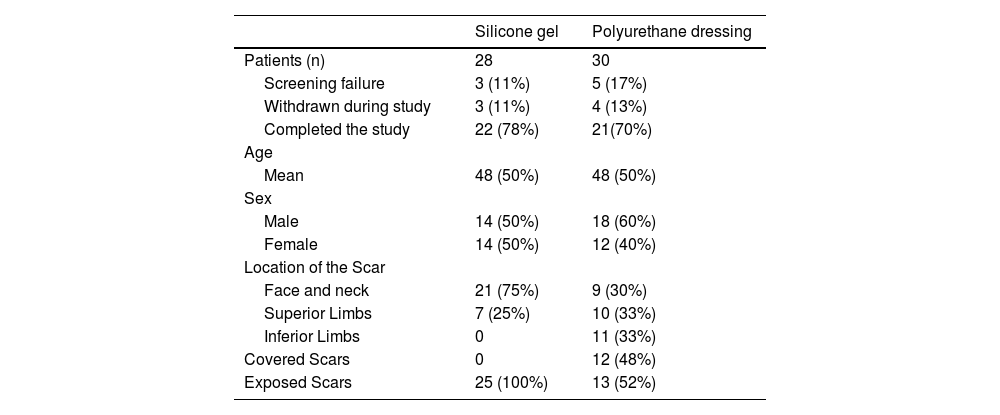
To assess the effectiveness and safety of a topical silicone gel (BE + Gel reductor y reparador de cicatrices) and a polyurethane dressing (BE + Apósito reductor y reparador de cicatrices) on the evolution of scars of patients who were previously recruited in the emergency care unit while seeking wound care.
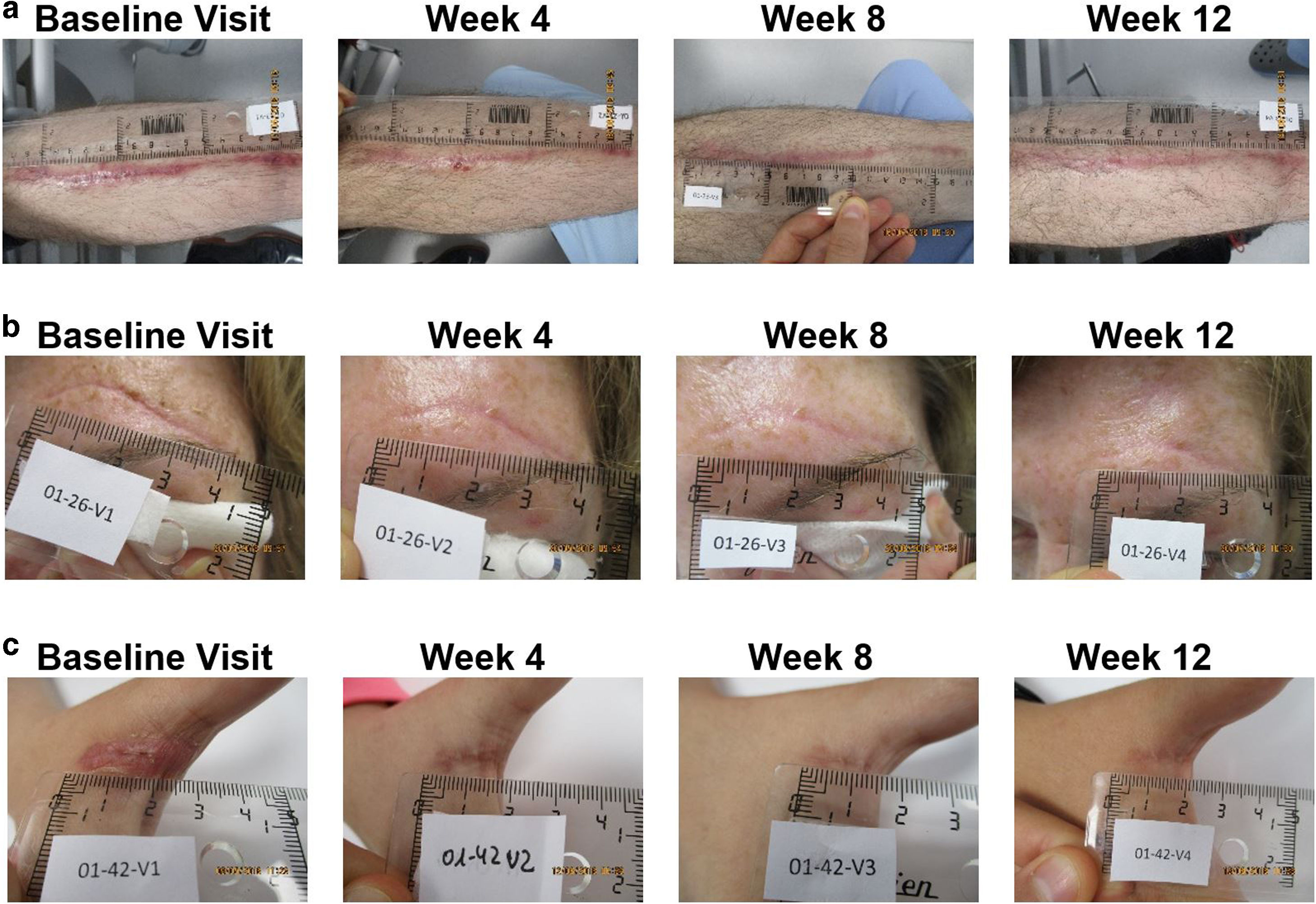
MethodA single center, stratified observational, open label study was performed in the emergency care unit of Donostia Universitary Hospital (recruitment) and in the Biodonostia Health Research Institute (intervention). Scars located in unexposed body areas with the dressing, and scars located in