Thiopurines such as azathioprine (AZA) and mercaptopurine (MP) are commonly utilized to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Their use is frequently restricted due to gastrointestinal intolerance (GI). Previous retrospective studies have reported that AZA-intolerant patients may benefit from a switch to MP; yet the effectiveness of this strategy has not been prospectively evaluated.
AimsTo assess GI tolerance to MP in patients who are intolerant to AZA, and to identify clinical predictors of GI intolerance to AZA or MP.
MethodsA prospective, observational, single-cohort study was performed in 92 thiopurine-naïve IBD patients. They were started on a 50mg dose of AZA and escalated to 2.5mg/kg per day by week 2. Those with GI intolerance were rechallenged with a 50% dose of AZA, after which another dose escalation attempt was made. If symptoms persisted, they were switched to MP.
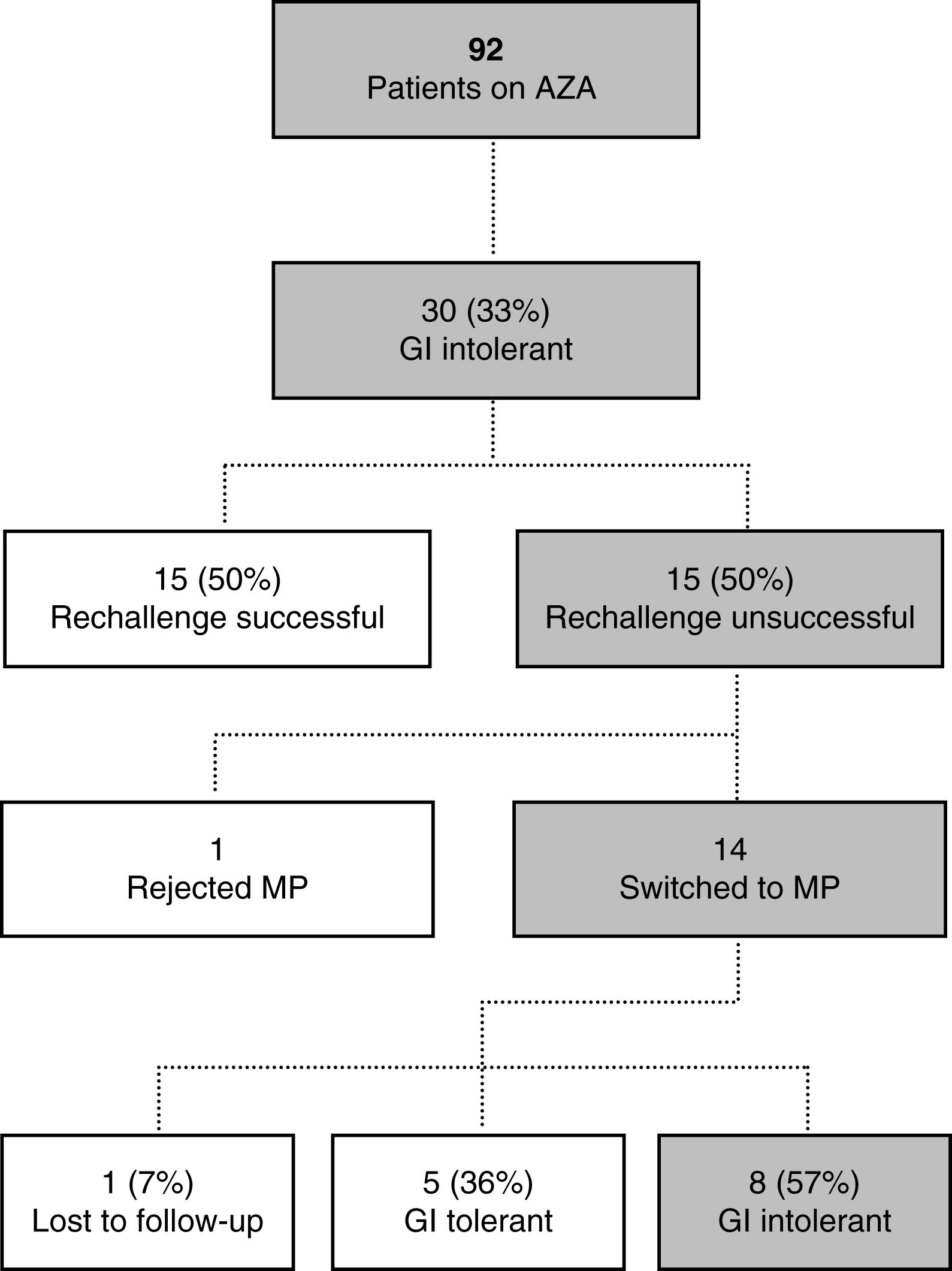
