To compare the efficacy of conventional puncture versus ultrasound-guided puncture for arterial blood gas sampling in adults.
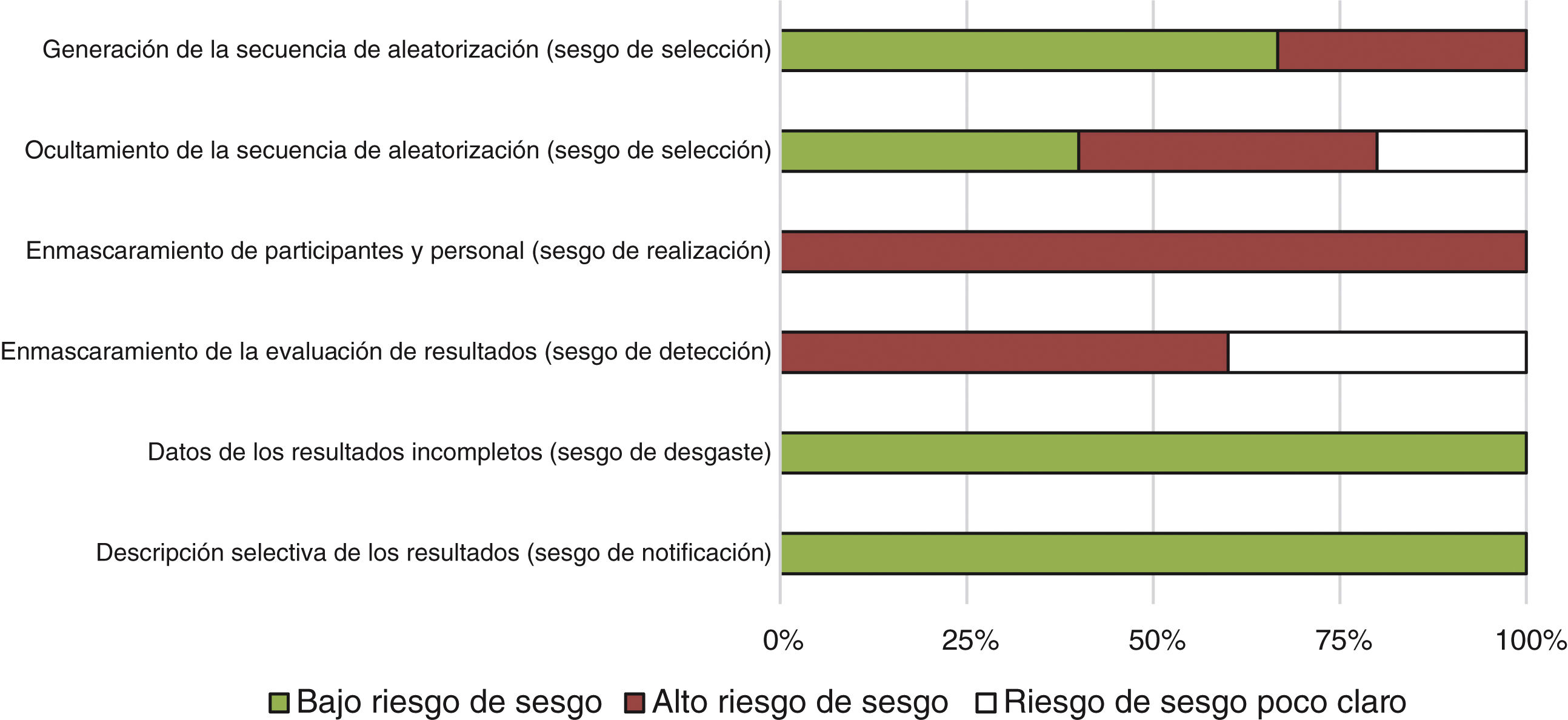
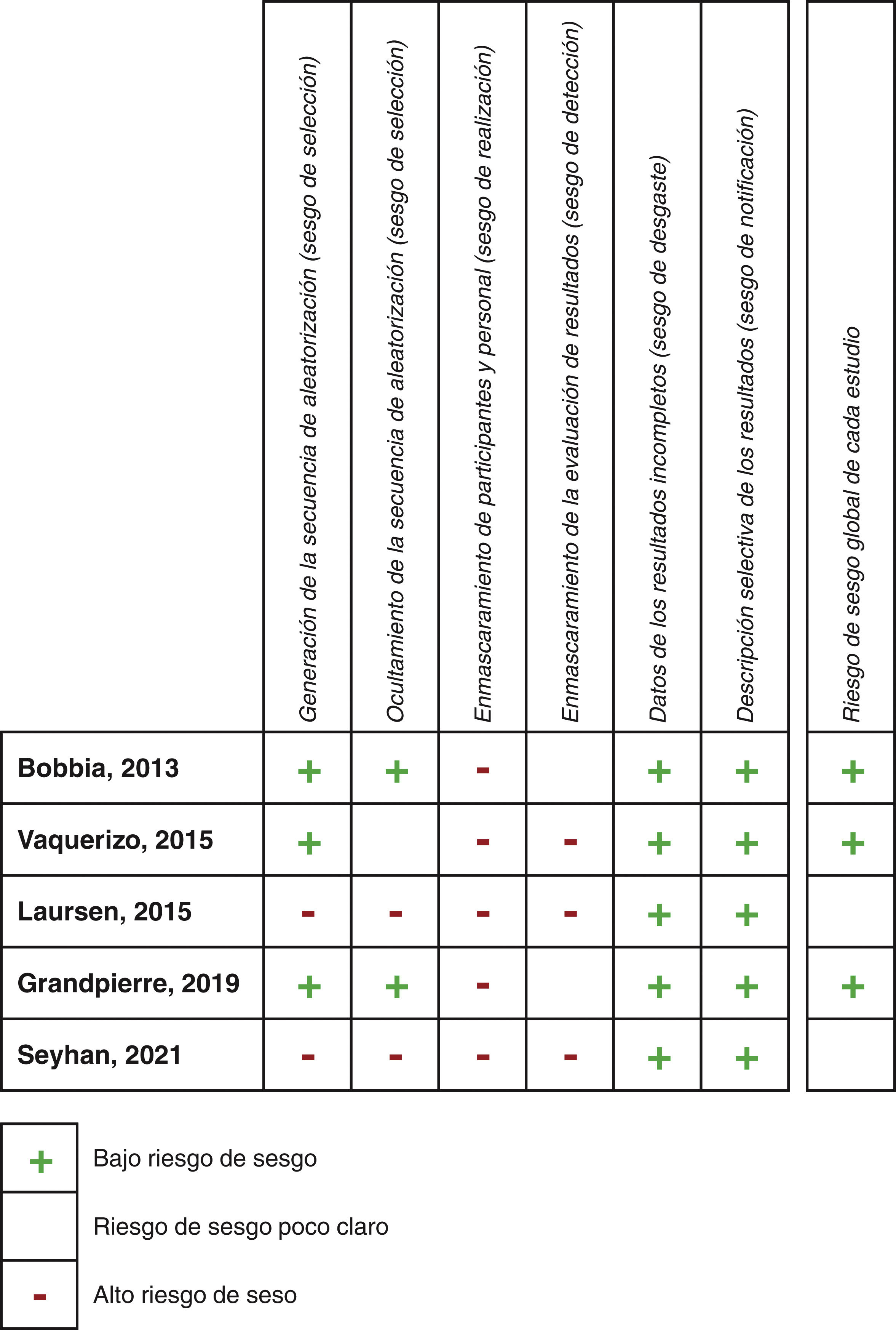
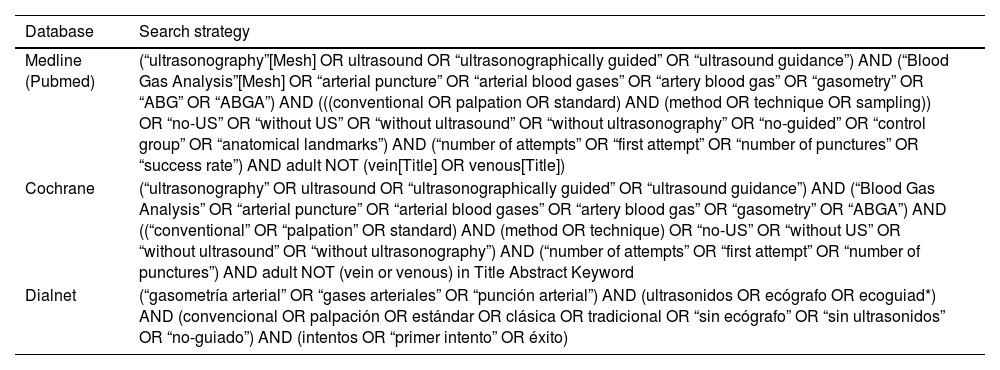
MethodA search protocol was developed and applied to three databases (Medline, Cochrane, and Dialnet). Clinical trials published between January 2013 and January 2023, in Spanish or English, were considered. Outcomes in terms of first-attempt success, number of attempts until success, time taken, self-reported iatrogenic pain, and patient or professional experience were collected. The risk of bias for each included study was assessed.
