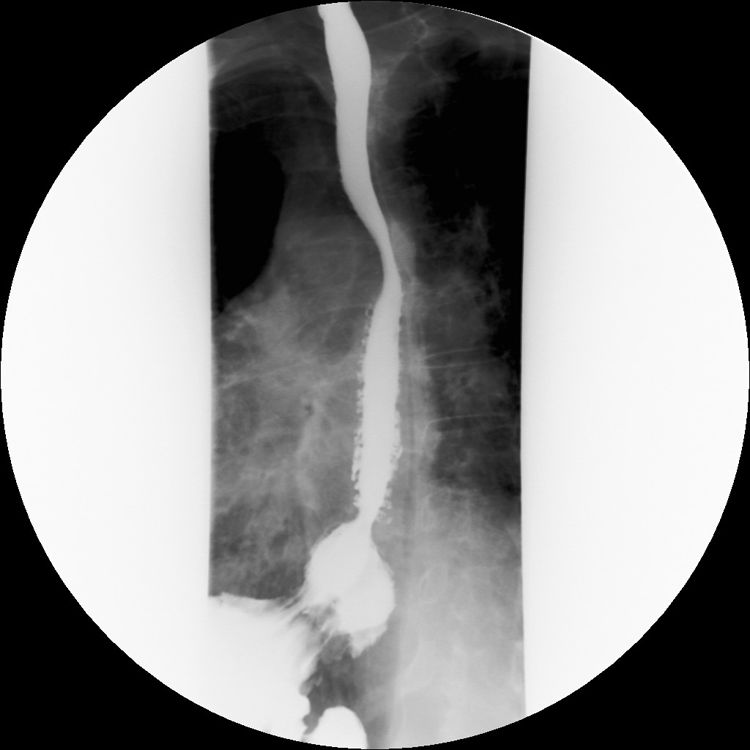
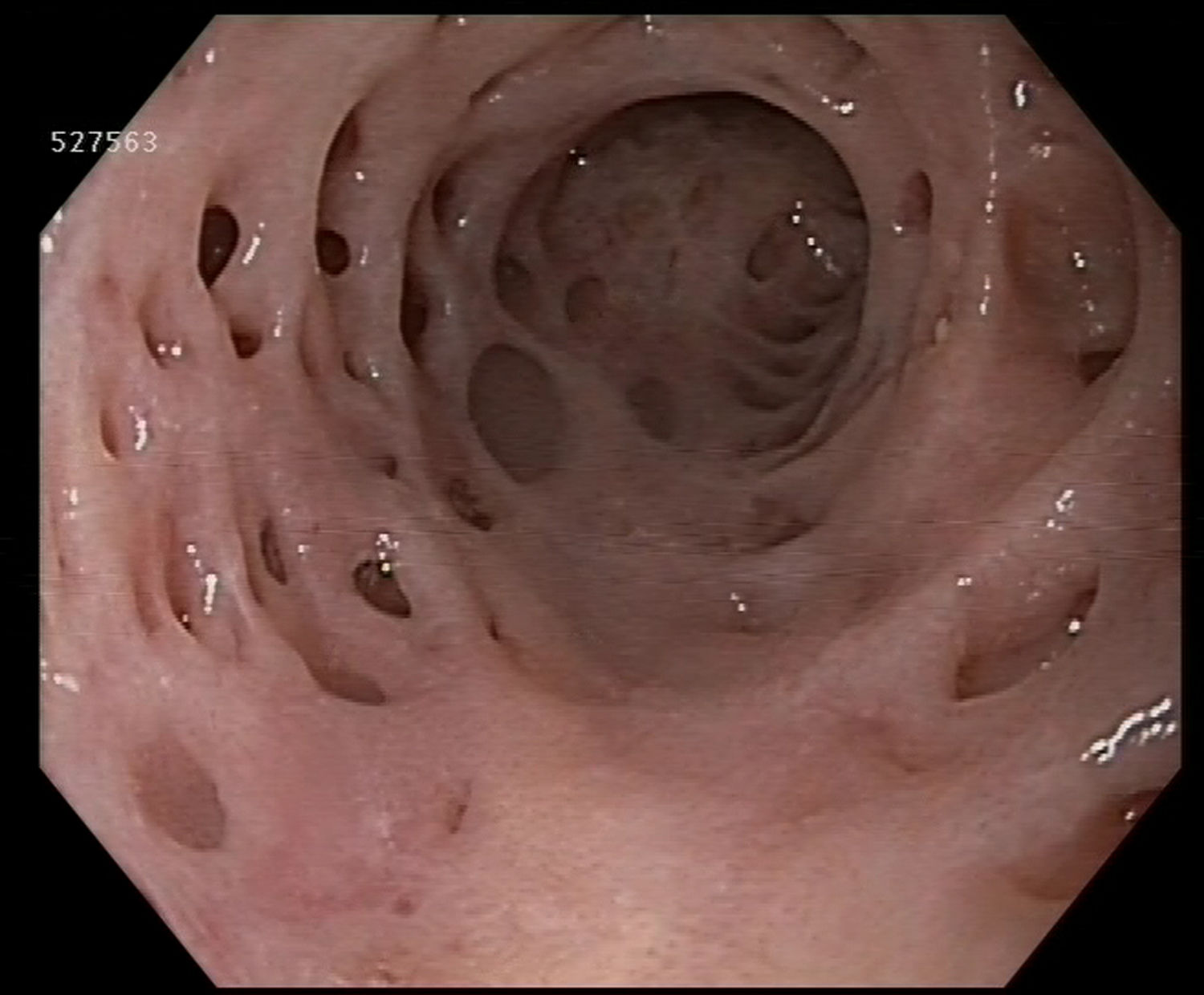
We present the endoscopic (Fig. 1) and radiological (Fig. 2) images of an oesophageal intramural pseudodiverticulosis (OIPD). It is a rare condition that occurs in fewer than 1% of upper gastrointestinal endoscopies (UGE) and it occurs as a result of hypertrophy of the submucosal mucous glands with cystic dilation of their excretion ducts. As such, it is not a true diverticulosis. With an unknown aetiology, it is associated with gastroesophageal reflux, oesophageal candidiasis and chronic alcohol use; conditions that our patient did not present. Although dysphagia is reported as the most common symptom, our 65-year-old male patient did not present with any symptoms, and the reason for the UGE was anaemia testing.2,3
Small diverticula (<5 mm) may occur as either diffuse or localised, as was the case in our patient whose lesions were all in the distal segment of the oesophagus. Reported accompanying lesions include peptic stenosis and oesophageal candidiasis, which were not observed in our patient. However, he did present with an oesophageal papilloma, removed with forceps and with a confirmatory biopsy.2,3
The treatment depends on the patient's symptoms. In our case, it was decided to not start any treatment as he had no symptoms and there were no associated lesions.1,2
Please cite this article as: Gisasola Dorronsoro P, Iriarte Rodríguez A, Aranzabal Aguilar P, Pseudodiverticulosis intramural esofágica, una entidad a conocer, Gastroenterología y Hepatología. 2022;45:373–374.