The postpartum period appears to be a vulnerable period for the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder in parents; yet it is often overlooked. This work aims to synthesize clinical data available on Postpartum Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (PP-OCD) and to highlight its psychopathological significance and implications in clinical practice using a systematic approach.
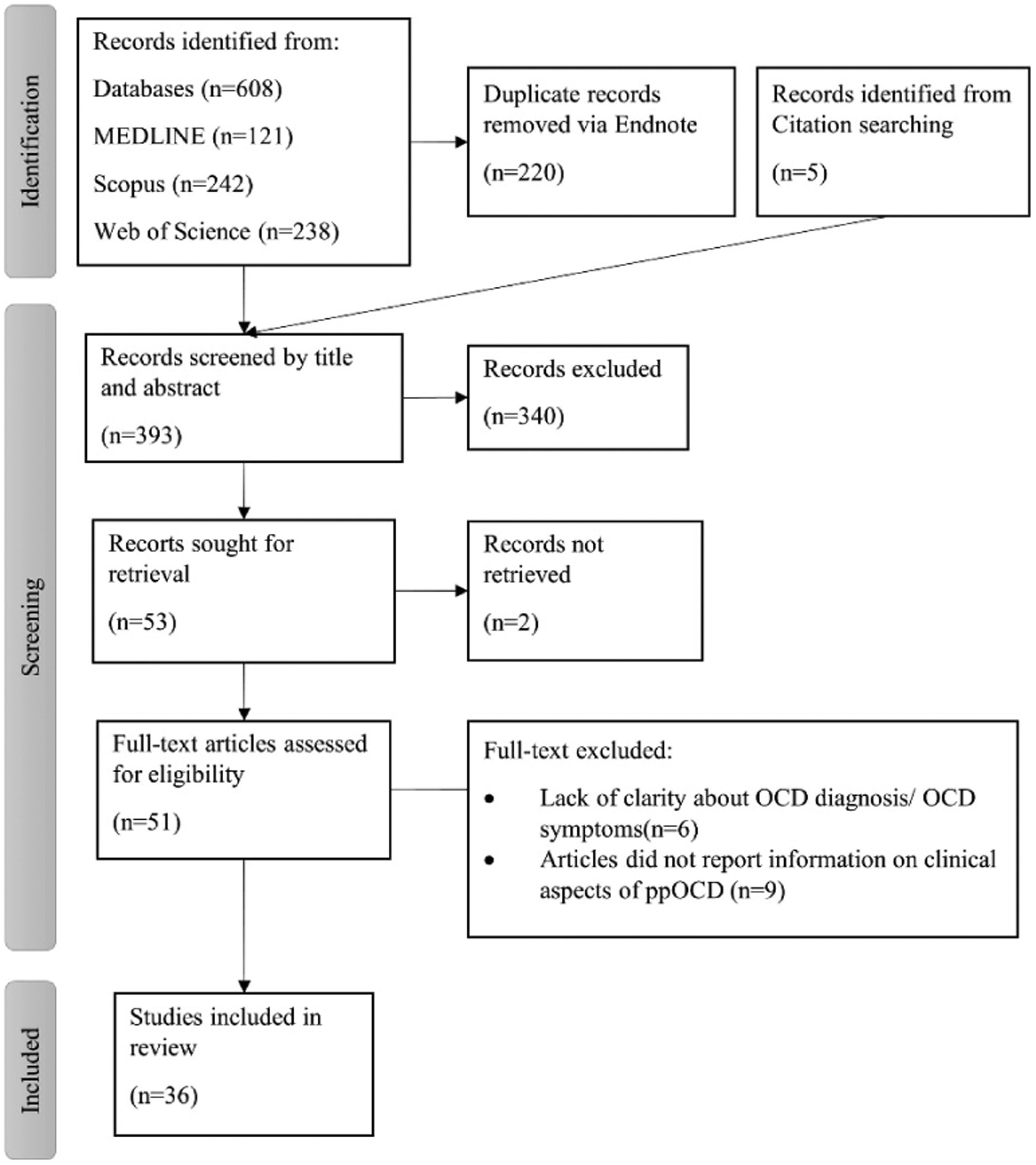
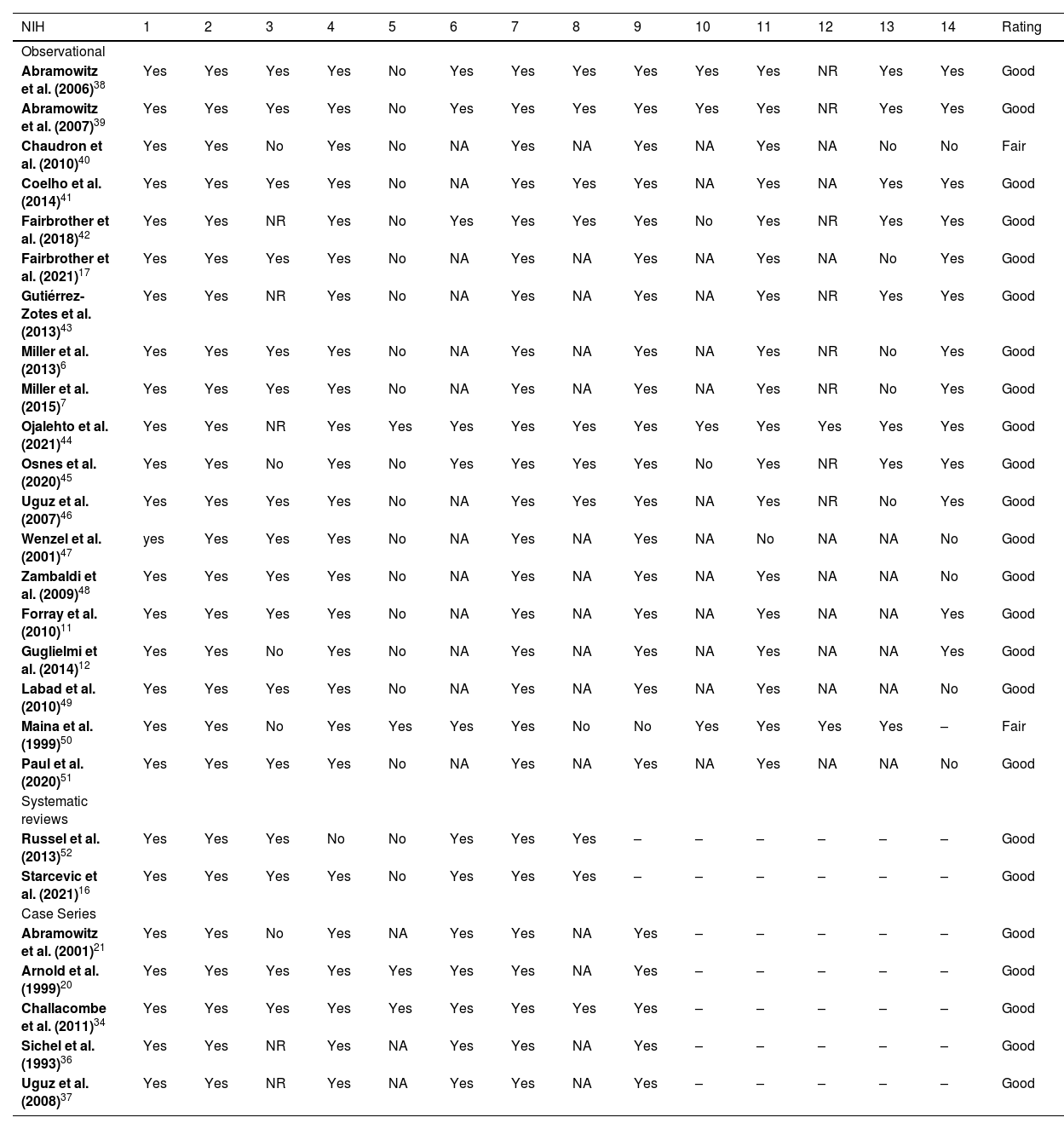
MethodsWe conducted a systematic research according to PRISMA guidelines in three databases – MEDLINE, Scopus and Web of Science. The references obtained were then screened and scanned for eligibility by two investigators. Risk of bias was assessed for each study with NIH tools.
