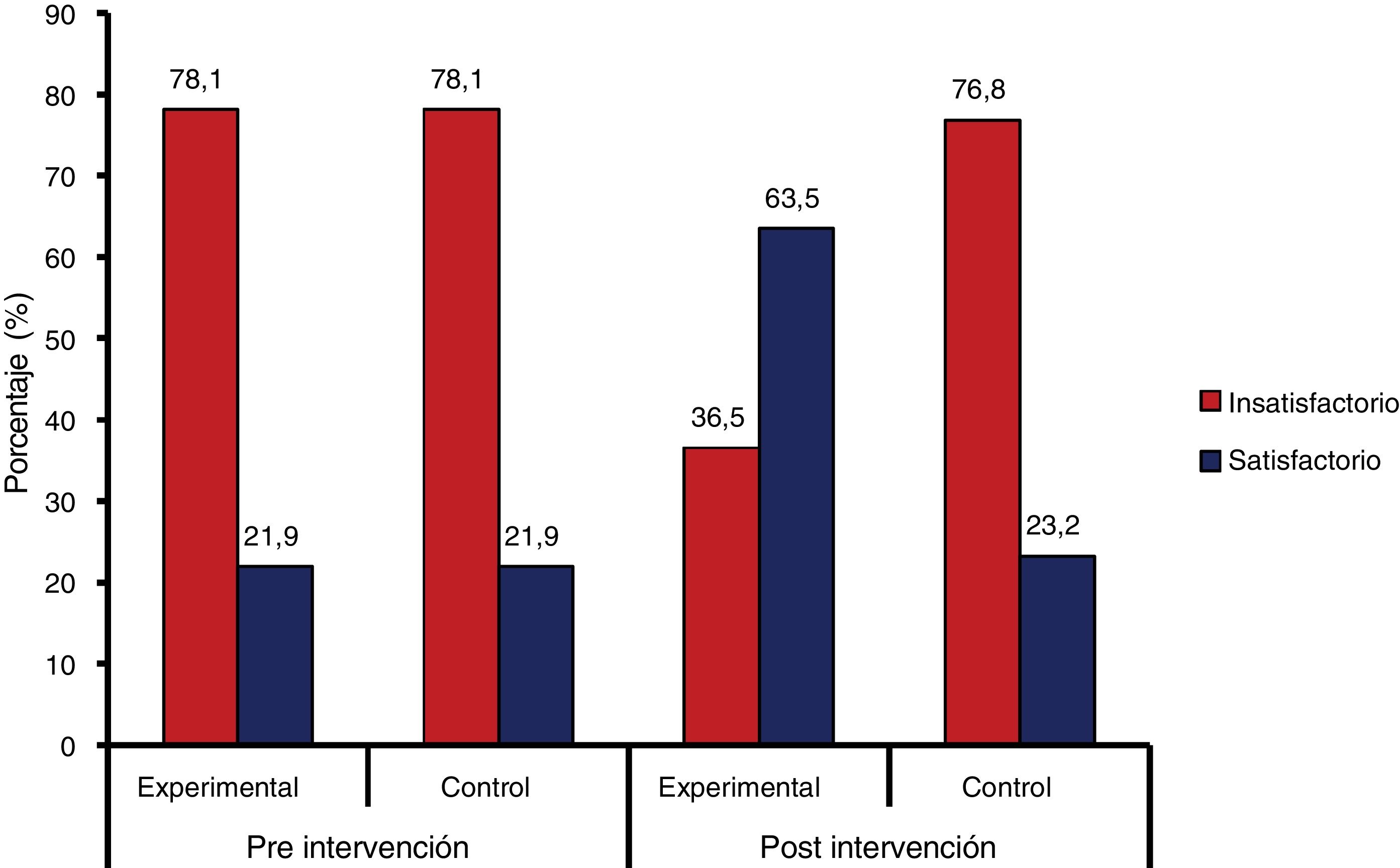
ResultadosEl conocimiento previo respecto a la detección y el manejo de la VPI entre las matronas en ambos grupos fue deficiente, ya que tan solo el 16,5% del grupo experimental y el 17,7% del grupo control tenían un buen conocimiento en la fase previa a la intervención. El grupo experimental tuvo una mejora significativa en el conocimiento de la detección y el manejo de la VPI, con un 82,1% con buenos conocimientos inmediatamente después de la intervención y un 92,0% a las 6 semanas después de la intervención (p=0,001). La práctica observada de detección y manejo de la VPI obtuvo mejora significativa, pasando de un 21,9% de práctica satisfactoria antes de la intervención, a un 63,5% después de la intervención (p=0,001) en el grupo experimental, no detectándose una mejora apreciable en la práctica en el grupo control (21,9 versus 36,5%; p=0,682).
ConclusiónEl uso programa de capacitación educativa adaptado mejoró el conocimiento de las matronas y su práctica sobre la detección y el manejo de la violencia de pareja íntima.
To assess the influence of an educational intervention on midwives’ knowledge, detection and management of intimate partner violence (IPV).
MethodsA quasi-experimental study involving 158 midwives from two districts in Ekiti State, Nigeria. The sample was divided into experimental and control groups (79 midwives per group). Data were collected using a questionnaire and an observation checklist. A customized educational training program on IPV detection and management was conducted in the experimental group. Measurement was performed before the intervention, immediately after and 6 weeks later. Data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics (Chi-square and binary logistic regression) with a level of significance set at P<.05.
ResultsPrior knowledge regarding IPV detection and management among midwives in both groups was poor, with only 16.5% of the experimental group and 17.7% of the control group having good knowledge in the pre-intervention phase. The experimental group had a significant improvement in knowledge of IPV screening and management, with 82.1% having good knowledge immediately after the intervention and 92.0% at 6 weeks after the intervention (P=.001). Observed practice of IPV detection and management improved significantly from 21.9% satisfactory practice before the intervention to 63.5% after the intervention (P=.001) in the experimental group, with no appreciable improvement in practice detected in the control group (21.9 versus 36.5%; P=.682).
ConclusionThe use of a customized educational training program improved midwives’ knowledge and practice in the detection and management of intimate partner violence.