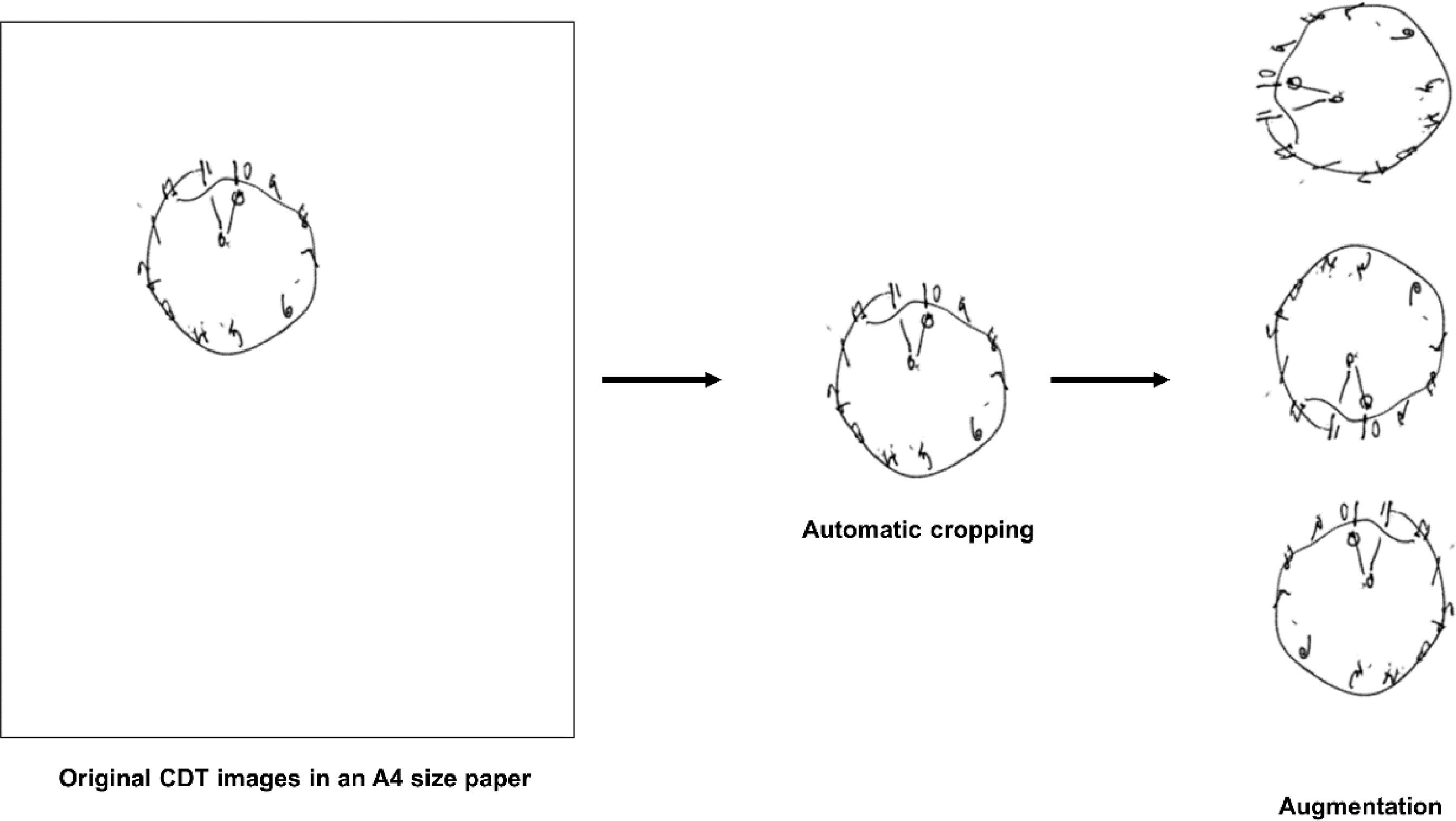
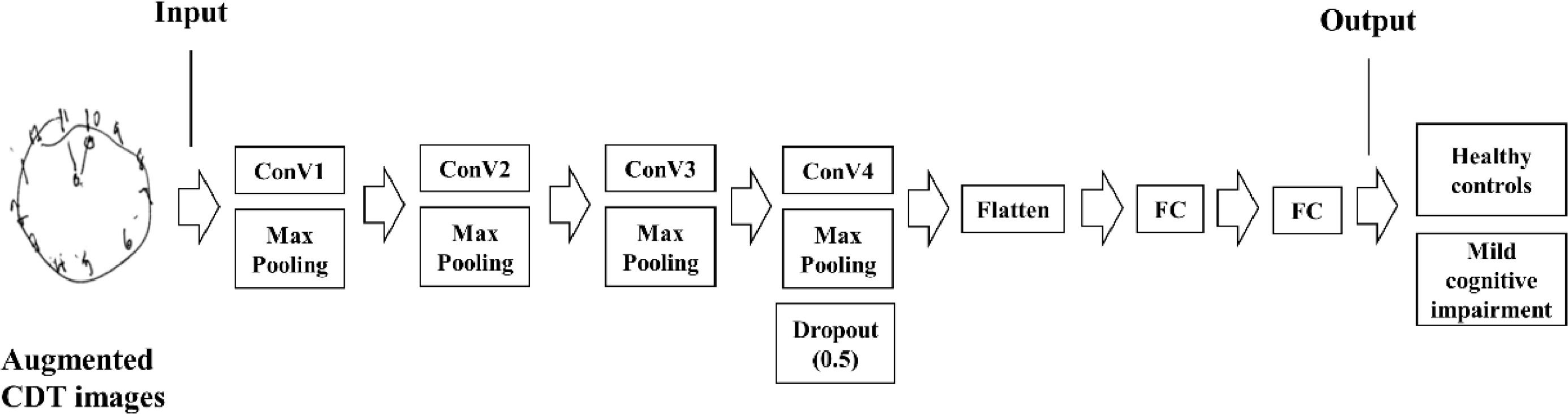
The Clock Drawing Test (CDT) is a tool to assess cognitive function. Despite its usefulness, its interpretation remains challenging, leading to a low reliability. The main objective of this study was to determine the feasibility of using the CDT with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a screening tool for amnestic type of mild cognitive impairment (a-MCI).
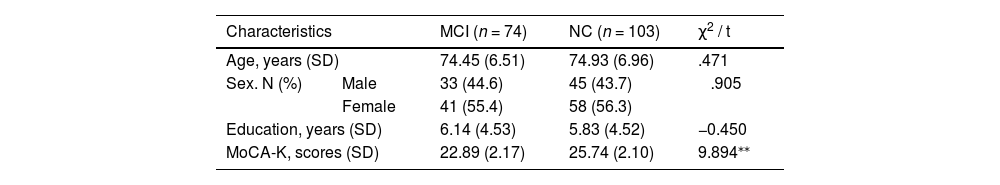
MethodsA total of 177 CDT images were obtained from 103 healthy controls (HCs) and 74 patients with a-MCI. CNNs were trained to classify MCI based on the CDT images. To evaluate the performance of the CDT with CNNs, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and f1-score were calculated. To compare discriminant power, the area under the curve of the CDT with CNNs and the Korean version of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA-K) was calculated by the receiving operating characteristic curve analysis.
