Although patients with advanced liver disease have been included in studies evaluating fibrates for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), the frequency of biochemical responses and adverse effects for this group of patients was not reported separately and comprehensively.
Aimsto evaluate the efficacy and safety of additional fenofibrate therapy in patients with advanced and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)-refractory PBC.
MethodsPatients were analyzed retrospectively to determine the clinical therapeutic effects of UDCA with additional fenofibrate therapy versus continued UDCA monotherapy. The liver transplantation (LT)-free survival and the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) normalization rates were estimated using Cox regression analyses and Kaplan–Meier plots with inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW).
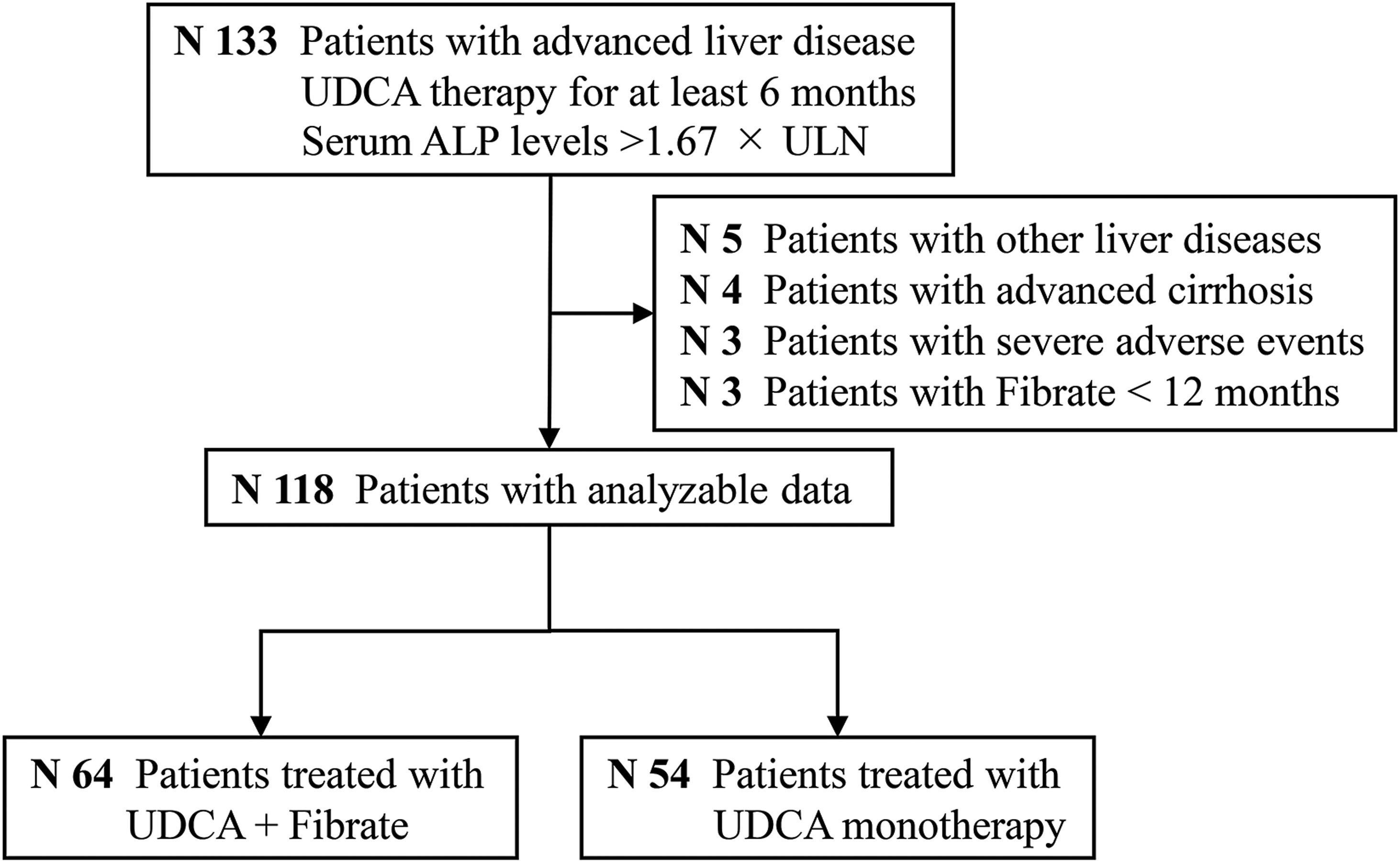
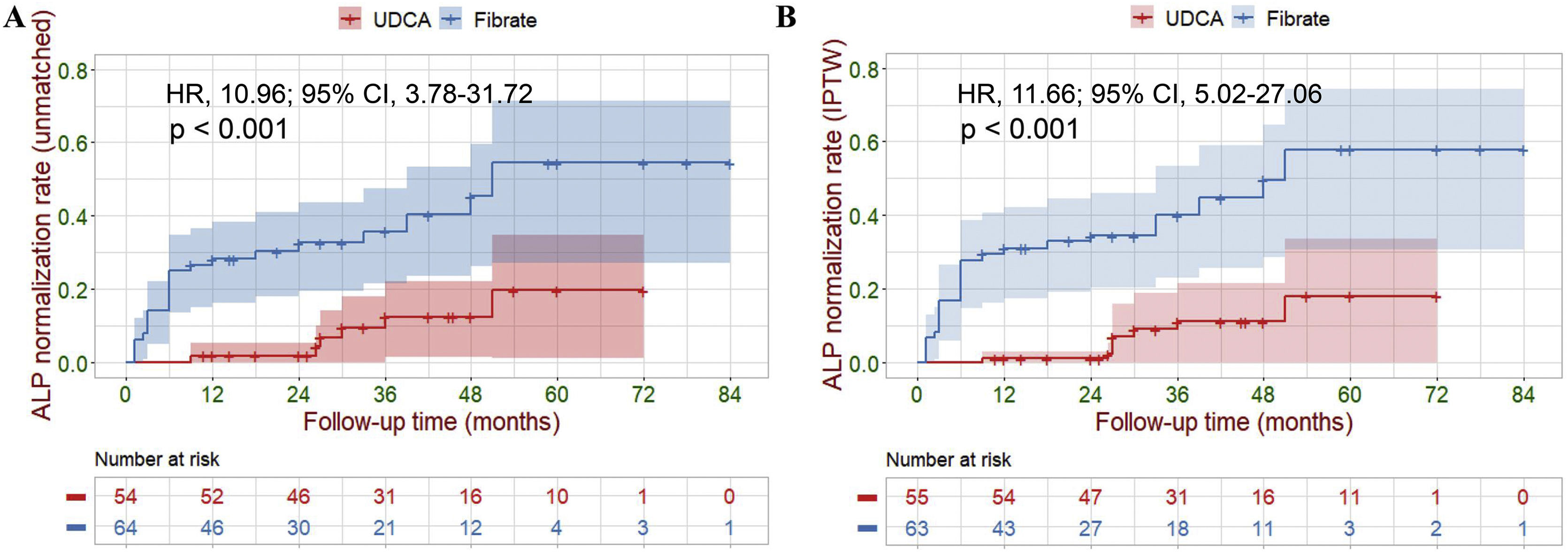
ResultsA total of 118 patients were included: 54 received UDCA alone and 64 received UDCA in combination with fenofibrate therapy. In the fenofibrate and UDCA groups, 37% and 11% of patients with advanced and UDCA-refractory PBC, respectively, achieved ALP normalization (P=0.001). Additional fenofibrate therapy improved both LT-free survival and ALP normalization rate after IPTW (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.23, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.07–0.75, P=0.015; and HR: 11.66, 95% CI: 5.02–27.06, P=0.001, respectively). These effects were supported by parallel changes in the rates of liver decompensation and histologic progression, and the United Kingdom (UK)-PBC and Globe risk scores. During the follow-up period, serum levels of ALP and aminotransferase decreased significantly, while total bilirubin, albumin, platelet, serum creatinine, and estimated glomerular filtration rate remained stable in fenofibrate-treated participants. No fenofibrate-related significant adverse events were observed in our cohort.
ConclusionsAdditional fenofibrate therapy significantly improved LT-free survival and ALP normalization in patients with advanced and UDCA-refractory PBC. Furthermore, adding-on fenofibrate therapy appeared to be safe and well tolerated in this population.
Aunque los pacientes con enfermedad hepática avanzada se han incluido en los estudios que evalúan los fibratos para el tratamiento de la colangitis biliar primaria, la frecuencia de las respuestas bioquímicas y los efectos adversos para este grupo de pacientes no se informó por separado y de forma exhaustiva.
