The outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in the esophagus have not been assessed in our country. Our primary aim was to analyze the effectiveness and safety of the technique.
Material and methodsAnalysis of the prospectively maintained national registry of ESD. We included all superficial esophageal lesions removed by ESD in 17 hospitals (20 endoscopists) between January 2016 and December 2021. Subepithelial lesions were excluded. The primary outcome was curative resection. We conducted a survival analysis and used logistic regression analysis to assess predictors of non-curative resection.
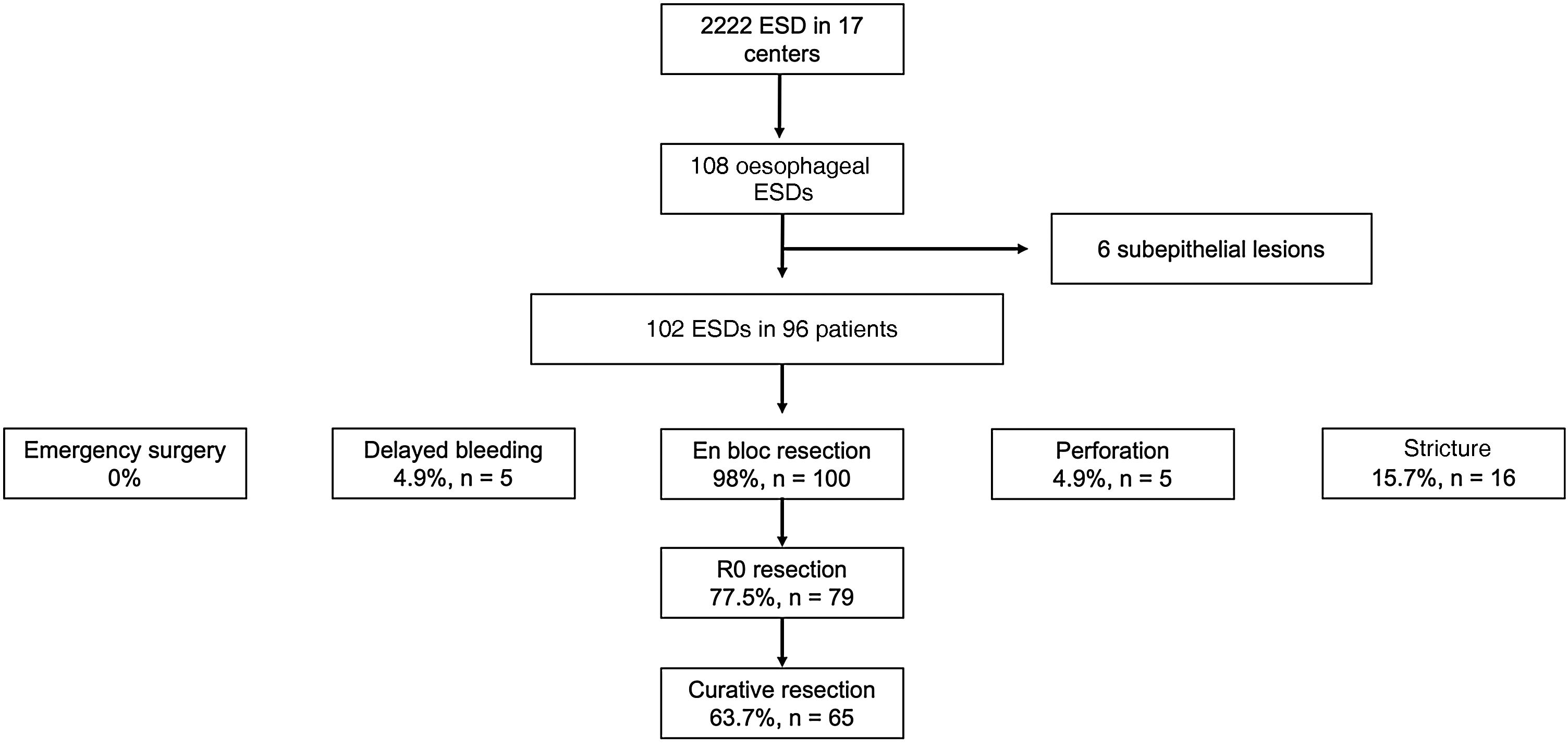
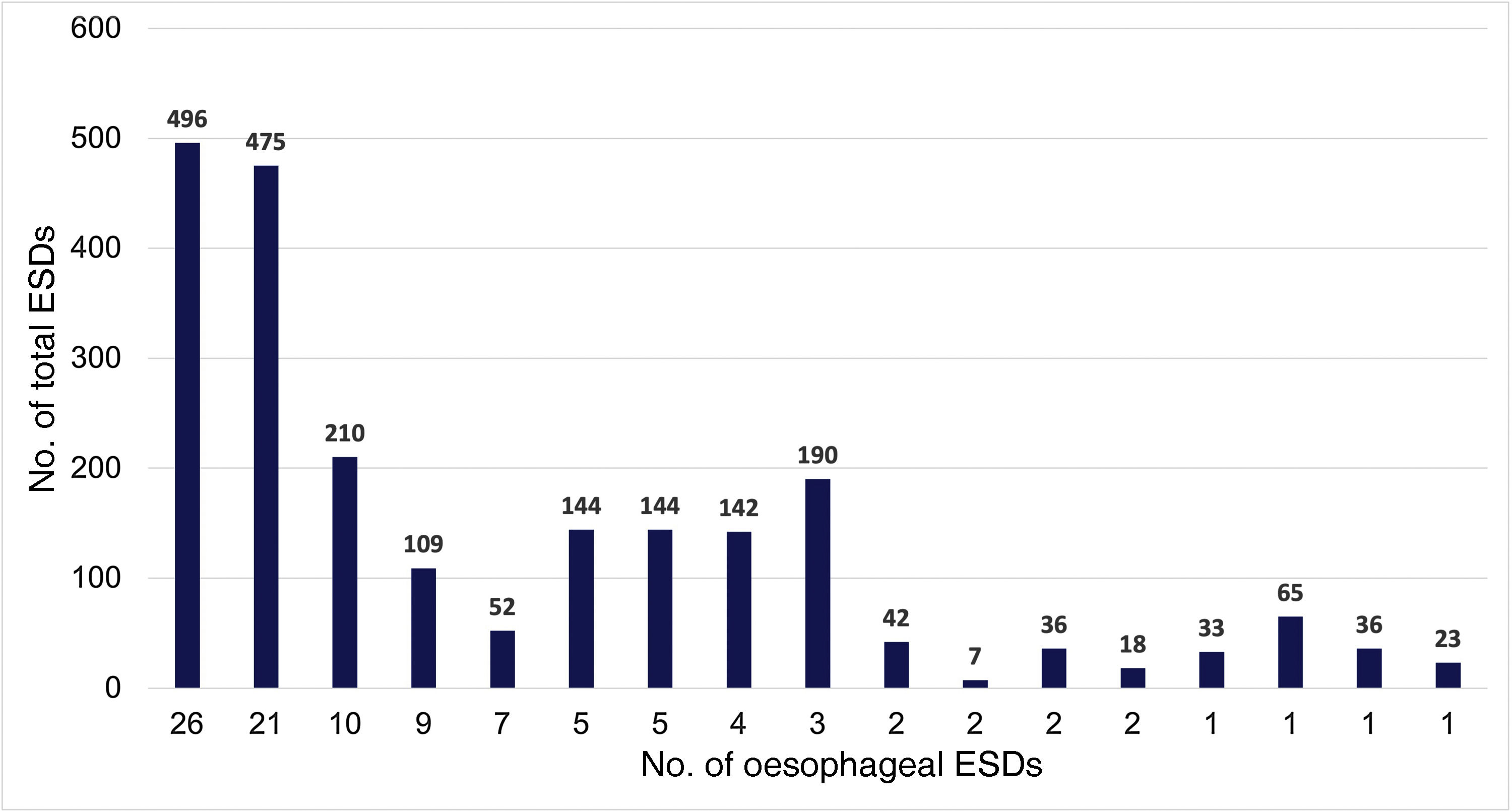
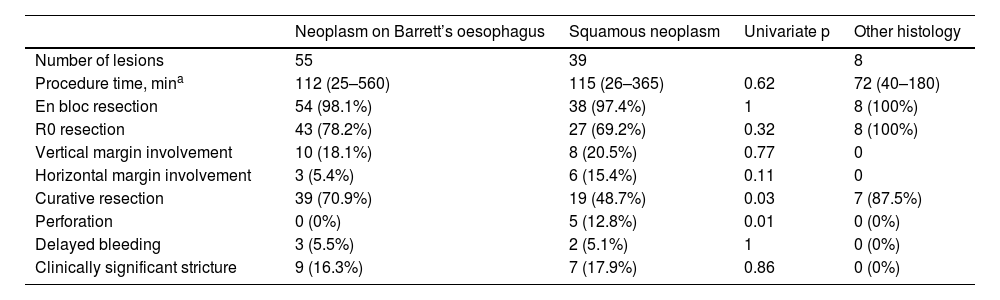
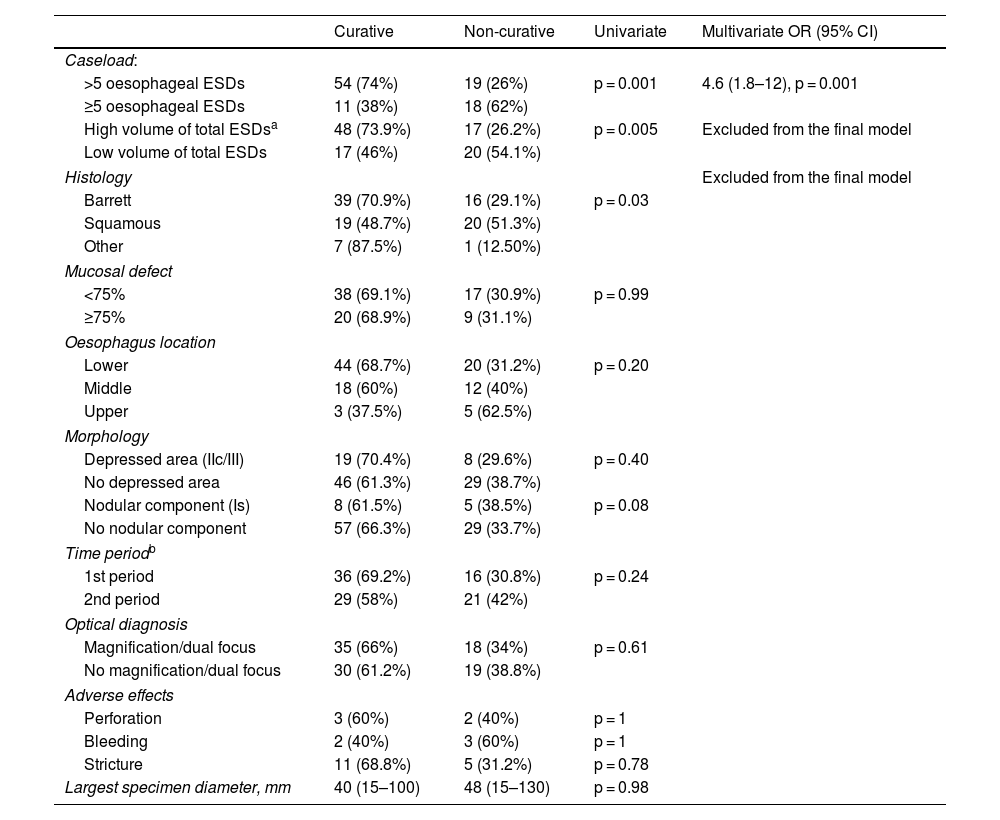
ResultsA total of 102 ESD were performed on 96 patients. The technical success rate was 100% and the percentage of en-bloc resection was 98%. The percentage of R0 and curative resection was 77.5% (n = 79; 95% CI: 68%–84%) and 63.7% (n = 65; 95% CI: 54%–72%), respectively. The most frequent histology was Barrett-related neoplasia (n = 55 [53.9%]). The main reason for