This this study aims to analyze risk factor of pulmonary tuberculosis smear (+) among people with diabetes mellitus in Makassar.
MethodThis is a case control design study implemented in 5 public health center in Makassar. With a sample of 90 people (45 cases and 45 controls), interviewed with a questionnaire. Bivariate analysis and regression model were performed to examined potential risk factor of pulmonary tuberculosis.
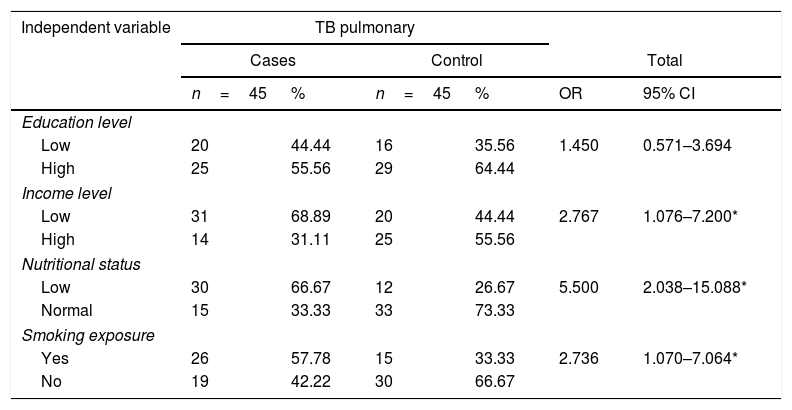
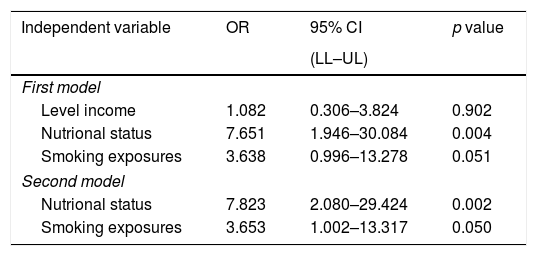
ResultThe result showed that significant risk factor for pulmonary TB were income level (OR=2.767, 95% CI: 1.076–7.200, p=0.019), nutritional status/BMI (OR=5.500, 95% CI: 2.038–15.088, p=0.000), smoking (OR=2.736, 95% CI: 1.070–7.064, p=0.019), meanwhile educational level are not risk factors of pulmonary TB (OR=1.450, 95% CI: 0.571–3.694, p=0.310).
ConclusionPulmonary TB control efforts are suggested not only to focus on curative aspects, but also through promotive and preventive aspects, especially to prevent people with DM from having risk factors such as duration of DM>5 years, contact history, low nutritional status, smoking habits and income level.