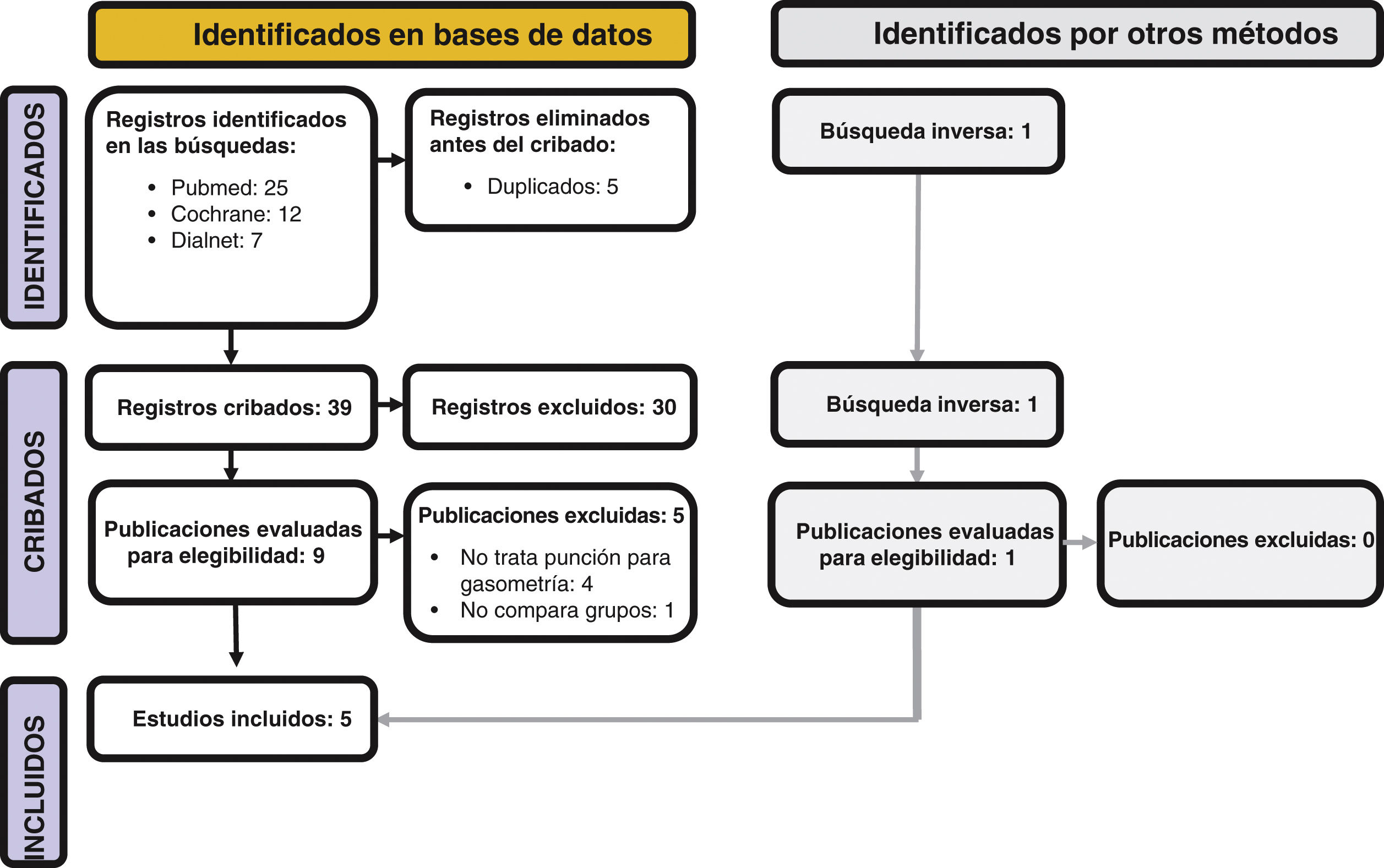
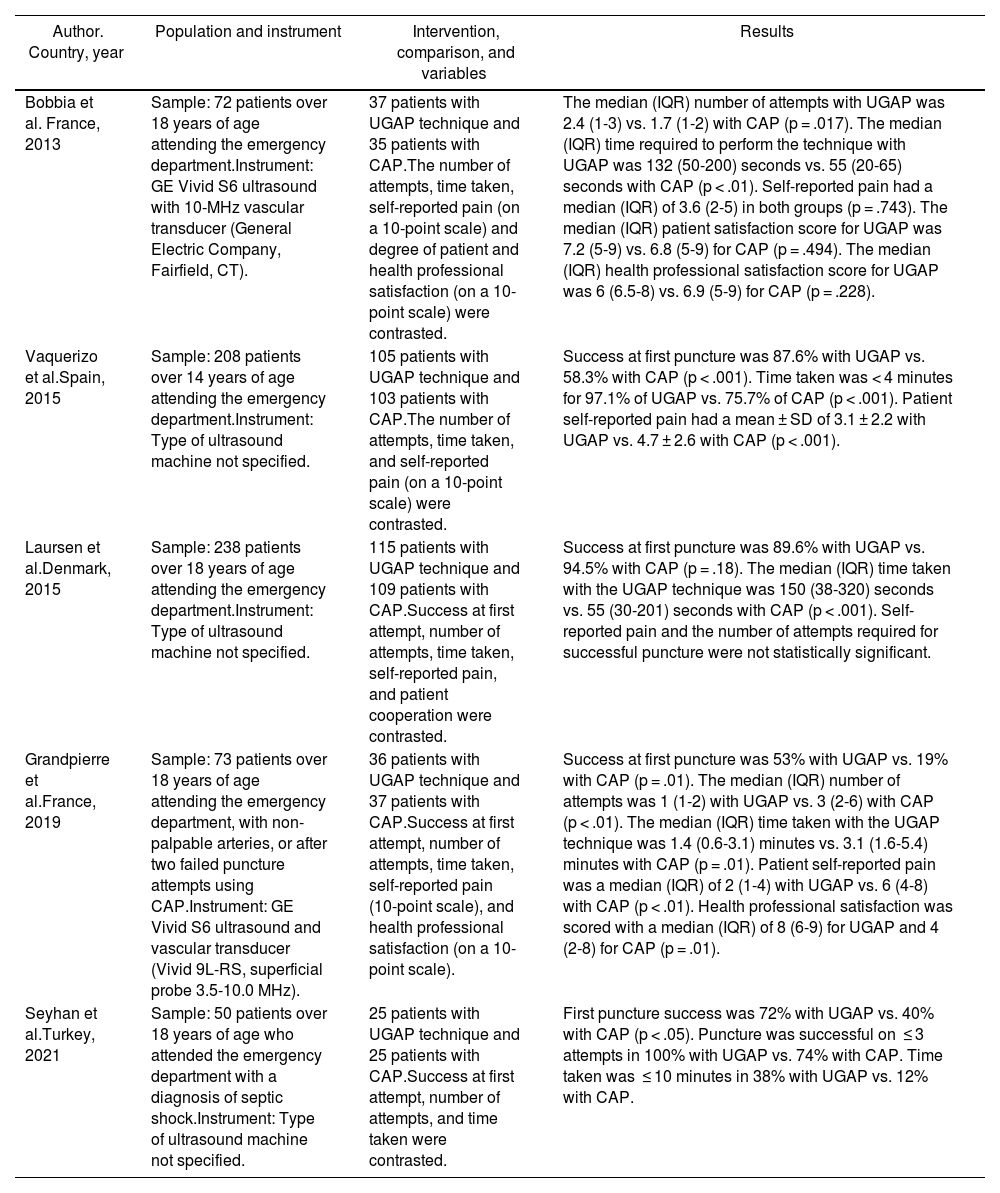
ResultsFive randomized clinical trials were selected, with sample sizes ranging from 50 to 238 adult patients treated in emergency settings. Three out of four studies showed higher first-attempt success rates when using ultrasound, and 2 out of 4 studies reported a decrease in iatrogenic pain. Discrepant findings were observed among the studies in terms of time taken and the number of attempts required for success.
ConclusionsAlthough current evidence is limited and the findings are heterogeneous, ultrasound-guided arterial puncture may have advantages over conventional puncture in terms of first-attempt success and in reducing iatrogenic pain.
Comparar la eficacia de la punción convencional frente a la ecoguiada para la extracción de gasometrías arteriales en adultos.
MétodoSe elaboró un protocolo de búsqueda que se empleó en tres bases de datos (Medline, Cochrane y Dialnet). Se consideraron ensayos clínicos publicados entre enero de 2013 y enero de 2023, en español o inglés. Se recabaron resultados en términos de éxito en el primer intento, número de intentos necesarios hasta el éxito, tiempo empleado, dolor iatrogénico autorreportado y experiencia de paciente o profesional. Se evaluó el riesgo de sesgo de cada estudio incluido.
ResultadosFueron seleccionados 5 ensayos clínicos aleatorizados, con tamaños muestrales comprendidos entre 50 y 238 pacientes adultos atendidos en urgencias. Tres de 4 estudios mostraron mayores tasas de éxito al primer intento cuando se emplearon el ecógrafo y 2 de 4 estudios objetivaron un descenso del dolor iatrogénico. Se encontraron resultados discordantes entre los estudios en las variables de tiempo empleado y número de intentos necesario hasta el éxito.
ConclusionesA pesar de que la evidencia actual es limitada y los resultados heterogéneos, la punción arterial ecoguiada podría tener ventajas frente a la punción clásica en términos de éxito en el primer intento y en la reducción del dolor iatrogénico.
Article
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.