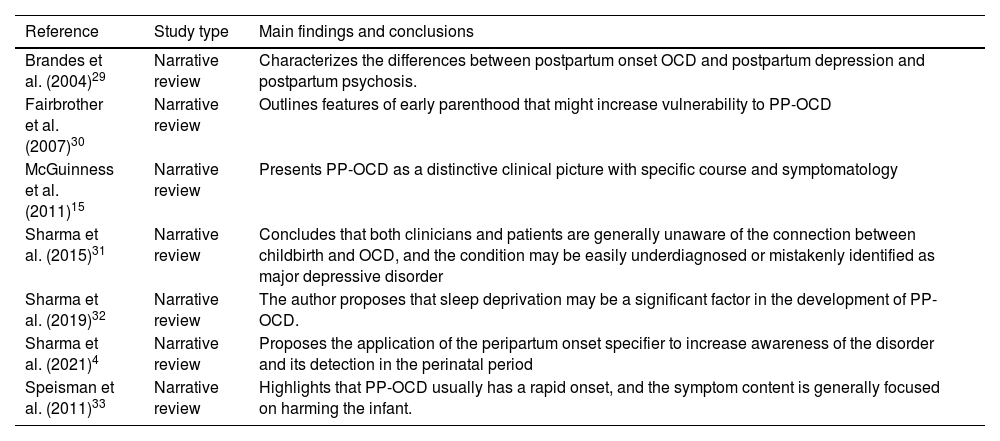
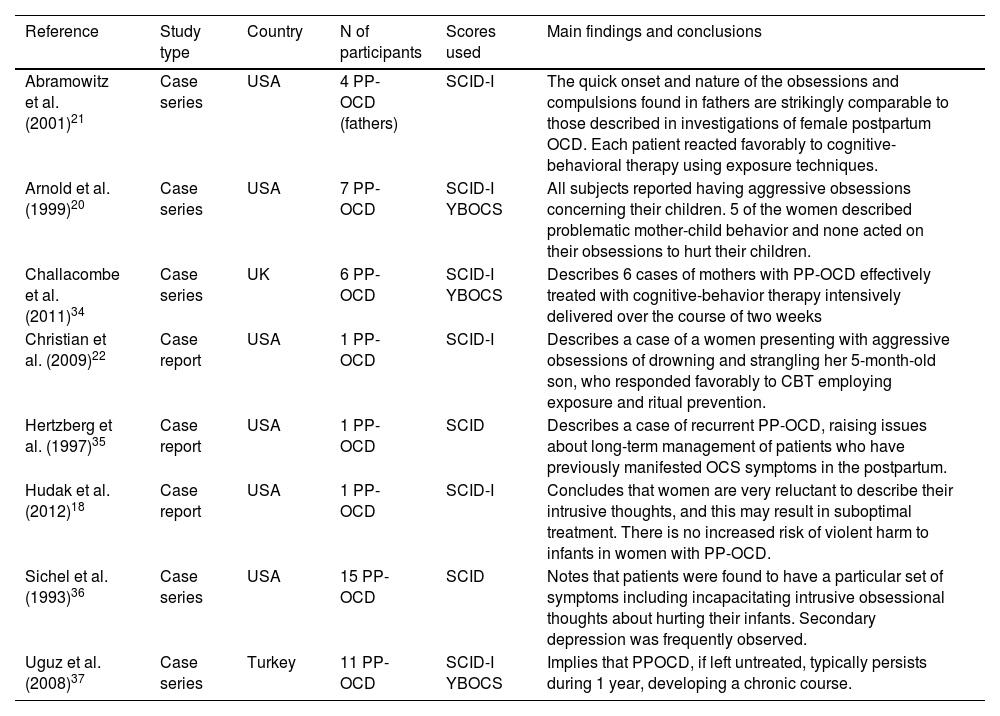
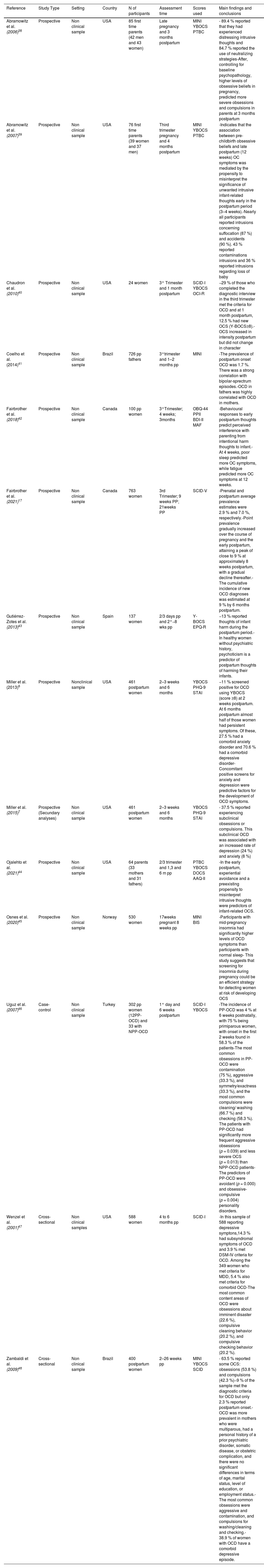
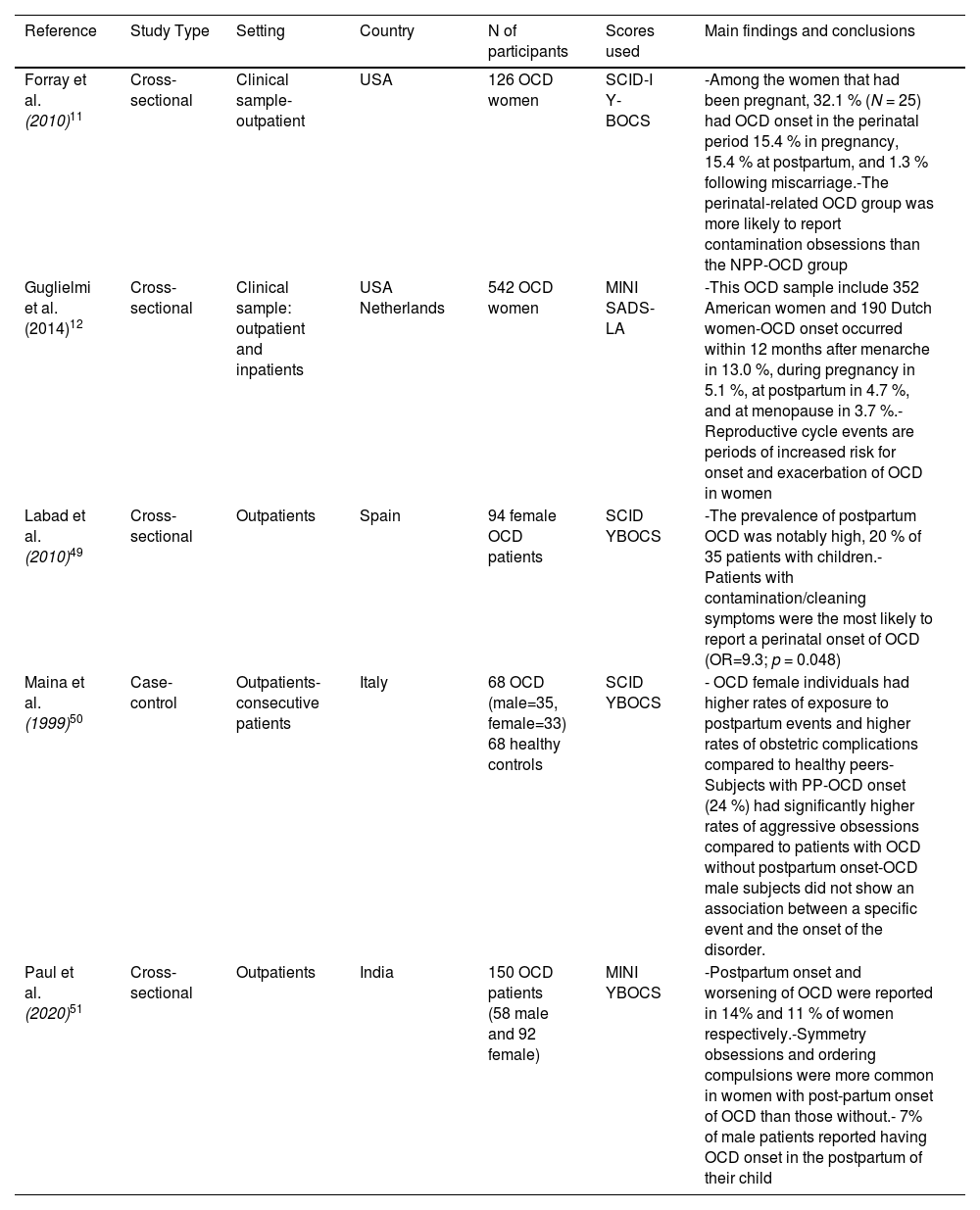
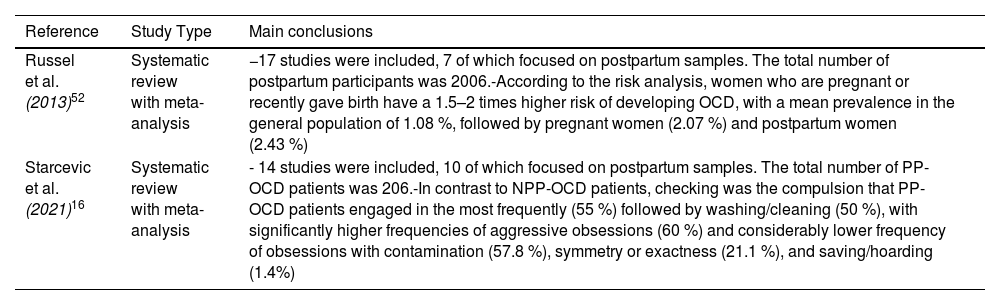
ResultsThe found prevalence of postpartum OCD ranged from 2.43 %-9 % among women and 1,7 % among men. Other epidemiological and clinical data were reviewed including particular symptomatology, characterized by a swift onset of primarily aggressive and contamination obsessions, as well as situational avoidance.
ConclusionIt is a clinical entity frequently underdiagnosed, which perinatal health practitioners should be familiar with, as it can interfere with parent-infant bonding if left untreated. Mothers with an history of depression, anxiety, insomnia, obsessive compulsive, and avoidant personality disorder or presenting inappropriate interpretation of infant related intrusive thoughts are particularly at risk of developing OCD in the postpartum period. These mothers should be informed about the nature of their infant centered obsessions and could be a target of prevention programs.