In Latin America and Colombia there are few studies about the clinical and therapeutic characteristics of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The objective of this study is to obtain an approximation to these data from a sample of patients from different reference centres in Colombia.
Patients and methodsCross-sectional study in adult and paediatric patients, with IBD, attended ambulatory in 6 institutions in different cities, between 2017 and 2020 information was collected on different dates, about demographic, clinical, and therapeutic aspects.
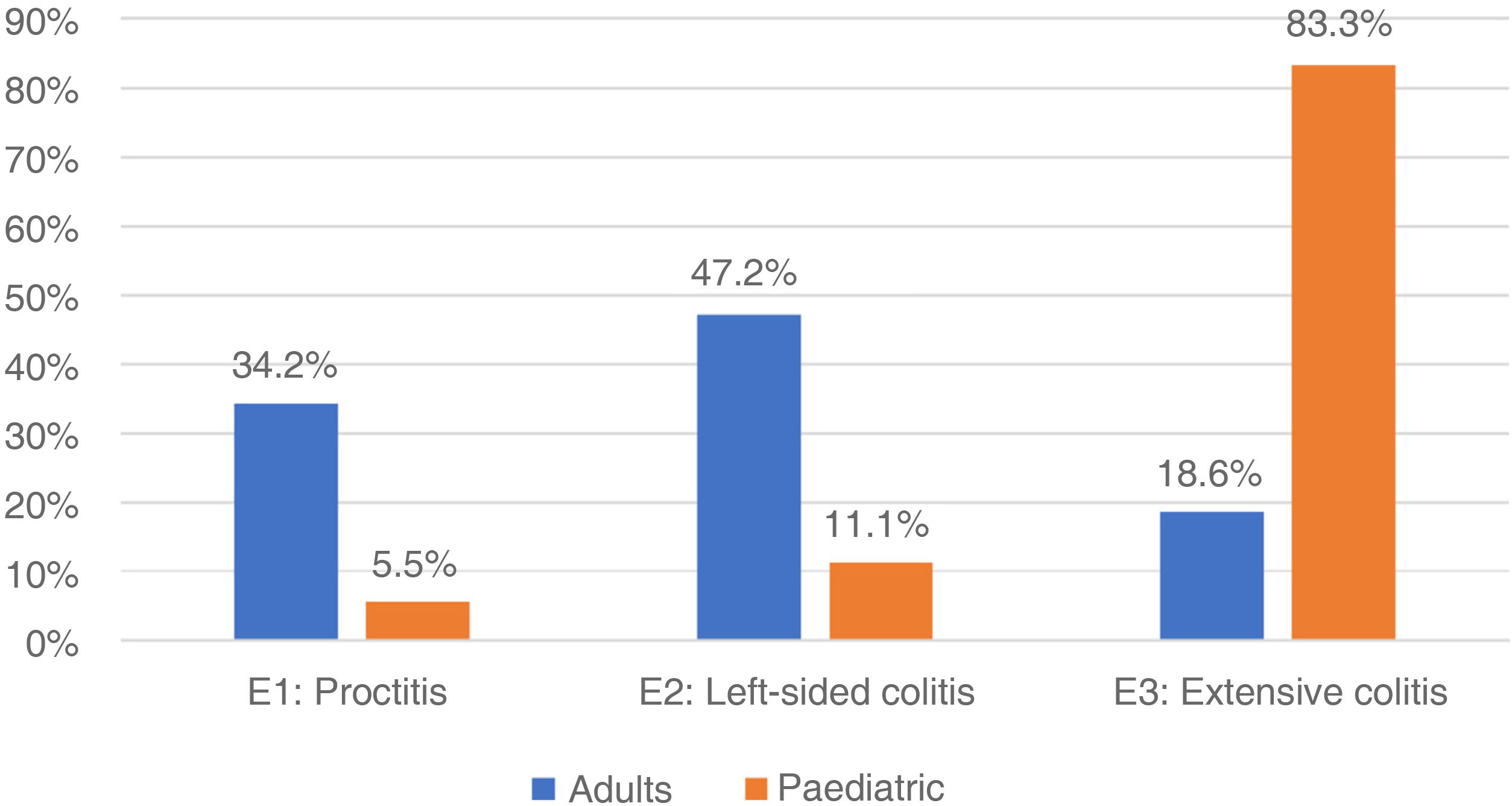
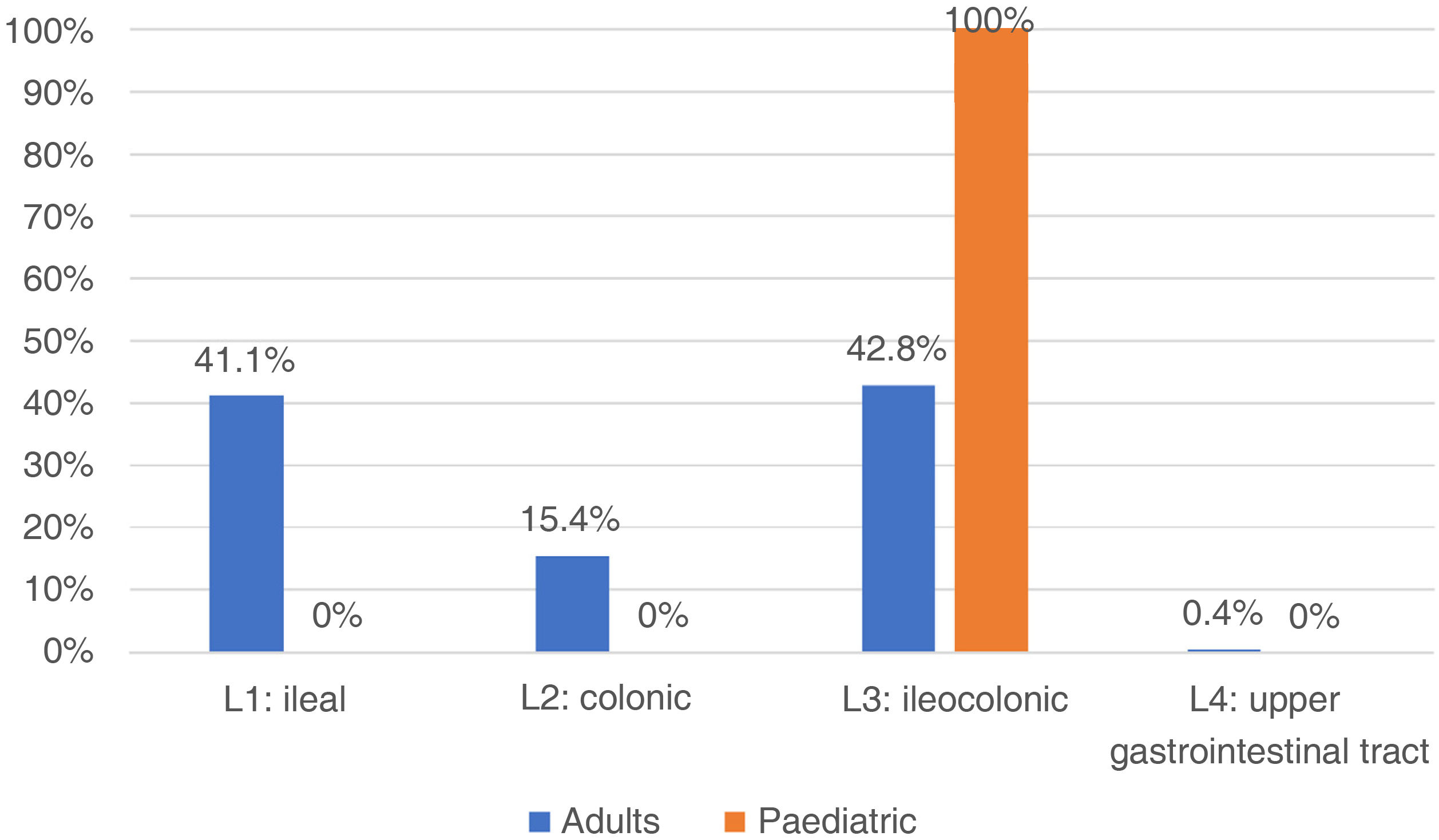
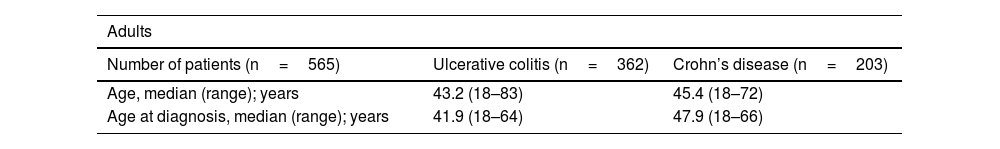
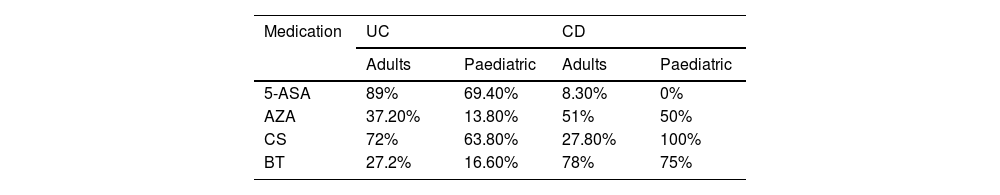
ResultsSix hundred and five subjects, 565 (93.4%) adults, mean age 43 years (SD 12.78), 64% with ulcerative colitis (UC). The age at diagnosis of UC was 41.9 years, while in Crohn’s disease (CD) it was 47.9 years. In UC, there was greater left involvement (47.2%), and in CD, 42.8% ileocolonic (L3). More than 50% were in mild activity or clinical remission. In UC, the biologic requirement was 27.2%, while in