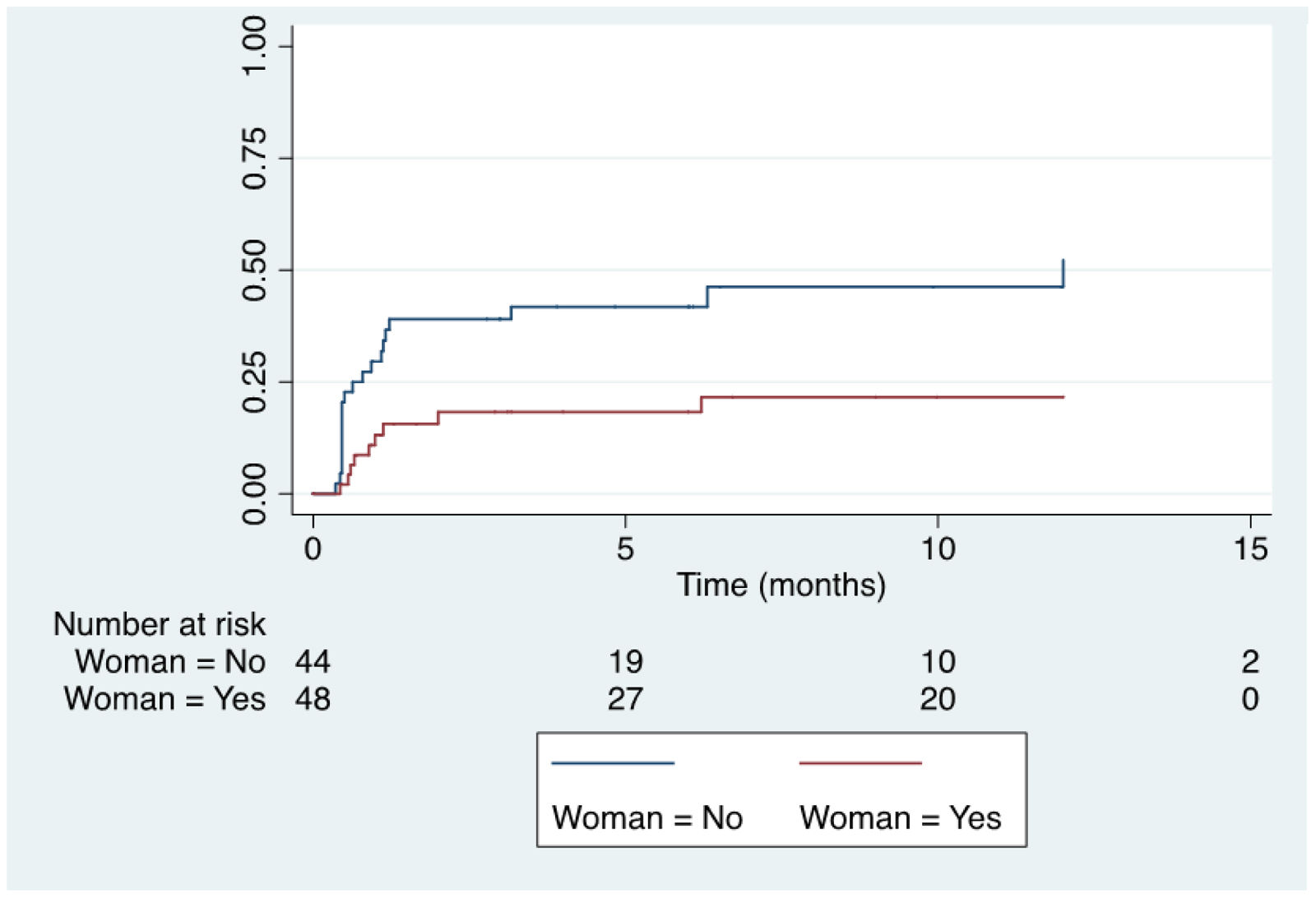
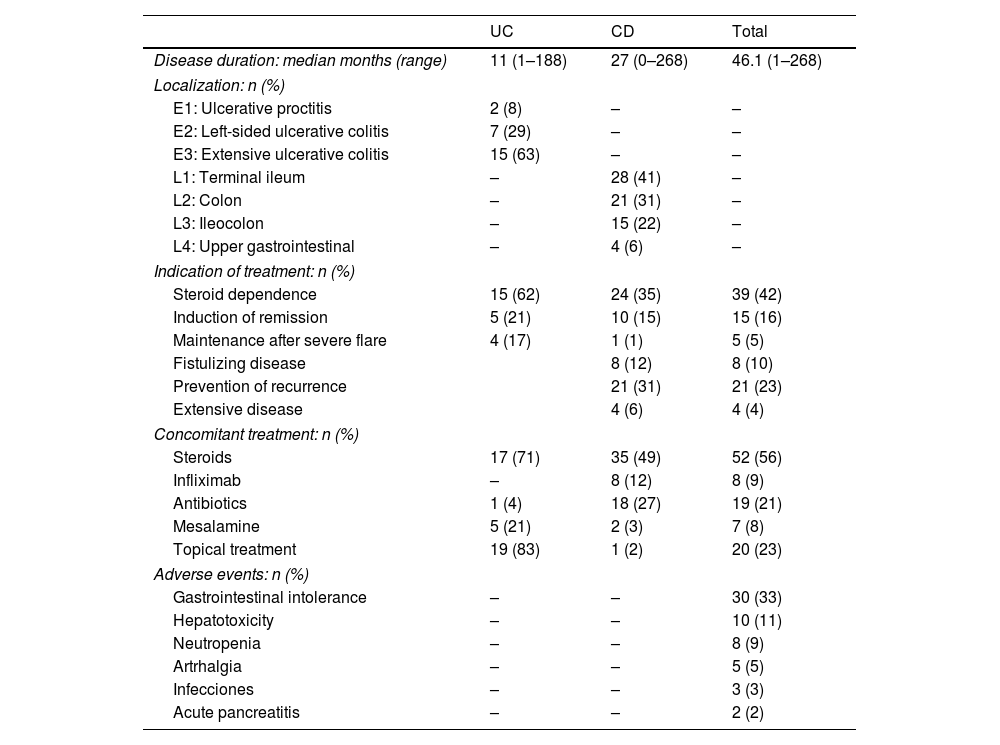
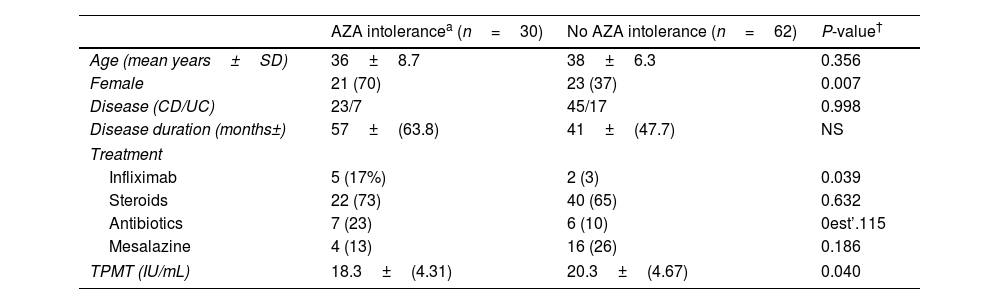
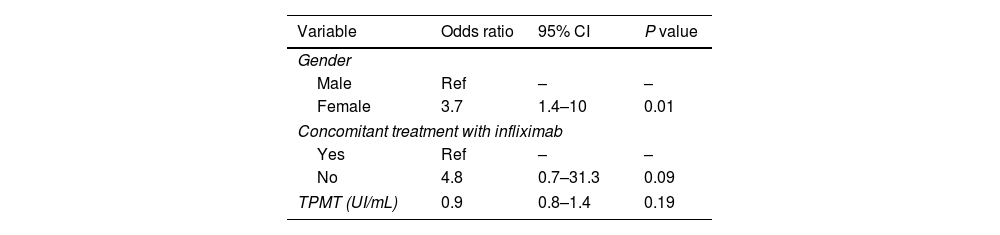
ResultsThirty (32.6%) of the recruited patients suffered from GI intolerance to AZA. Of these, 15 did not present recurrence of symptoms after rechallenge with lower doses. Of 15 intolerant patients, 14 were switched to MP. Within the MP cohort, 8 patients (57%) were also intolerant to MP, 5 (36%) had no symptoms, and 1 (7%) was lost to follow-up. Female gender was the only independent predictor of GI intolerance to AZA.
ConclusionsUp to half of the AZA-intolerant patients tolerated a 50% dose rechallenge that was successfully escalated. A switch to MP was tolerated in over a third of cases whom rechallenge failed. Our strategy (challenge–rechallenge–switch) achieved an overall GI tolerance to thiopurines in most of the patients.
