The aim of the study is to explore the correlation between self-care management and health outcomes among pregnant women in Makassar City, Indonesia.
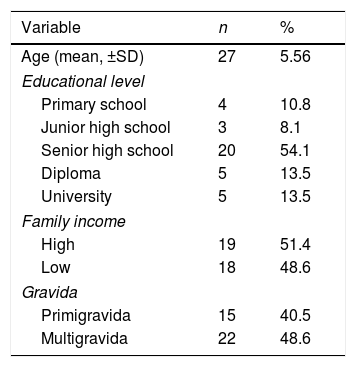
MethodThis study used a quantitative method with longitudinal design study. There were 37 pregnant women with more than 28 weeks gestation participated in this study selected using purposive sampling technique.
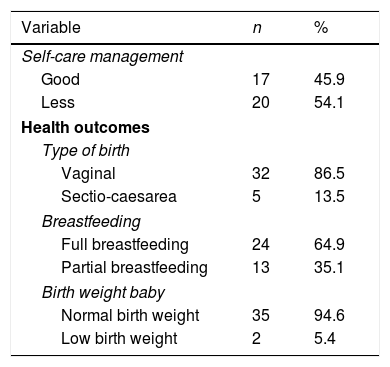
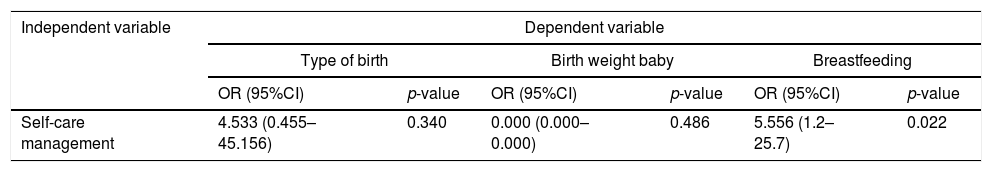
ResultResult from this study show that more pregnant women had low self-care management only self-care management only correlate with breastfeeding (OR: 95%CI) 5.556 and p-value 0.022). Other variables such as types of birth and baby's weight have no correlation with self-care management.
ConclusionSelf-care management is one indicator to see someone can reach health outcome. This study revealed that pregnant women with good self-care management would five times higher to have a good understanding of breastfeeding and will breastfeed their babies fully.