This study was conducted to assess the effect of ML supplementation in women during pregnancy and lactation on growth and morbidity of 6–11 month-old infants.
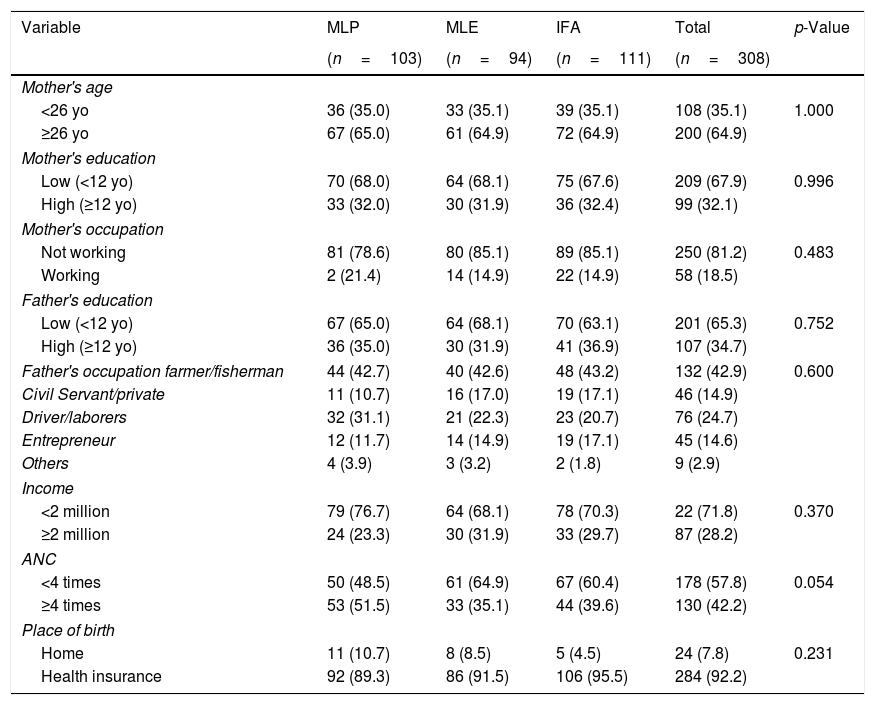
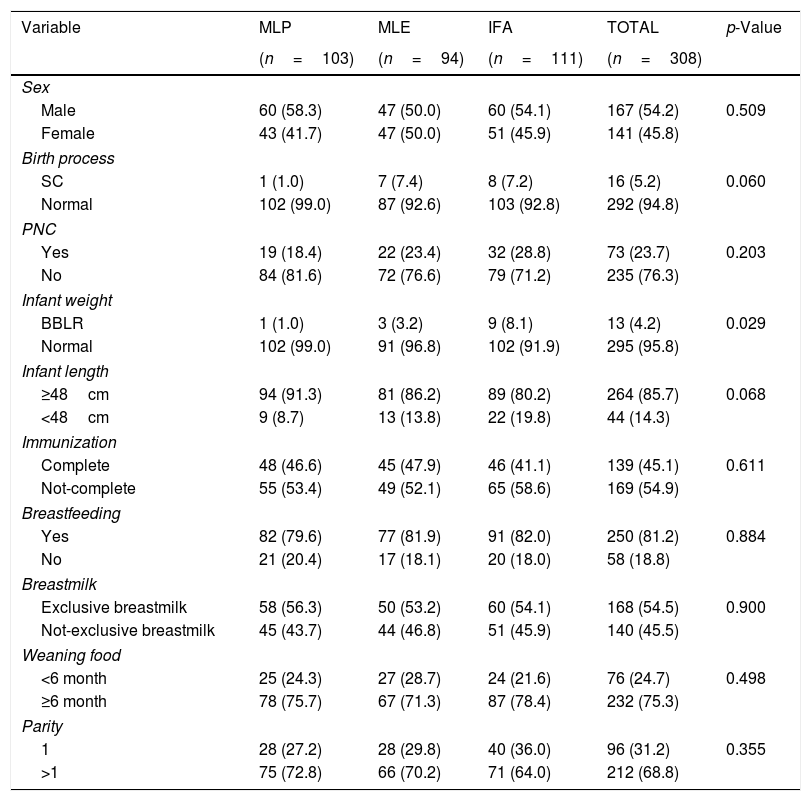
MethodThis study was an intervention study and followed with Cohort to the infants at 6–11 month-old. The subjects were pregnant women who were divided into three groups: a group who received ML powder (MLP, n=103), a group receiving ML extract (MLE, n=94), and a group consuming iron folic acid (IFA, n=111). Growth and morbidity measurement were assessed each month. The data was analyzed using ANOVA test and Chi-squares.
