Inhaled sedation uses halogenated drugs (isoflurane and sevoflurane) in a liquid state that, through a vaporizer, change to a gaseous state and reach the patient by the respiratory route. These drugs have a rapid onset of action, with minimal metabolism and elimination takes place almost exclusively through the airways. They do not cause significant tolerance, tachyphylaxis or significant abstinence. Inhaled sedation enables a rapid and more predictable awakening and reduced the need for opioids and neuromuscular relaxants (than intravenous sedation). In addition, have bronchodilatory, anticonvulsing and potential antiinflammatory and cardioprotective effects.
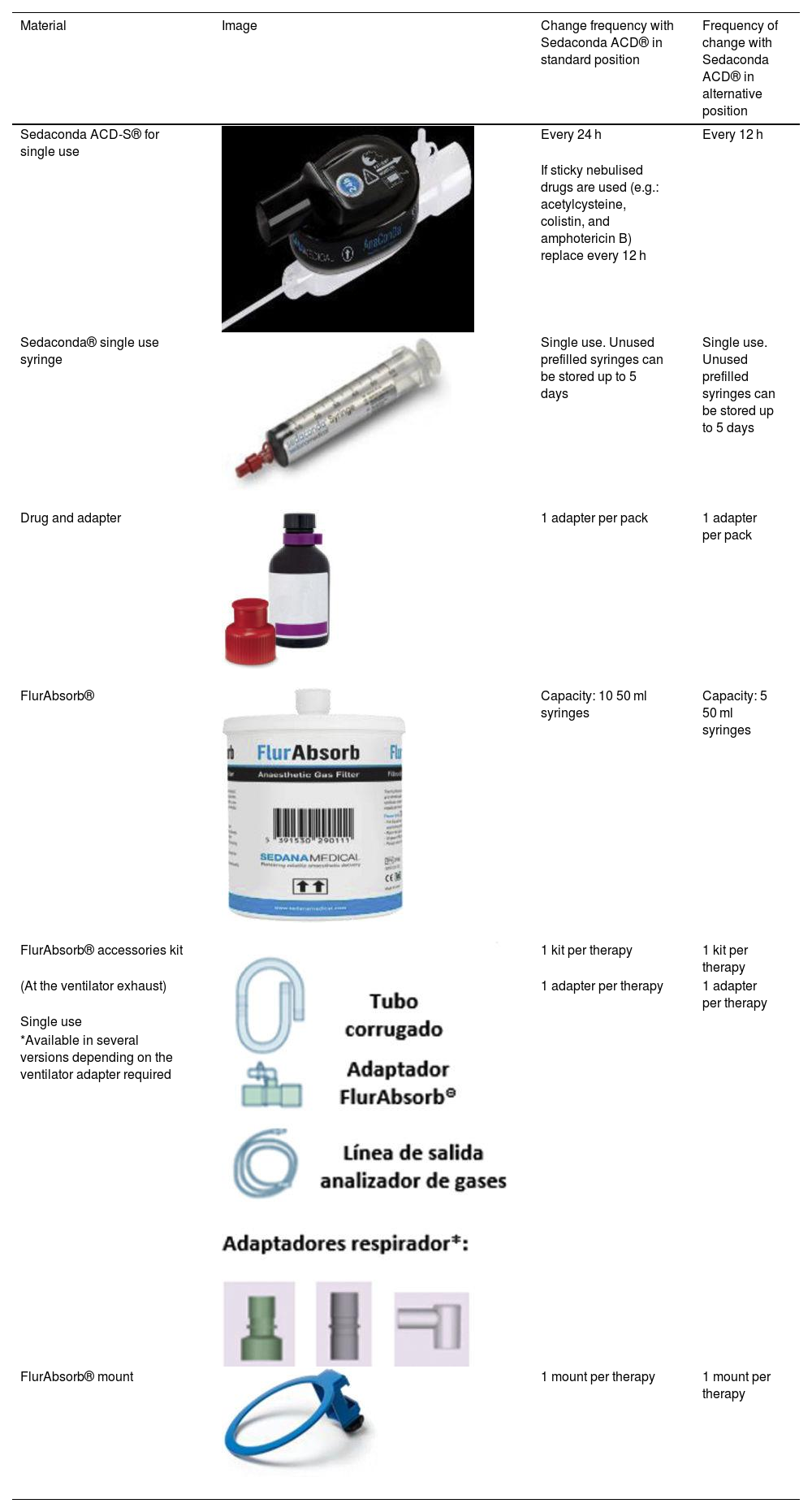
To date, inhaled sedation has been practically exclusive to the areas of anesthesia and surgery. For its therapeutic application in the environment of the Intensive Care Units (ICU) there are two devices, Sedaconda ACD® and Mirus®. Its design, adaptable to different respirators and with a safe scavenging gas system, has facilitated its introduction in the ICUs. Scientific evidence supports the use of isoflurano and Sevoflurano (with limitations), especially in cases of moderate-deep sedation, and for people with acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute bronchospasm, status epilepticus, people who are difficult to sedate, prolonged sedation (only isoflurano) and patients post cardiac arrest or who need daily neurological assessment.
Halogenated sedation is safe and effective for the critical patient undergoing mechanical ventilation. However, it is not exempt from risks and requires learning by professionals who will prescribe and/or apply. Nurses must know the characteristics of the drug, its handling, and be an expert in the route of administration so that the therapy is safe for the patient and health professionals.
La sedación inhalatoria utiliza fármacos halogenados (isoflurano y sevoflurano) en estado líquido que, mediante un vaporizador, pasan a un estado gaseoso y llegan al paciente por vía respiratoria. Tienen un inicio de acción rápido, con baja metabolización hepática y rápida eliminación por exhalación pulmonar. Entre sus beneficios destacan un despertar rápido y predecible del paciente y un menor consumo de fármacos opiáceos y relajantes neuromusculares (respecto a la sedación endovenosa tradicional). No provocan tolerancia o taquifilaxia ni abstinencia significativa. Además, poseen propiedades broncodilatadoras, anticonvulsivantes y potenciales efectos antiinflamatorios y cardioprotectores.
Hasta la fecha, la sedación inhalatoria ha sido prácticamente exclusiva de las áreas de anestesia y quirófano. Para su aplicación terapéutica en el entorno de las unidades de cuidados intensivos (UCI) existen dos dispositivos Sedaconda ACD® y MIRUS®. Su diseño, adaptable a diferentes respiradores y con un sistema para la evacuación segura de gases, ha facilitado su introducción en las UCI. La evidencia científica avala el empleo de isoflurano y sevoflurano (con limitaciones), especialmente en casos de sedación moderada-profunda, y para personas con síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo, broncoespasmo agudo, estatus comicial, casos de sedación difícil, sedación prolongada (sólo isoflurano) y pacientes post parada cardiorrespiratoria o con necesidades de valoración neurológica diaria.
La sedación con halogenados es segura y eficaz para el paciente crítico sometido a ventilación mecánica. No obstante, no está exenta de riesgos y requiere un aprendizaje por parte de los profesionales que la van a prescribir y/o aplicar. Las enfermeras deben conocer las características del fármaco, su manejo, y ser expertas en la vía de administración para que la terapia resulte segura para el paciente y el personal sanitario.
Article
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.