La parálisis de Bell (PB) es la mononeuropatía del nervio facial que provoca alteraciones de la movilidad voluntaria homolateral, impotencia oral e imposibilidad de cerrar el párpado. Actualmente, el abordaje es multidisciplinar, combinando farmacología y diversas modalidades de fisioterapia. El objetivo del presente trabajo es llevar a cabo una revisión sistemática de la literatura sobre tratamientos de fisioterapia en PB.
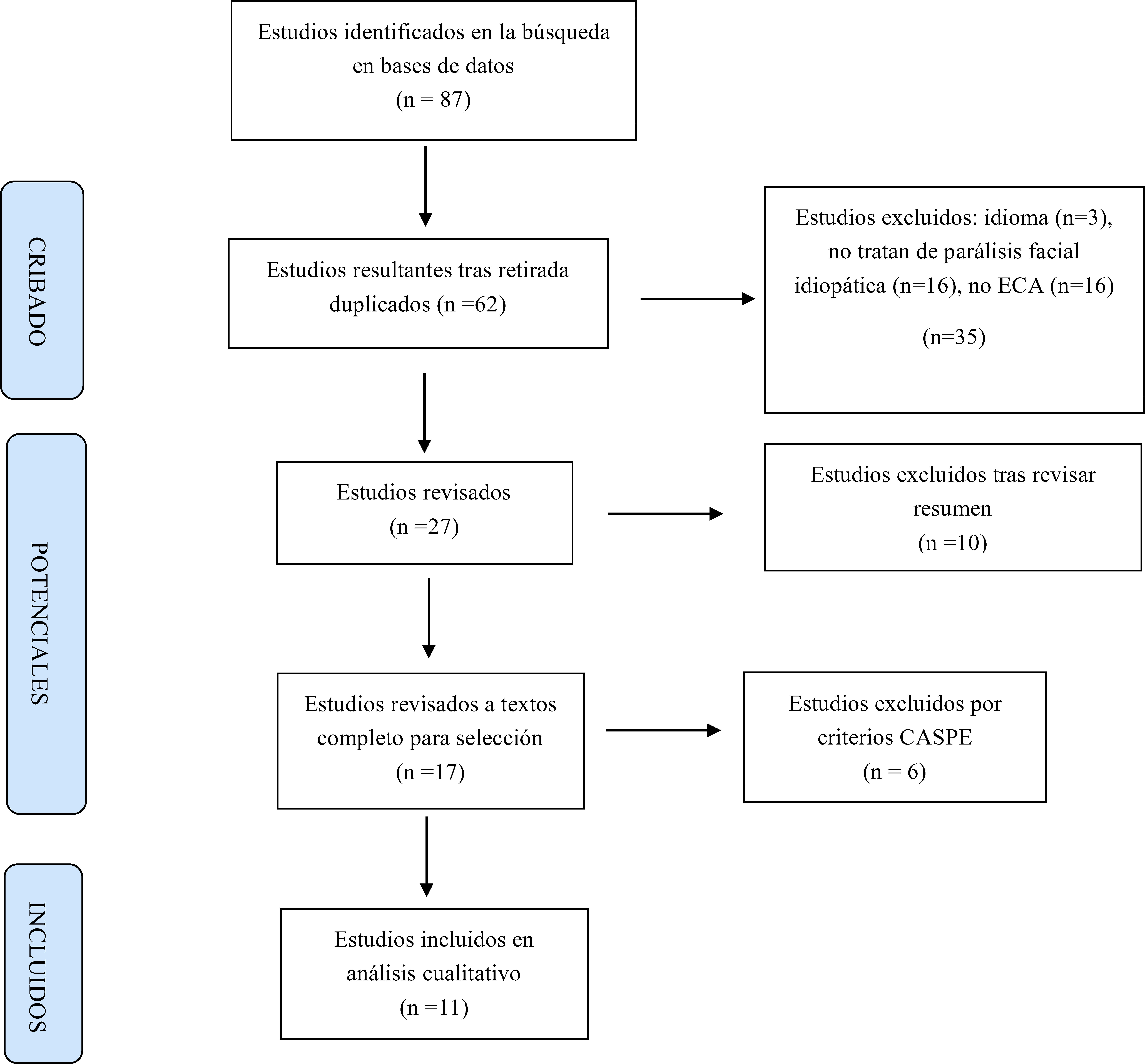
Material y métodosSe efectuó una búsqueda PEDro, Pubmed, Cochrane y Embase de los ensayos clínicos aleatorizados publicados desde 2013 a 2020 que versaran sobre tratamientos de fisioterapia en PB. Se realizó un cribado siguiendo los criterios de inclusión planteados y se efectuó un análisis cualitativo de los estudios siguiendo los criterios CONSORT.