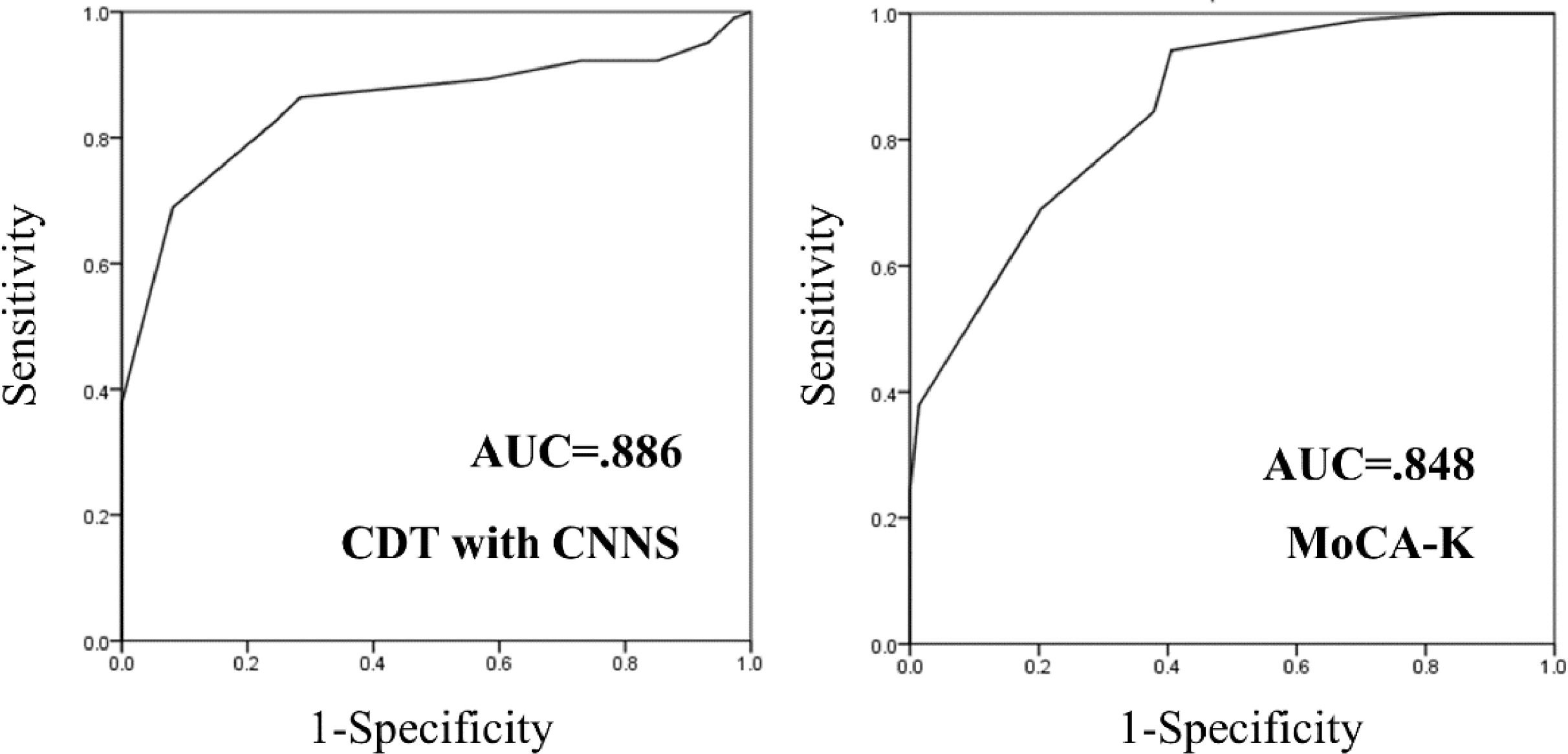
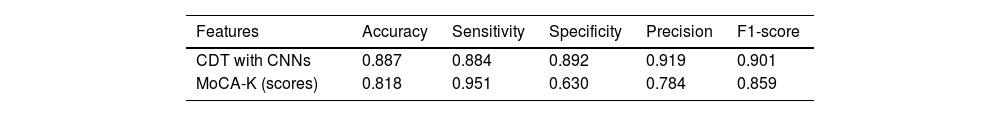
ResultsThe CDT with CNNs was more accurate in discriminating a-MCI (CDT with CNNs = 88.7%, MoCA-K = 81.8%). Furthermore, the CDT with CNNs could better discriminate a-MCI than the MoCA-K (AUC: CDT with CNNs = 0.886, MoCA-K = 0.848).
ConclusionThese results demonstrate the superiority of the CDT with CNNs to the MoCA-K for distinguishing a-MCI from HCs. The CDT with CNNs could be a surrogate for a conventional screening tool for a-MCI.