CD, 78%. Overall hospitalisation requirement was 39.5%, and the need for surgery was 37.5% in UC and 62.5% in CD. Also, 40 pediatric patients, 90% female, with UC being more frequent (80%). In UC, 83.3% presented extensive colitis, and in CD, all with ileocolonic localization (L3). More than 95% were in mild activity or remission. Biologic therapy was required in 16.6% and 75% for UC and CD, respectively. The frequency of hospitalisations and surgery was 2.7%.
ConclusionsThis study shows some unique characteristics of patients with IBD in Colombia. An earlier diagnosis is required, with a better therapeutic approach.
En Latinoamérica y Colombia hay pocos estudios acerca las características clínicas y terapéuticas de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII). Se plantea como objetivo obtener una aproximación a dichos datos a partir de una muestra de pacientes de diferentes centros de referencia en Colombia.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio de corte transversal en pacientes adultos y pediátricos, con EII, atendidos ambulatoriamente en seis instituciones en diferentes ciudades, entre 2017–2020 se recolectó información en fechas distintas, acerca aspectos demográficos, clínicos y terapéuticos.
ResultadosSeiscientos cinco sujetos, 565 (93,4%) adultos, edad promedio de 43 años (DE 12,78), 64% con colitis ulcerosa (CU). La edad de diagnóstico de CU fue 41,9 años, mientras en enfermedad de Crohn (EC) fue 47,9 años. En CU, mayor compromiso izquierdo (47,2%), y en EC, 42,8% ileocolónico (L3). Más de 50% en actividad leve o remisión clínica. En CU, el requerimiento de biológico fue de 27,2%. mientras en EC, 78%. Requerimiento global de hospitalización en 39,5%, y necesidad de cirugía, de 37,5% en CU y 62,5% en EC. También, 40 pacientes pediátricos, 90% mujeres, siendo CU más frecuente (80%). En CU, 83,3% presentaron colitis extensa, y en EC, todas con localización ileocolónica (L3). Más de 95% en actividad leve o remisión. Requerimiento de biológico, en 16,6 y 75%, para CU y EC, respectivamente. La frecuencia hospitalizaciones y cirugía fue 2,7%.
ConclusionesEste estudio muestra algunas características únicas de los pacientes con EII en Colombia. Se requiere de un diagnóstico más temprano, con un mejor enfoque terapéutico.