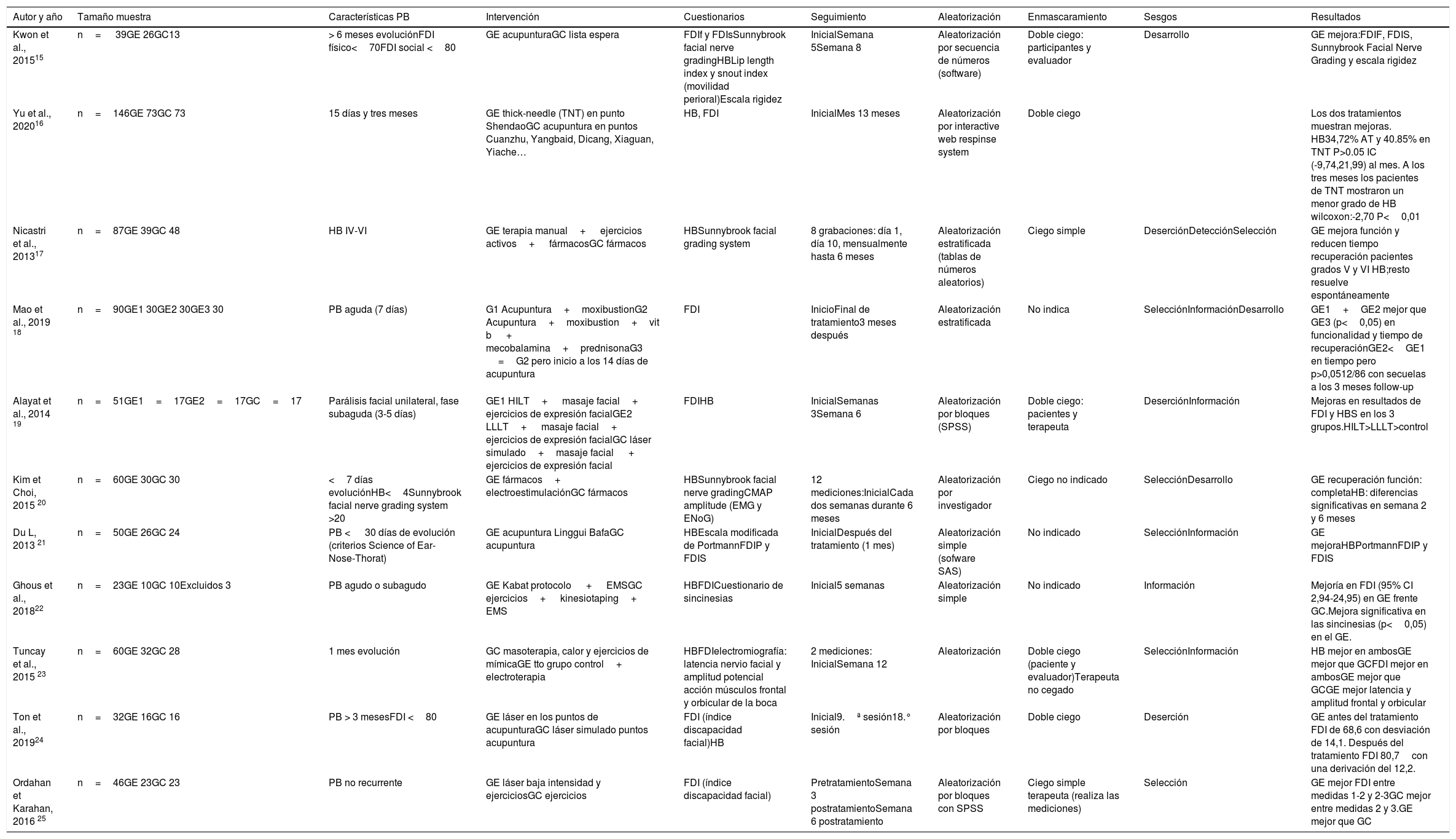
ResultadosSe analizaron 11 publicaciones que aplicaban terapia láser, terapia manual y ejercicios activos, acupuntura, técnica thick-needle, electroestimulación y la combinación de estas. Existía mucha heterogeneidad, tanto en las muestras de población utilizadas y criterios de inclusión planteados, como en las variables y escalas seleccionadas. En todos, aparecían sesgos de diferente origen. Los resultados respaldan el uso de terapia láser de alta intensidad, acupuntura, la acupuntura con láser, la electroestimulación y la técnica thick-needle en el tratamiento de la PB. La terapia manual combinada con ejercicios activos solo redujo el tiempo de recuperación en afectaciones más severas; mientras que los ejercicios de Kabat muestran eficacia en la disminución de sincinesias.
ConclusionesLa literatura analizada respalda el uso de terapia láser, acupuntura, acupuntura con láser, electroestimulación y ejercicios de Kabat como tratamiento de PB, lo que puede resultar útil para tomar decisiones clínicas y desarrollar nuevas líneas de investigación. Pero la calidad de los estudios requeriría reproducir parcial o totalmente las intervenciones ajustando sus diseños.
Bell's palsy (PB) is a peripheral mononeuropathy of the facial nerve that leads to loss of ipsilateral voluntary movement, oral impairment and inability to close the eyelid. The approach is currently multidisciplinary combining pharmacological treatment and physical rehabilitation. The main objective of this study is a systematic review of the literature on physical rehabilitation in patients with PB.
Material and methodsA search of randomized controlled trials on physical rehabilitation after PB published from 2013 to 2020 was performed using the undertaken following the abovementioned inclusion criteria and a qualitative analysis was carried out following the CONSORT criteria.
ResultsEleven publications were analysed. There was much heterogeneity both in the population samples used and the proposed inclusion criteria, as well as in the variables and scales selected. All of these studies had different biases. Laser therapy, manual therapy and active exercises, acupuncture, thick-needle therapy and electrostimulation were used as physiotherapy modalities. The results support the use of high intensity laser therapy, acupuncture, acupuncture with laser, electrostimulation and thick-needle therapy to treat PB. Manual therapy combined with active exercises only reduced recovery time in patients with severe damage; whereas Kabat exercises reduced synkinesis.
ConclusionsThe literature analysed supports the use of laser therapy, acupuncture, acupuncture with laser, electrostimulation and Kabat exercises as a PB treatment, which can be useful for clinical decision-making and developing new lines of research. Because of the quality of the studies, it would be necessary to reproduce the interventions partially or totally adjusting their designs.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".