This study aimed to analyze the factors related to stunting in children aged 0–59 months.
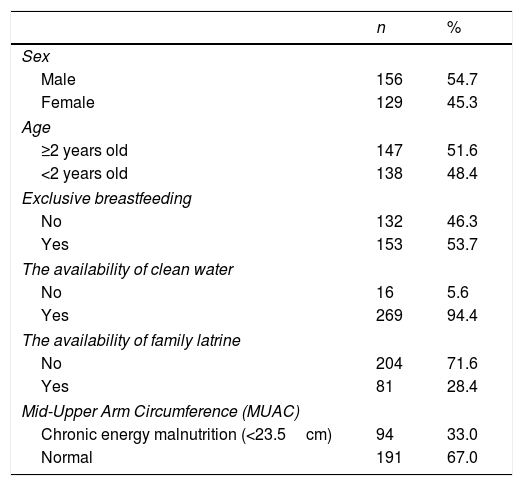
MethodsThis cross-sectional study involved a total sampling of 285 children <5 years. Data collected were age, sex, exclusive breastfeeding, Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC), water source and family latrine. Chi-square and multivariate logistic regression were performed.
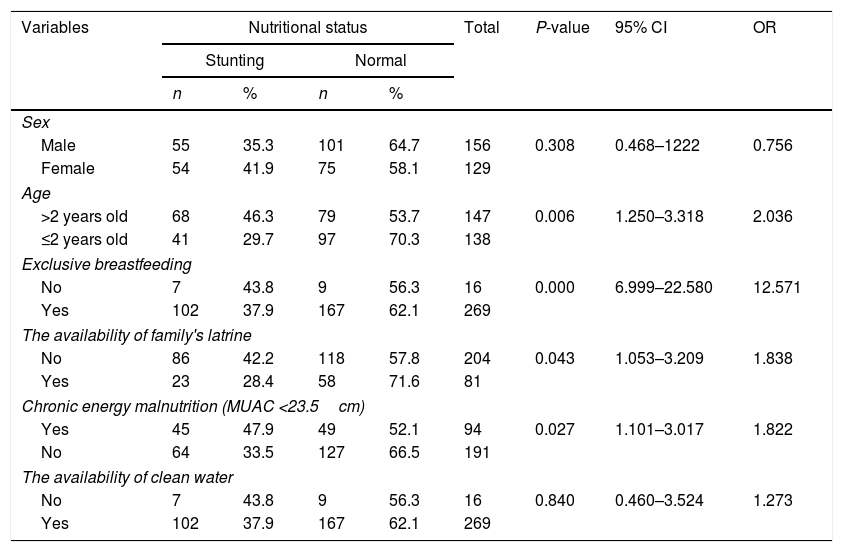
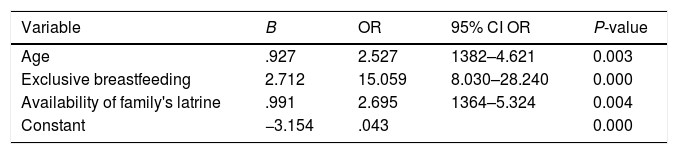
ResultsThe results showed that age, exclusive breastfeeding, MUAC, the availability of family latrine were significantly related with the incidence of stunting (P<0.05). Furthermore, the results of multivariate analysis showed that the risk factors that most affected stunting were non-exclusive breastfeeding (OR=15.059; 95% CI 8.030–28.240), poor family latrine (OR=2.695; 95% CI 1.364–5.324) and age (OR=2.527; 95% CI 1.382–4.62).
ConclusionsThe strongest risk factors for stunting are non-exclusive breastfeeding, poor family's latrines, and the sex of the children. It is recommended that to strengthen multisectoral interventions to reduce stunting.