This study compares mercury measurements at several community's sites for air, soil and water samples.
MethodThis observational analytic applied accidentally random sampling for communities and environmental samples. Total mercury (THg) contaminated concentration sample derived from surround cement processes. Samples of air, water column and soil were collected in one time.
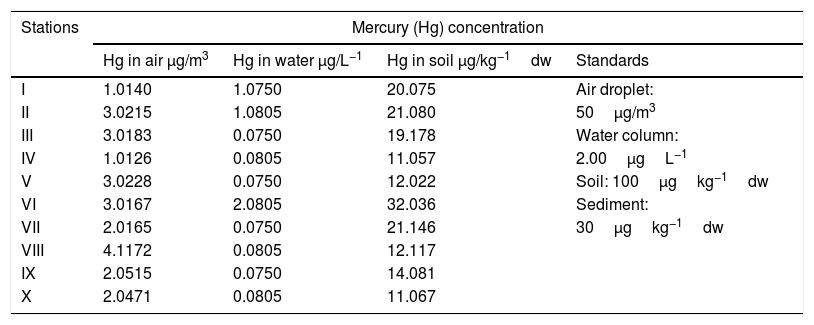
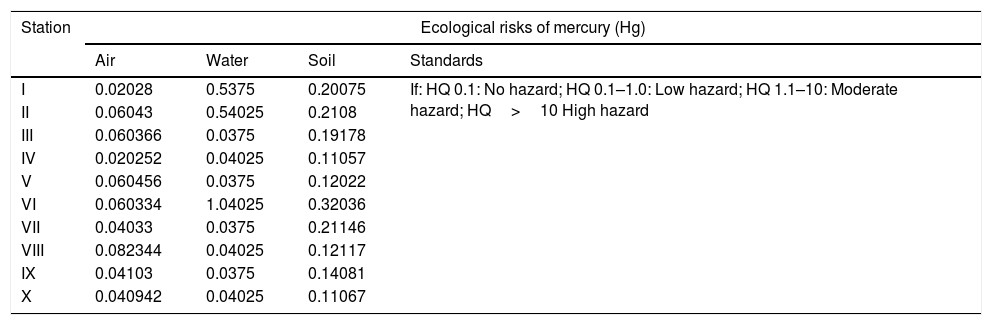
Resultsit implied that THg concentration value in the air, water and soil range from 1.0126 to 4.1172μg/m3, 0.0750 to 2.0805μg/L−1 and 11.057 to 32.036μg/kg−1dw, respectively. In the average, the magnitude of Hg level was in the surface soils>Air>surface water, respectively. The value of ecological risks was range from 3.0–4.4, 0.16–0.22 in the air, 3.0–4.4, 0.16–0.22 in water and 3.0–4.4, 0.16–0.22 in surface soil, respectively.
ConclusionMercury Risk values are still lower than standard and ecological risks still low hazard, those value however may increase due to occurrence of accumulation on those sites.