Gastric cancer (GC) is the first cause of cancer-related death in Chile and 6th in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC). Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is the main gastric carcinogen, and its treatment reduces GC incidence and mortality. Esophageal-gastro-duodenoscopy (EGD) allows for the detection of premalignant conditions and early-stage GC. Mass screening programs for H. pylori infection and screening for premalignant conditions and early-stage GC are not currently implemented in LAC. The aim of this study is to establish recommendations for primary and secondary prevention of GC in asymptomatic standard-risk populations in Chile.
MethodsTwo on-line synchronous workshops and a seminar were conducted with Chilean experts. A Delphi panel consensus was conducted over 2 rounds to achieve >80% agreement on proposed primary and secondary prevention strategies for the population stratified by age groups.
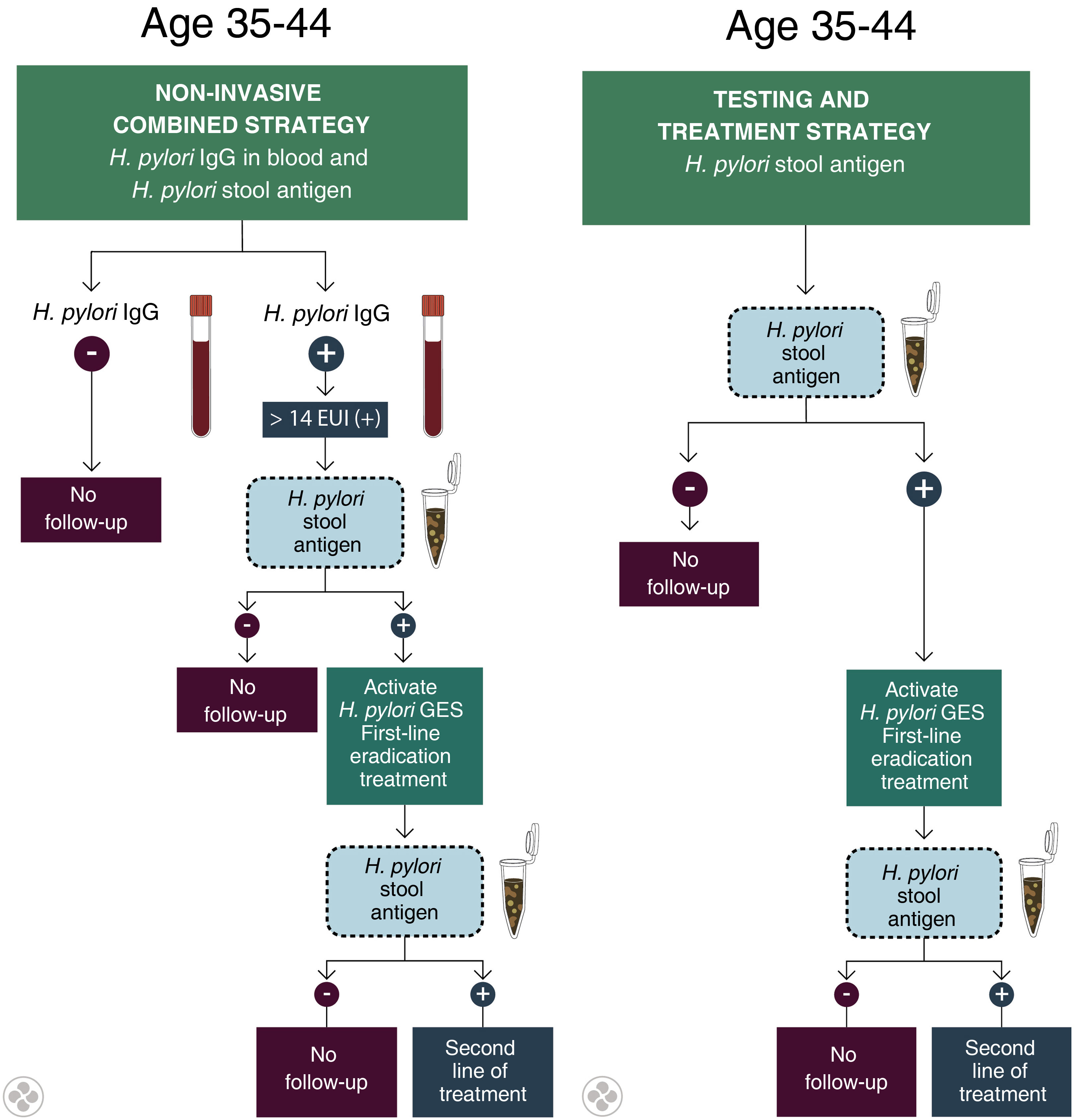
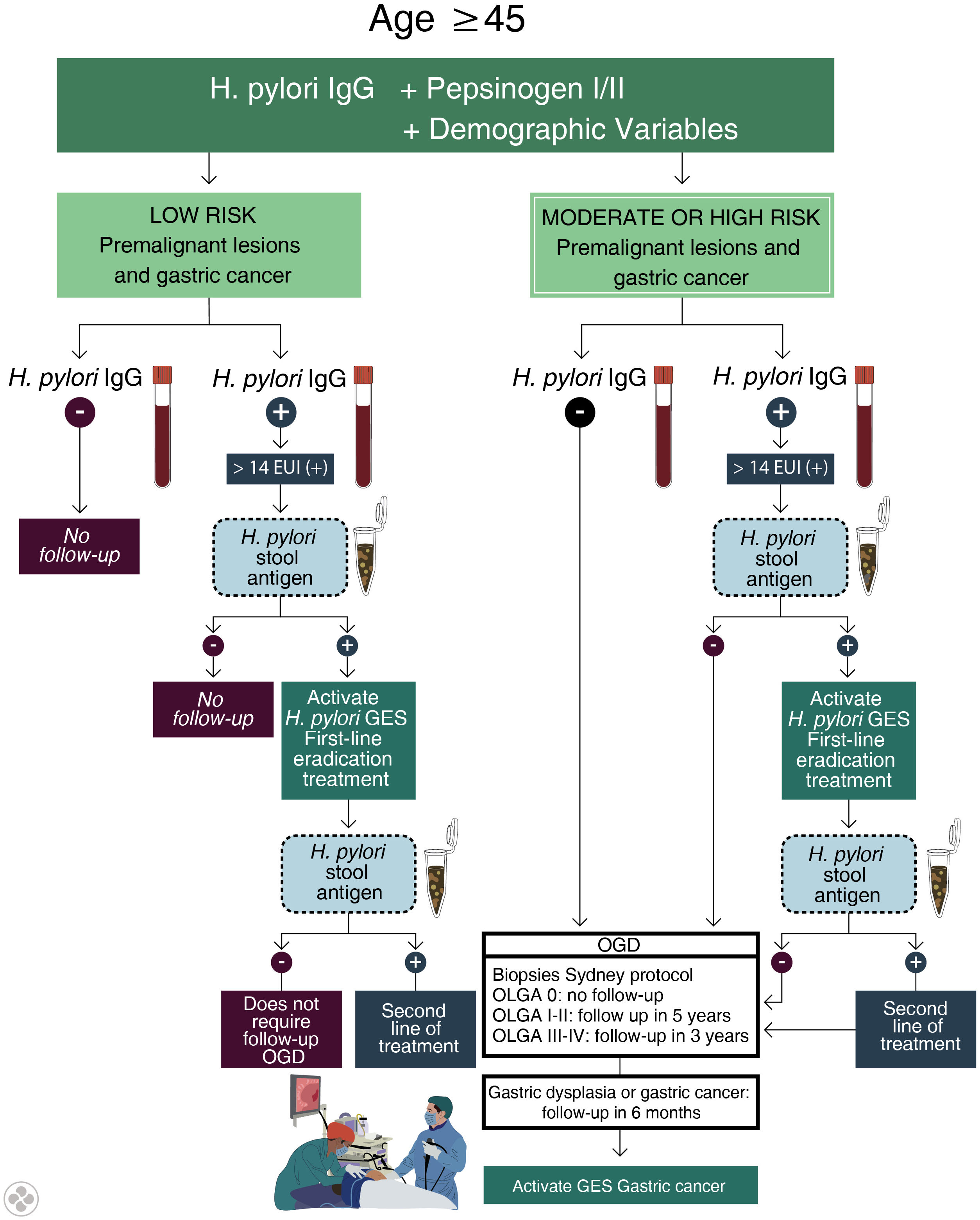
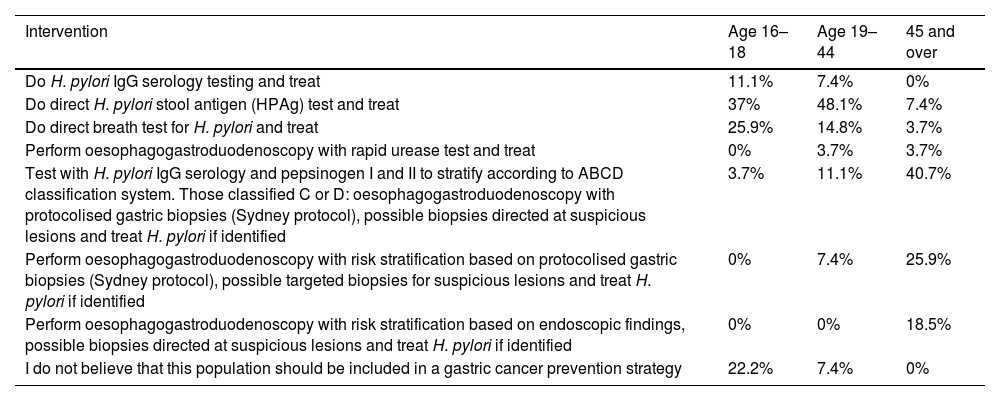
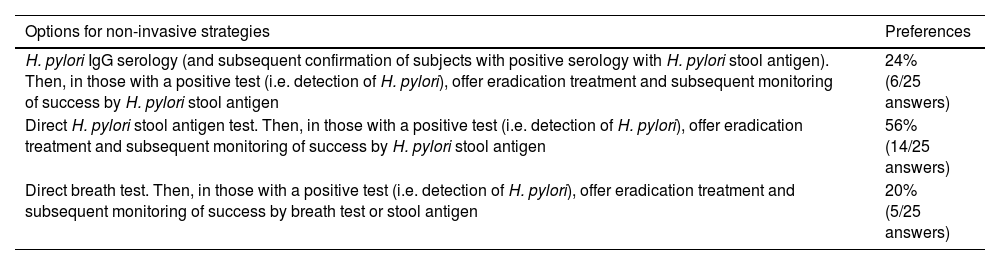
Results10, 12, and 12 experts participated in two workshops and a seminar, respectively. In the Delphi panel, 25 out of 37 experts (77.14%) and 28 out of 52 experts (53.85%) responded. For the population aged 16–34, there was no consensus on non-invasive testing and treatment for H. pylori, and the use of EGD was excluded. For the 35–44 age group, non-invasive testing and treatment for H. pylori is recommended, followed by subsequent test-of-cure using non-invasive tests (stool antigen test or urea breath test). In the ≥45 age group, a combined strategy is recommended, involving H. pylori testing and treatment plus non-invasive biomarkers (H. pylori IgG serology and serum pepsinogens I and II); subsequently, a selected group of subjects will undergo EGD with gastric biopsies (Sydney Protocol), which will be used to stratify surveillance according to the OLGA classification (Operative Link for Gastritis Assessment); every 3 years for OLGA III–IV and every 5 years for OLGA I–II.
ConclusionA “test-and-treat” strategy for H. pylori infection based on non-invasive studies (primary prevention) is proposed in the 35–44 age group, and a combined strategy (serology and EGD) is recommended for the ≥45 age group (primary and secondary prevention). These strategies are potentially applicable to other countries in LAC.
El cáncer gástrico (CG) es la primera causa de muerte oncológica en Chile y la sexta en América Latina y el Caribe (LAC). Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) es el principal carcinógeno gástrico y su tratamiento reduce la incidencia y mortalidad por CG. La endoscopia digestiva alta (EDA) permite la detección de condiciones premalignas y CG incipiente. No existen programas de búsqueda masiva de la infección por H. pylori ni cribado de las condiciones premalignas ni CG incipiente en LAC. El objetivo de este estudio es establecer recomendaciones para la prevención primaria y secundaria de CG en población asintomática de riesgo estándar en Chile.