exposed areas with either the gel or the dressing. Investigators assessed interventions at day 1 and on weeks 4, 8 and 12. Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) and a photographical assessment were used to determine the scars evolution, and the subjective perception of the scar was evaluated by means of a questionnaire administered to the patients.
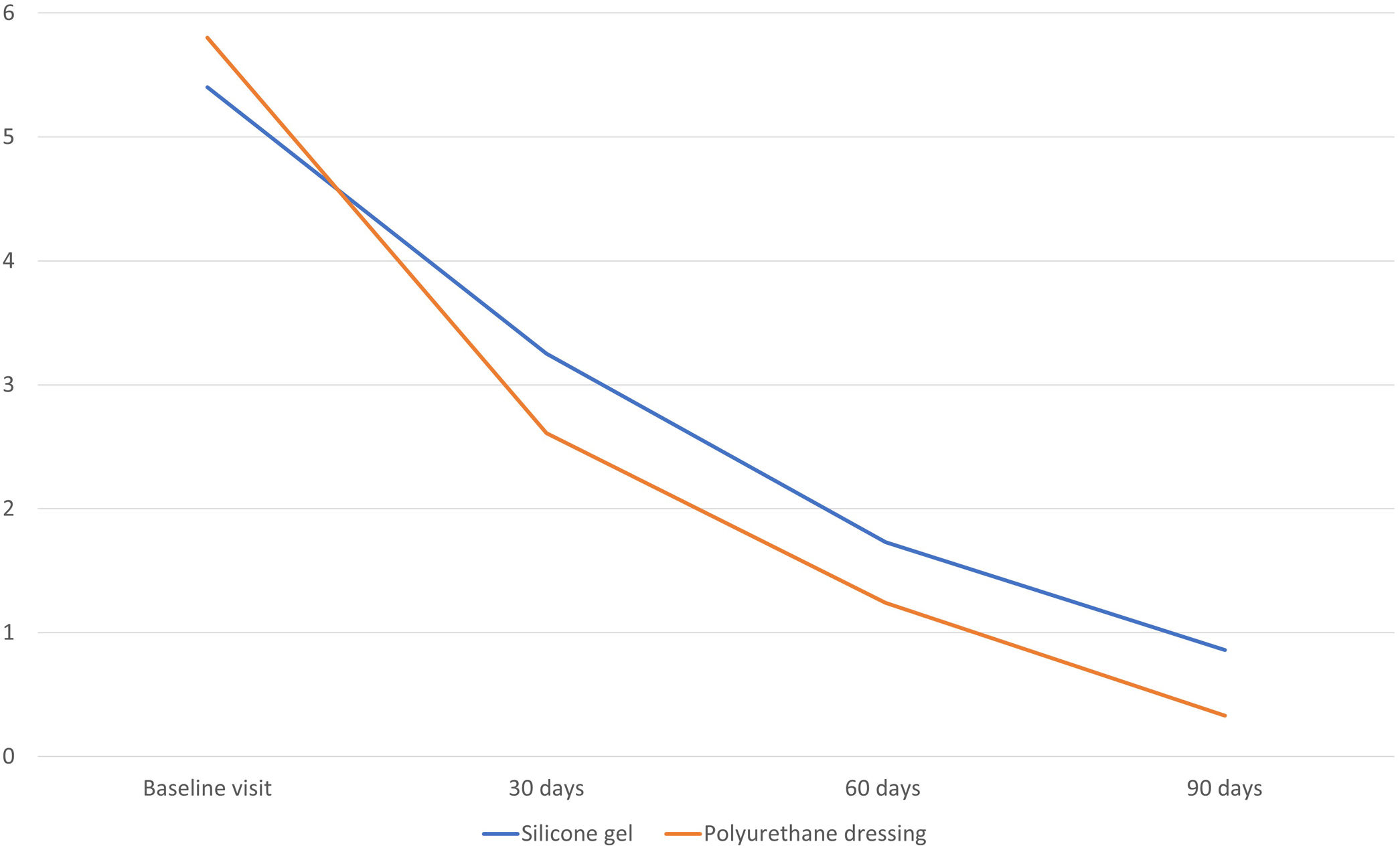
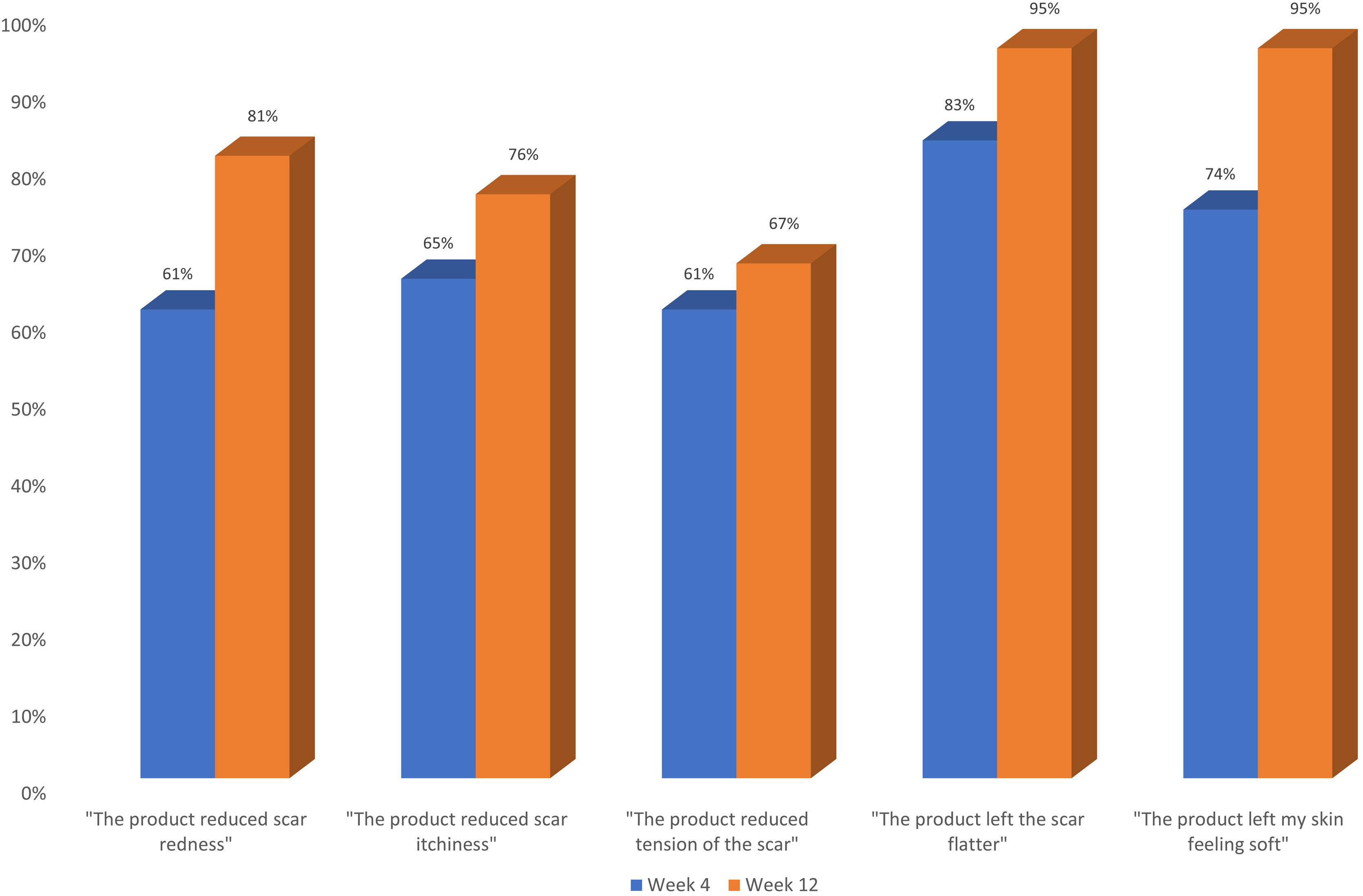
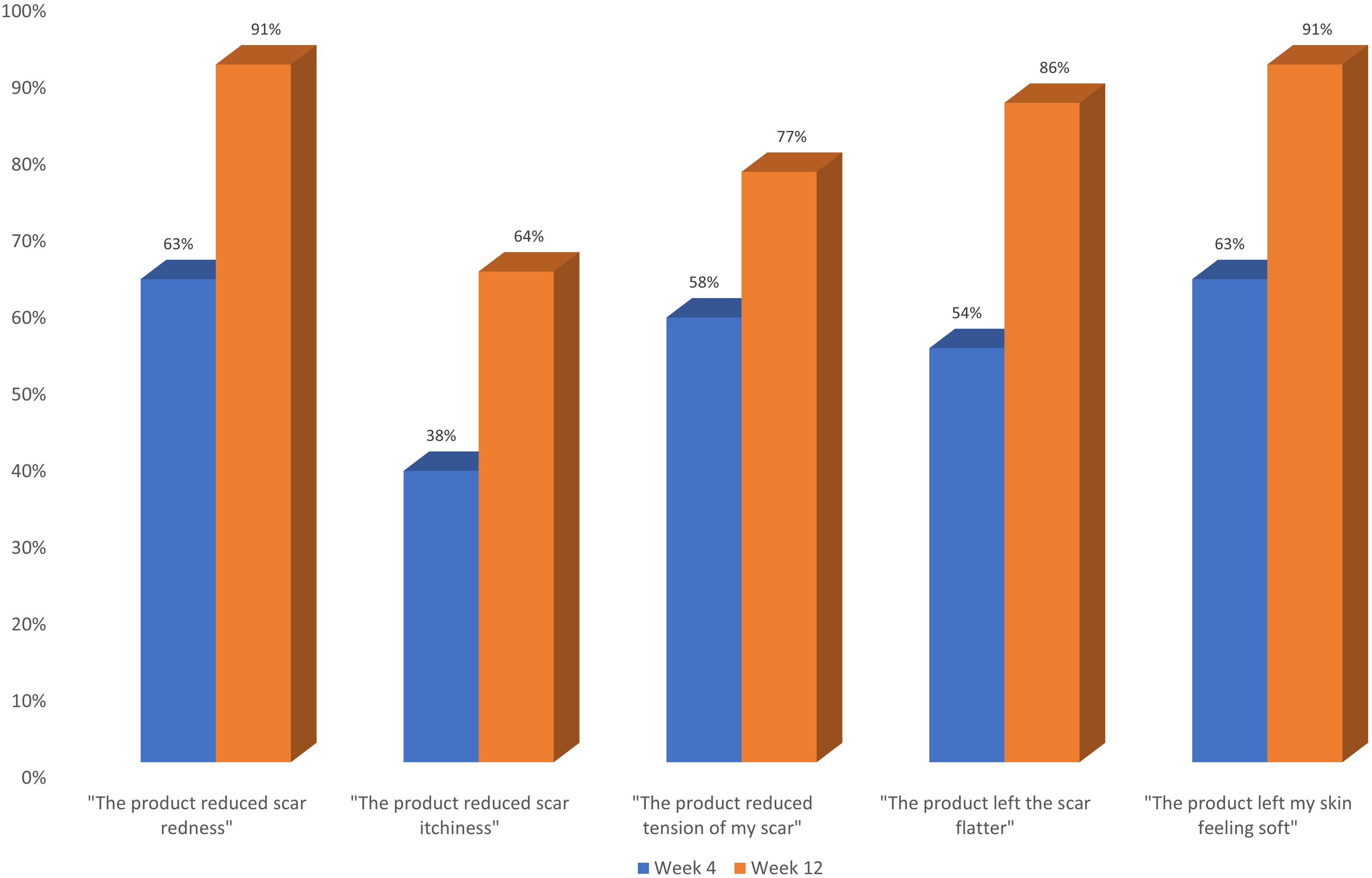
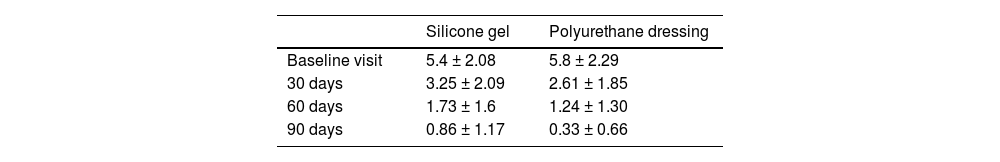
ResultsPatients whose scars were treated with the silicone gel had an average initial VSS score of 5.4 ± 2.08. This value was reduced to 0.86 ± 1.17 after 90 days