non-curative resection was deep submucosal invasion (n = 25). The centers with a lower volume of ESD obtained worse results in terms of curative resection. The rate of perforation, delayed bleeding and post-procedural stenosis were 5%, 5% and 15.7%, respectively. No patient died or required surgery due to an adverse effect. After a median follow-up of 14 months, 20 patients (20.8%) underwent surgery and/or chemoradiotherapy, and 9 patients died (mortality 9.4%).
ConclusionsIn Spain, esophageal ESD is curative in approximately two out of three patients, with an acceptable risk of adverse events.
Los resultados de la disección submucosa endoscópica (DSE) en el esófago no han sido evaluados en nuestro país. Nuestro objetivo principal fue analizar la efectividad y la seguridad de la técnica.
Material y métodosAnálisis del registro nacional prospectivo de DSE. Se incluyeron todas las lesiones superficiales esofágicas extirpadas mediante DSE en 17 hospitales (20 endoscopistas) entre enero de 2016 y diciembre de 2021. Se excluyeron las lesiones subepiteliales. La variable principal fue el porcentaje de resección curativa. Se realizó un análisis de regresión logística para conocer los predictores de resección no curativa y un análisis de supervivencia.
ResultadosSe realizaron un total de 102 DSE en 96 pacientes. El éxito técnico fue del 100% y el porcentaje de resección en bloque, del 98%. El porcentaje de resección R0 y curativa fue del 77,5% (n = 79; IC 95%: 68%–84%) y del 63,7% (n = 65; IC 95%: 54%–72%), respectivamente. La histología más frecuente fue la neoplasia sobre esófago de Barrett (n = 55 [53,9%]). El principal motivo de resección no curativa fue la invasión submucosa profunda (n = 25). Los centros con menor volumen de casos obtuvieron cifras inferiores de resección curativa. El porcentaje de perforación, sangrado diferido y estenosis posprocedimiento fue del 5%, del 5% y del 15,7%, respectivamente. Ningún paciente falleció ni requirió cirugía por un efecto adverso. Tras una mediana de seguimiento de 14 meses, 20 pacientes (20,8%) recibieron cirugía y/o quimio-radioterapia, y 9 fallecieron (mortalidad del 9,4%).
ConclusionesEn nuestro medio, la DSE esofágica es curativa en aproximadamente dos de cada tres pacientes, con un riesgo aceptable de efectos adversos.