MétodosSe realizaron dos talleres y un seminario sincrónicos con modalidad a distancia, con expertos chilenos. Se realizó un consenso por panel Delfi de 2 rondas hasta lograr >80% de acuerdo respecto a las estrategias de prevención primaria y secundaria propuestas para la población estratificada según grupos etarios.
ResultadosSe realizaron 2 talleres y un seminario con participación de 10, 12 y 12 expertos, respectivamente. En el panel Delfi respondieron 25 de 37 (77,14%) y 28 de 52 expertos (53,85%). Para la población de 16–34 años no hubo consenso sobre testear y tratar de forma no invasiva para H. pylori y se descartó el uso de EDA. Entre 35–44 años se recomienda testear y tratar de forma no invasiva para H. pylori y evaluar posteriormente su erradicación con pruebas no invasivas (antígeno en deposiciones de H. pylori o prueba de aire espirado). En el grupo ≥45 años se recomienda una estrategia combinada mediante testear y tratar para H. pylori sumado a biomarcadores no invasivos (serología IgG contra H. pylori y pepsinógenos I y II séricos); luego un grupo seleccionado de sujetos, será derivado a EDA con biopsias gástricas (Protocolo Sydney), que serán utilizadas para estratificar riesgo según clasificación Operative Link for Gastritis Assessment (OLGA); cada 3 años en OLGA III-IV y cada 5 años en OLGA I-II.
ConclusiónSe propone una estrategia de testear y tratar la infección por H. pylori (prevención primaria) en base a estudios no invasivos en la población de 35-44 años y una estrategia combinada (serología y EDA) en población ≥45 años (prevención primaria y secundaria). Estas estrategias son potencialmente aplicables por otros países de LAC.