of treatment. Patients treated with the polyurethane dressing had an average initial VSS score of 5.8 ± 2.29. After 90 days of treatment, this average score was reduced to 0.33 ± 0.66. Positive evolution of scars was also supported by photographs and by a patient questionnaire.
ConclusionsBoth treatments appear to be safe and effective, objectively, and subjectively, in the context of scar evolution.
Evaluar la efectividad y seguridad de un gel de silicona tópico (BE + Gel reductor y reparador de cicatrices) y un apósito de poliuretano (BE + Apósito reductor y reparador de cicatrices) sobre la evolución de cicatrices en pacientes que fueron previamente reclutados en urgencias por heridas.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio observacional estratificado, abierto y monocéntrico en la unidad de urgencias del Hospital Universitario de Donostia (reclutamiento) y en el Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Biodonostia (intervención). Se trataron las cicatrices ubicadas en áreas del cuerpo no expuestas con el apósito y las ubicadas en áreas expuestas con el gel o el apósito. Los investigadores evaluaron las intervenciones el día 1 y en las semanas 4, 8 y 12. Se utilizó la Escala de cicatrices de Vancouver (VSS) y una evaluación fotográfica para determinar la evolución de las cicatrices, evaluándose la percepción subjetiva de esta mediante un cuestionario administrado a los pacientes.
ResultadosLos pacientes cuyas cicatrices fueron tratadas con el gel de silicona tuvieron una puntuación inicial promedio de 5,4 ± 2,08 en VSS. Este valor se redujo a 0,86 ± 1,17 después de 90 días de tratamiento. Los pacientes tratados con el apósito de poliuretano tuvieron una puntuación inicial promedio de 5,8 ± 2,29 en VSS. Después de los 90 días, esta puntuación media se redujo a 0,33 ± 0,66. La evolución positiva de las cicatrices también fue apoyada por fotografías y cuestionarios a pacientes.
ConclusionesAmbos tratamientos parecen ser seguros y efectivos, objetiva y subjetivamente, en el contexto de la evolución de las cicatrices.