To assess adherence to and the adverse effects of the SARS-COV vaccine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Patients and methodsThis is an observational, analytical, cross-sectional study. Sociodemographic and clinical data, SARS-COV vaccine data, medications for IBD with use during the vaccination period, and adverse events during the vaccination period were collected. Carried out logistic regressions with robust variance estimation to estimate the odds ratio with the respective 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) to assess the factors associated with non-serious adverse effects following vaccine doses as outcome variables.
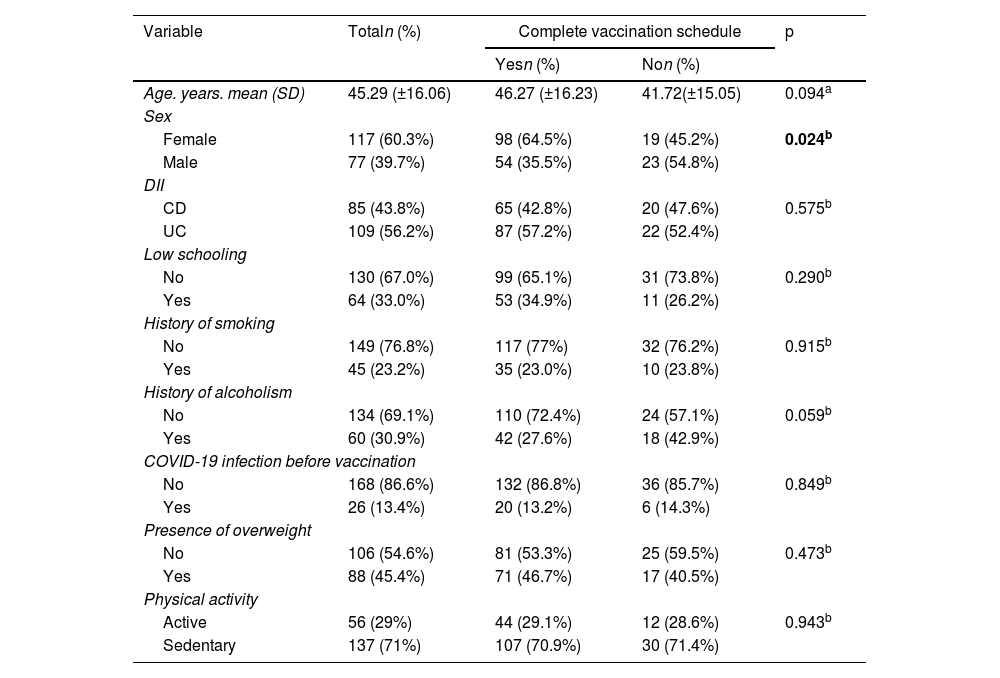
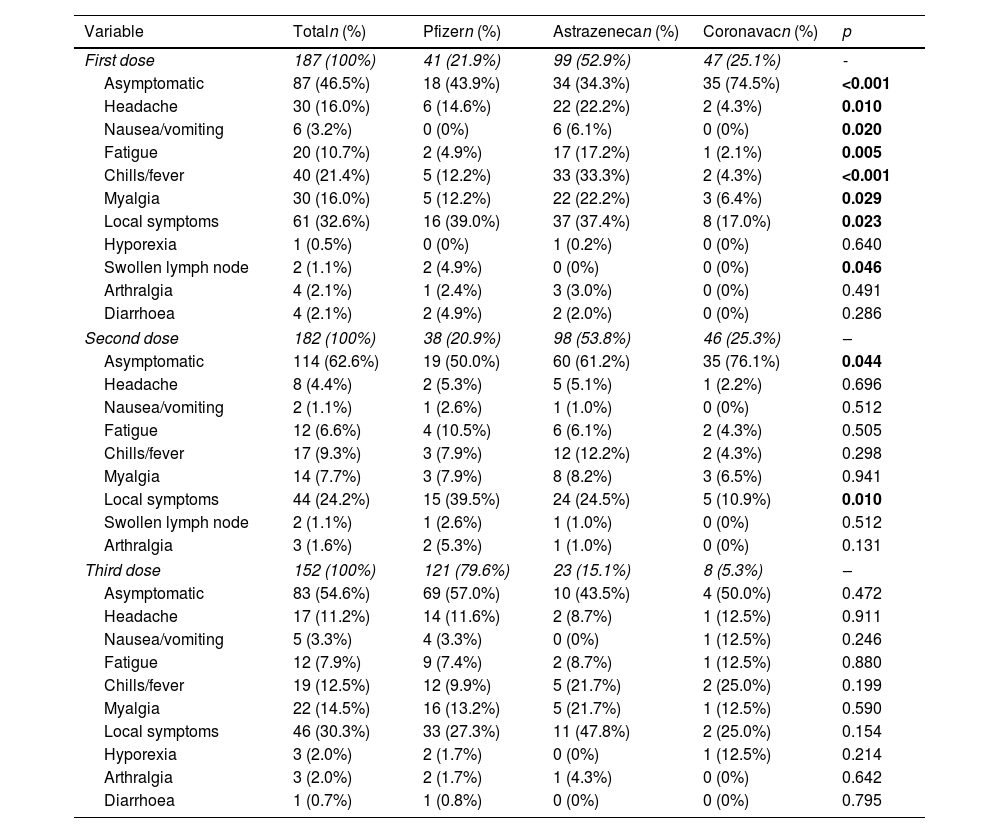
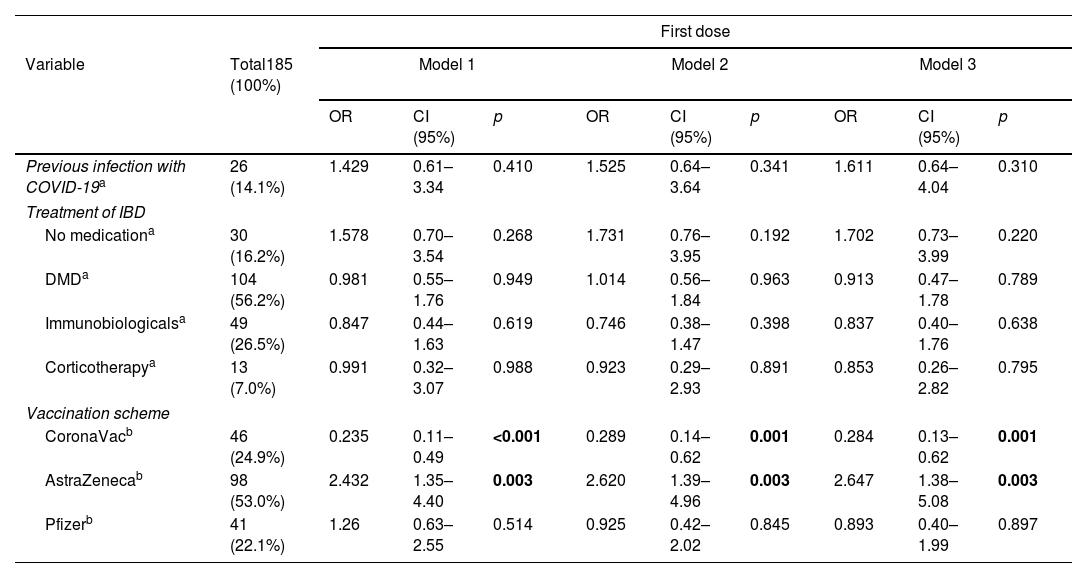
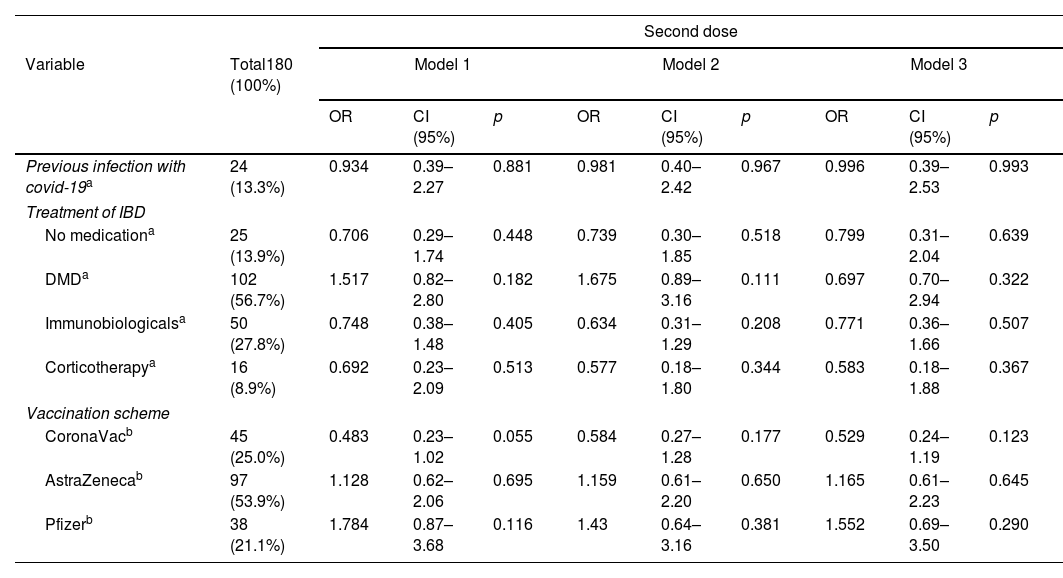
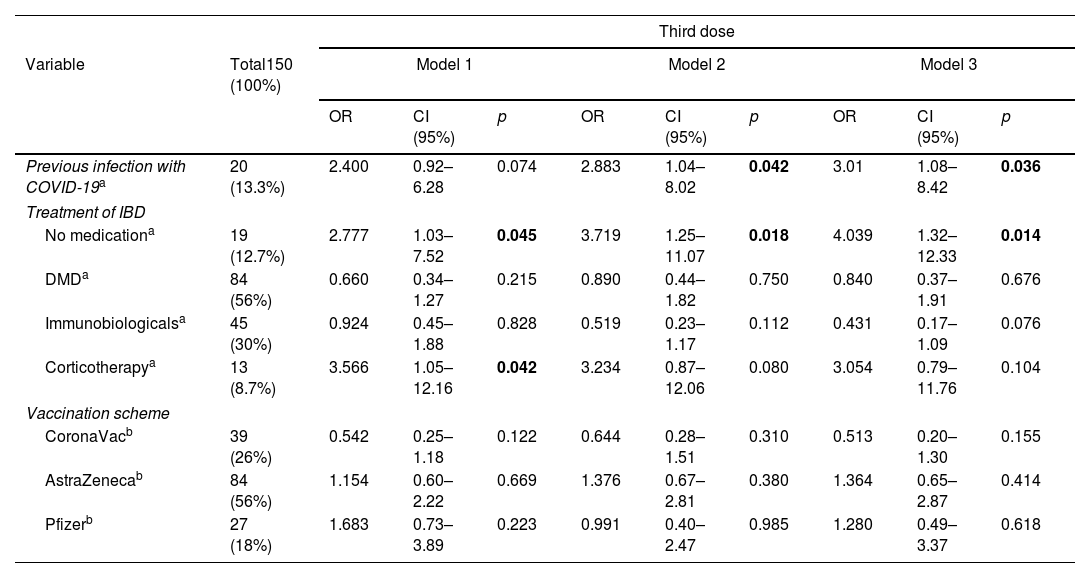
Results194 patients participated, with vaccine compliance of 78.3% for three doses of any vaccine (n=152). Local symptoms and mild systemic symptoms predominated, regardless of the type of vaccine. The first dose of the SARS-COV vaccine with AstraZeneca had a higher percentage of patients with vaccine symptoms. AstraZeneca vaccine increased the