There is increasing evidence that proactive monitoring is useful in improving the control of inflammatory bowel disease, although it remains controversial. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of proactive TDM based on the Bayesian approach to optimise the IFX dose compared with the standard of care dosing in patients with IBD.
MethodsRetrospective observational cohort of inflammatory bowel disease patients>18 years. Patients were classified into two groups according to the strategy used to optimise the dose of IFX: a standard therapy group (ST-group) with clinically based dose adjustment and therapeutic drug monitoring group (TDM-group), with estimation of pharmacokinetic parameters calculated by Bayesian prediction.
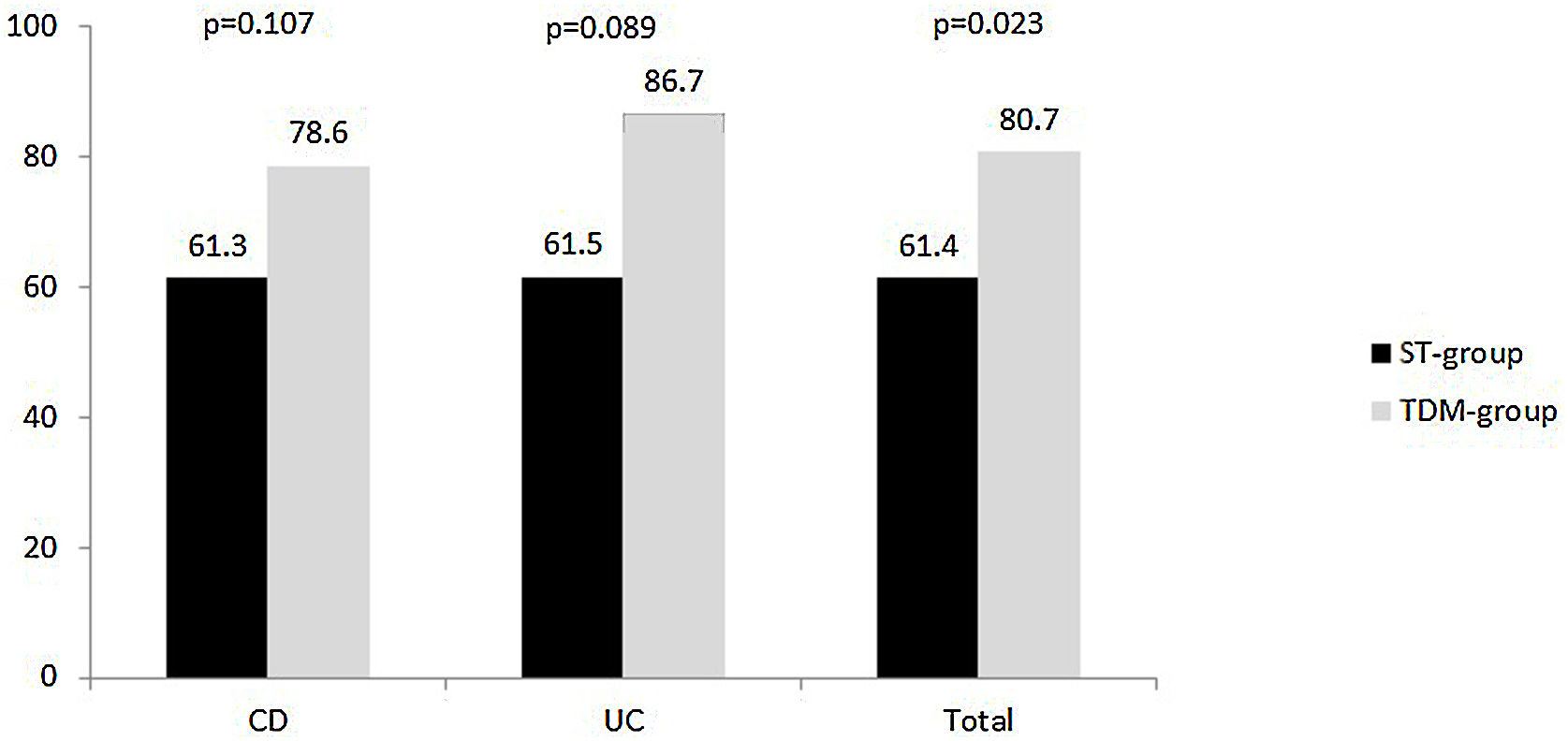
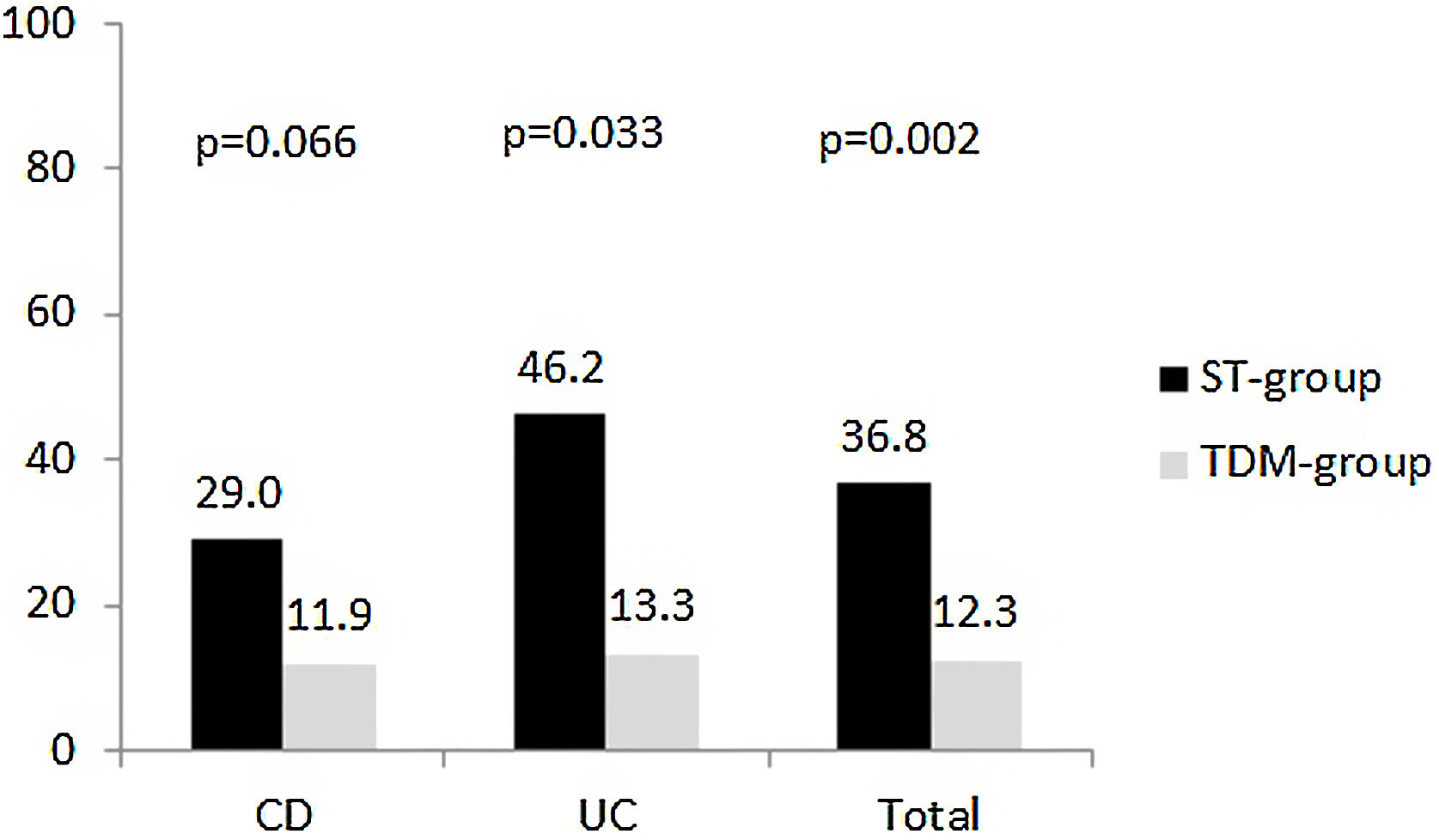
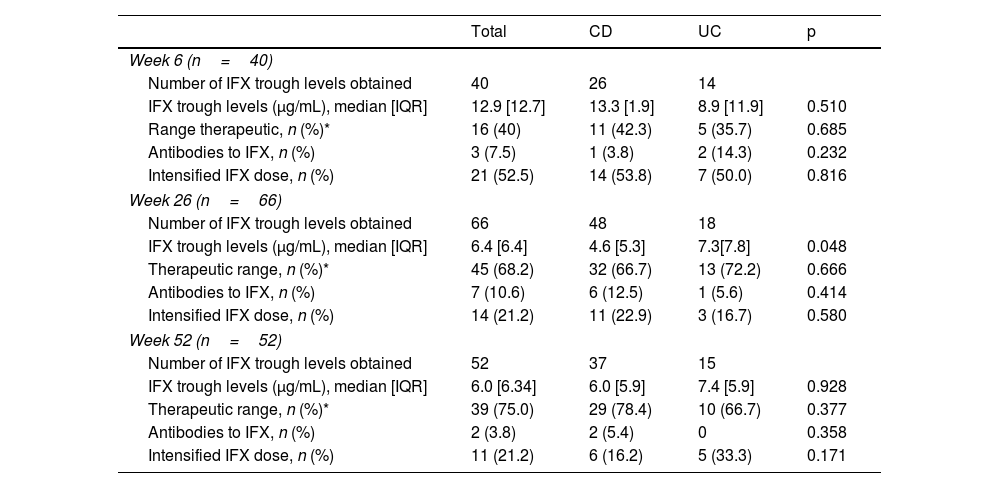
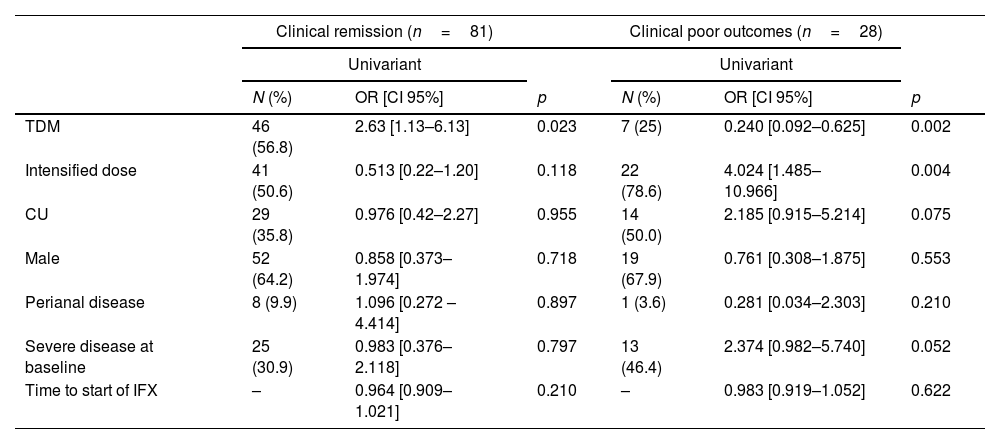