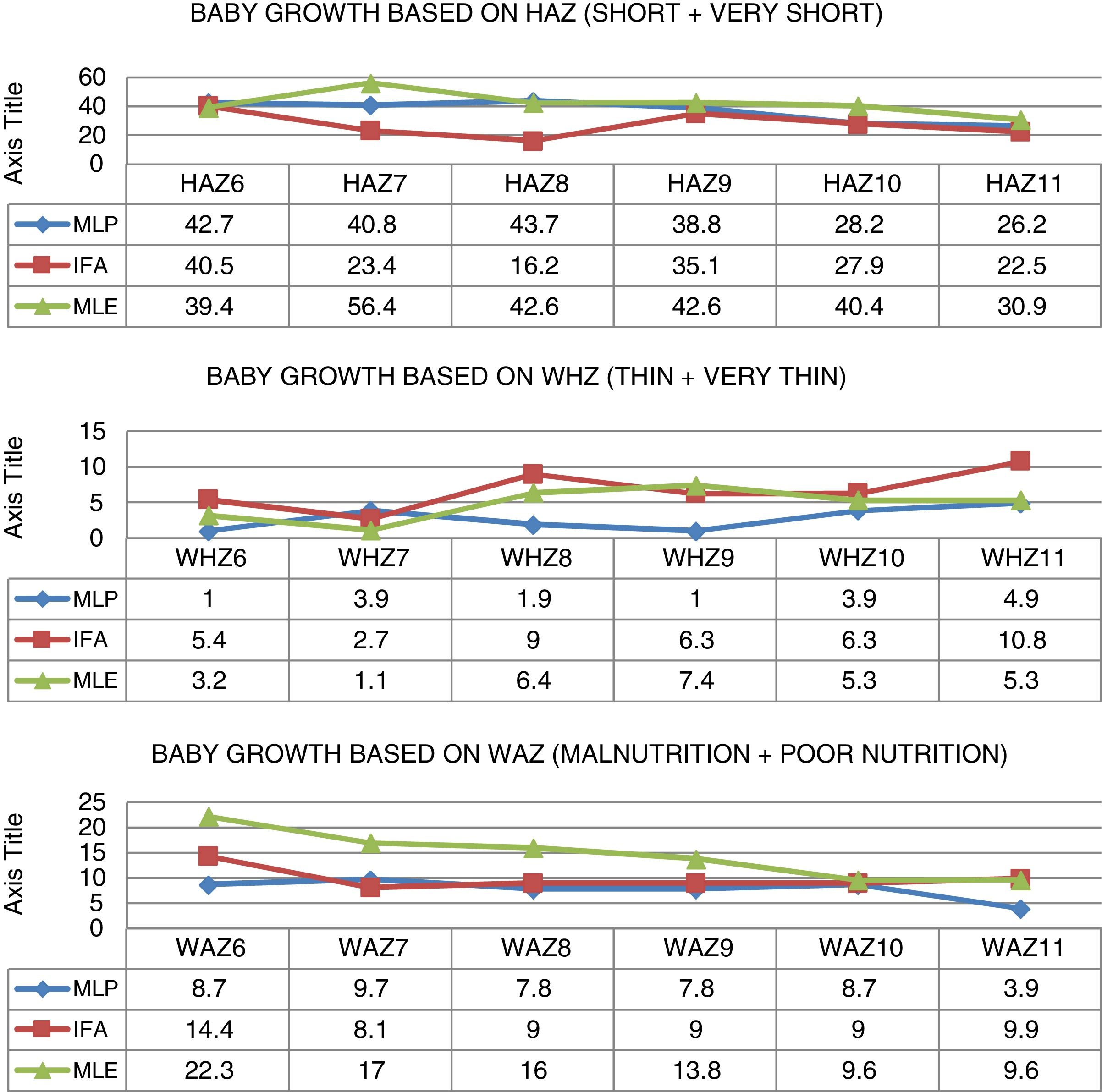
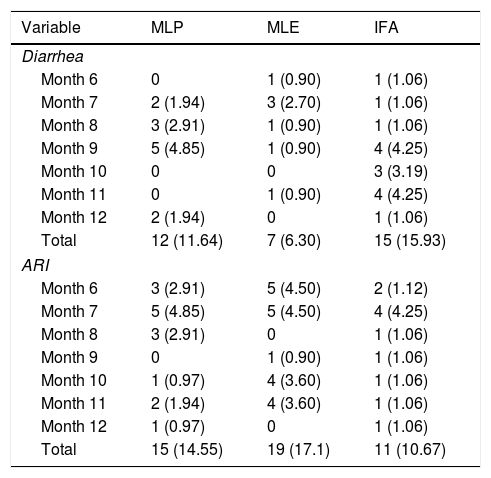
ResultsThe study showed that prevalence of malnutrition at 6–11 month-old infants ranged from 7.8% to 14.9% for malnutrition and 2.6–7.1% of wasting and there were not significantly different among all age groups (p>0.05). Moreover, prevalence of stunting was 26.3–40.9% and there were significant difference among groups in some age periods. The prevalence of stunting was significantly lower in IFA compared to MLP and MLE groups (p<0.05). Diarrhea and upper respiratory infection were found but lower across the age periods (0.65–4.55%).
ConclusionThe study concluded that ML supplement in pregnant and lactating women could not protect infants from stunting.