chance of non-serious adverse effects in IBD patients by 2.65 times (95% CI: 1.38–5.08; p=0.003), regardless of age, gender, physical activity, excess weight, use of disease-modifying drugs, immunobiological and corticosteroids. CoronaVac vaccine was associated with asymptomatic patients at the first dose and reduced the chance of adverse effects by 0.28 times (OR: 0.284; 95%CI: 0.13–0.62; p=0.002).
ConclusionLocal symptoms and mild systemic symptoms predominated, regardless of the type of vaccine. Using CoronaVac in the first dose reduced the chances of adverse effects, while AstraZeneca increased the risk of adverse effects.
Evaluar la adherencia y los efectos adversos de la vacuna SARS-CoV-2 en los pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII).
Pacientes y métodosSe trata de un estudio observacional, analítico y transversal. Se recogieron los datos sociodemográficos y clínicos; los datos de la vacuna SARS-CoV-2, los medicamentos para la EII con el uso durante el período de vacunación y los efectos adversos tras la vacunación. Se realizaron regresiones logísticas con estimación robusta de la varianza para estimar la odds ratio con los respectivos intervalos de confianza del 95% (IC 95%) para evaluar los factores asociados a los efectos adversos no graves tras las dosis de vacuna como variables de resultado.
ResultadosParticiparon 194 pacientes, con adherencia vacunal del 78,4% para 3 dosis de cualquier vacuna (n=152). Predominaron los síntomas locales y los síntomas sistémicos leves, independientemente del tipo de vacuna. La primera dosis de la vacuna SARS-CoV-2 con AstraZeneca tuvo un mayor porcentaje de pacientes con síntomas vacunales. La vacuna AstraZeneca aumentó 2,65 veces (IC 95%: 1,38-5,08; p=0,003) la probabilidad de efectos adversos no graves en pacientes con EII, independientemente de la edad, el sexo, la actividad física, el exceso de peso, el uso de fármacos modificadores de la enfermedad, inmunobiológicos y corticosteroides. La vacuna CoronaVac® se asoció a pacientes asintomáticos en la primera dosis y redujo la probabilidad de efectos adversos 0,28 veces (OR: 0,284; IC 95%: 0,13-0,62; p=0,002).
ConclusiónSe observó un predominio de los síntomas locales y los síntomas sistémicos leves, independientemente del tipo de vacuna. El uso de CoronaVac® en la primera dosis redujo las posibilidades de efectos adversos, mientras que AstraZeneca aumentó el riesgo de efectos adversos.