ResultsA total of 153 patients were included. Of these, 75 were in the TDM-group. Clinical response at week 52 was evaluated in 114 patients. The proportion of patients who achieved clinical remission was higher in the TDM than in the ST-group (80.7% vs 61.4%, respectively, p=0.023). A total of 28 patients (24.6%) met the parameters for the composite variable ‘poor clinical outcome’ at week 52. The proportion of patients who reached this outcome was lower in the TDM-group than in the ST-group (12.3% vs 36.8%, respectively, p=0.002).
ConclusionsProactive therapeutic drug monitoring using Bayesian approach is associated with higher secondary response and fewer long-term complications.
Cada vez hay más evidencia de que la monitorización proactiva es útil para mejorar el control de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII), aunque sigue siendo controvertida. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la eficacia de la monitorización de fármacos terapéuticos (TDM) proactiva basada en el enfoque bayesiano en comparación con el manejo estándar en pacientes con EII.
MétodosCohorte observacional retrospectiva de pacientes con EEI > 18 años. Los pacientes se clasificaron en dos grupos de acuerdo con la estrategia utilizada para optimizar la dosis de infliximab (IFX): un grupo de terapia estándar (grupo-ST) con ajuste de dosis basado en la clínica y un grupo de monitorización terapéutica del fármaco (grupo-TDM), con estimación de parámetros farmacocinéticos calculados mediante estimación bayesiana.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 153 pacientes. De estos, 75 estaban en el grupo-TDM. La respuesta clínica en la semana 52 se evaluó en 114 pacientes. La proporción de pacientes que alcanzaron la remisión clínica fue mayor en el grupo-TDM que en el grupo-ST (80,7 vs. 61,4%, respectivamente, p = 0,023). Un total de 28 pacientes (24,6%) cumplieron los parámetros de la variable compuesta «resultado clínico deficiente» en la semana 52. La proporción de pacientes que alcanzaron este resultado fue menor en el grupo-TDM que en el grupo-ST (12,3 vs. 36,8%, respectivamente, p = 0,002).
ConclusionesLa TDM proactiva mediante el enfoque bayesiano se asocia con una mayor respuesta secundaria y menos complicaciones a largo plazo.