Las tiopurinas como la azatioprina (AZA) y la mercaptopurina (MP) se utilizan comúnmente para tratar la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII). Su uso está frecuentemente restringido debido a la intolerancia gastrointestinal. Estudios retrospectivos anteriores han informado que los pacientes intolerantes a la AZA pueden beneficiarse de un cambio a MP; sin embargo, la eficacia de esta estrategia no ha sido evaluada prospectivamente.
ObjetivosEvaluar la tolerancia gastrointestinal a MP en pacientes que son intolerantes a AZA e identificar predictores clínicos de intolerancia gastrointestinal a AZA o MP.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo, observacional y de cohorte única en 92 pacientes con EII que nunca habían recibido tiopurinas. Comenzaron con una dosis de 50mg de AZA y se aumentó a 2,5mg/kg por día en la semana 2. En aquellos con intolerancia gastrointestinal se administró una dosis del 50% de AZA que se fue incrementando en función de la tolerancia. Si los síntomas persistían, se cambiaba a MP.
ResultadosTreinta (32,6%) de los pacientes reclutados presentaron intolerancia gastrointestinal a la AZA. De estos, 15 no presentaron recurrencia de los síntomas después de la nueva exposición. De los 15 pacientes que no toleraron una dosis más baja, 14 recibieron MP. De los que recibieron MP, 8 pacientes (57%) también eran intolerantes a MP, 5 (36%) no tenían síntomas y uno (7%) se perdió durante el seguimiento. El género femenino fue el único predictor independiente de intolerancia gastrointestinal a la AZA.
ConclusionesHasta la mitad de los pacientes intolerantes a la AZA toleran una nueva exposición al 50% de la dosis. Se toleró un cambio a MP en más de un tercio de los casos en los que la reexposición fracasó. Nuestra estrategia logró la tolerancia gastrointestinal a tiopurinas en la mayoría de los pacientes.