ObjetivosEvaluar la eficacia y la seguridad del tratamiento adicional con fenofibrato en pacientes con colangitis biliar primaria avanzada y refractaria al ácido ursodesoxicólico.
MétodosSe analizaron los pacientes de forma retrospectiva para determinar los efectos terapéuticos clínicos del ácido ursodesoxicólico con terapia adicional de fenofibrato frente a la monoterapia continuada con ácido ursodesoxicólico. La supervivencia sin trasplante de hígado y las tasas de normalización de la fosfatasa alcalina se estimaron mediante análisis de regresión de Cox y gráficos de Kaplan-Meier con ponderación de la probabilidad inversa del tratamiento.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 118 pacientes: 54 recibieron ácido ursodesoxicólico solo y 64 recibieron ácido ursodesoxicólico en combinación con el tratamiento con fenofibrato. En los grupos de fenofibrato y ácido ursodesoxicólico, 37 y 11% de los pacientes con colangitis biliar primaria avanzada y refractaria al ácido ursodesoxicólico, respectivamente, lograron la normalización de la fosfatasa alcalina (p=0,001). El tratamiento adicional con fenofibrato mejoró tanto la supervivencia libre de trasplante de hígado como la tasa de normalización de la fosfatasa alcalina tras la ponderación de la probabilidad inversa del tratamiento (cociente de riesgos: 0,23, intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC 95%]: 0,07-0,75, p=0,015; y cociente de riesgos: 11,66, IC 95%: 5,02–27,06, p=0,001, respectivamente). Estos efectos se vieron respaldados por cambios paralelos en las tasas de descompensación hepática y de progresión histológica, y por las puntuaciones de riesgo de colangitis biliar primaria del Reino Unido y de Globe. Durante el periodo de seguimiento, los niveles séricos de fosfatasa alcalina y aminotransferasa disminuyeron significativamente, mientras que la bilirrubina total, la albúmina, las plaquetas, la creatinina sérica y la tasa de filtración glomerular estimada permanecieron estables en los participantes tratados con fenofibrato. No se observaron acontecimientos adversos significativos relacionados con el fenofibrato en nuestra cohorte.
ConclusionesEl tratamiento adicional con fenofibrato mejoró significativamente la supervivencia libre de trasplante hepático y la normalización de la fosfatasa alcalina en pacientes con colangitis biliar primaria avanzada y refractaria al ácido ursodesoxicólico. Además, el tratamiento adicional con fenofibrato parece ser seguro y bien tolerado en esta población.