Herpes zoster (HZ) is a prevalent disease caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and associated with chronic morbidity, particularly with post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has been associated with an increased risk of HZ, mainly when immunosuppressive treatment (IMT) is used. However, studies assessing the risk of HZ in IBD are scarce.
AimsTo evaluate the incidence rate and risk factors of HZ in IBD.
MethodsRetrospective study in IBD patients with a positive VVZ serology from two referral hospitals from the area of Barcelona. Diagnosis of HZ and its clinical features were recorded.
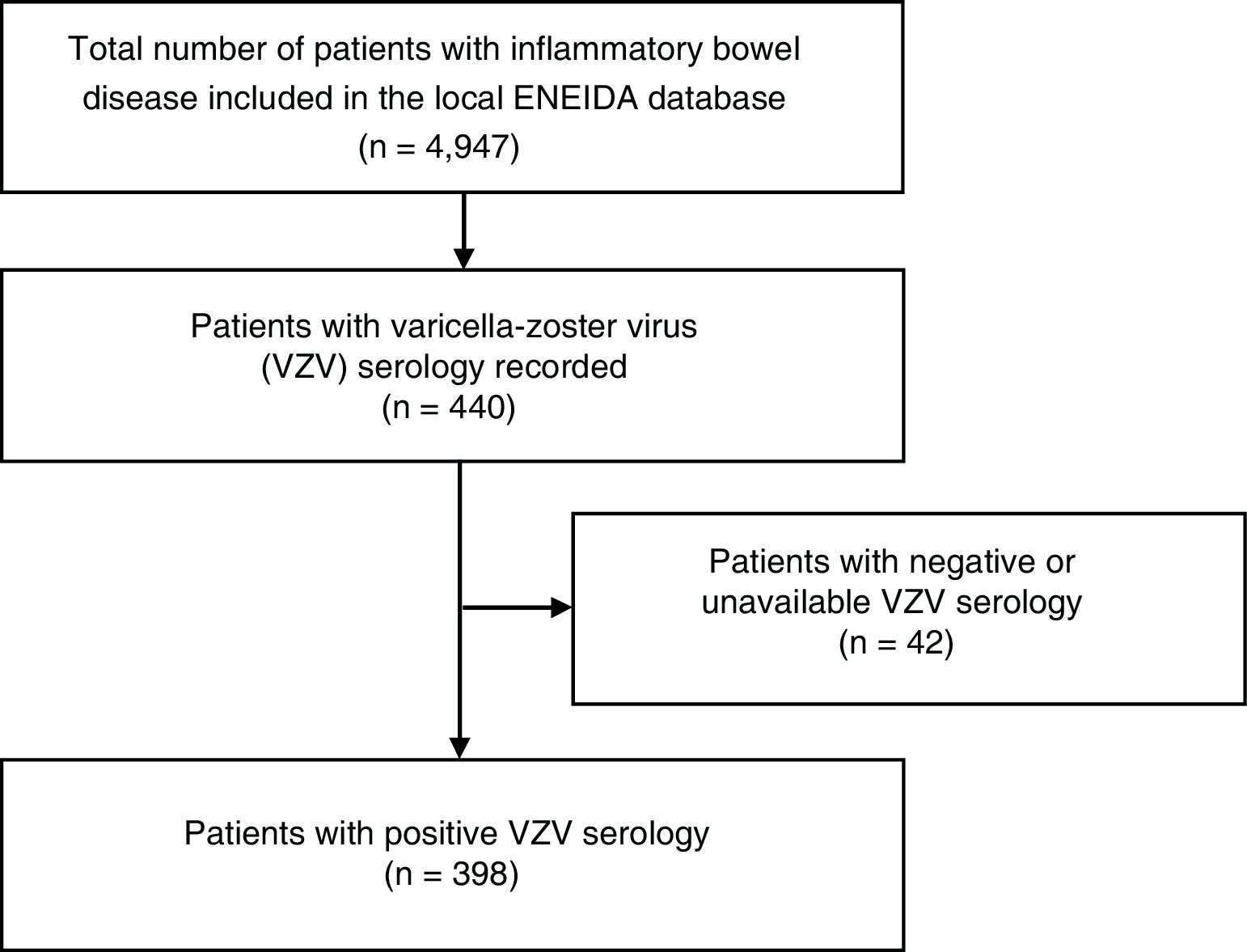
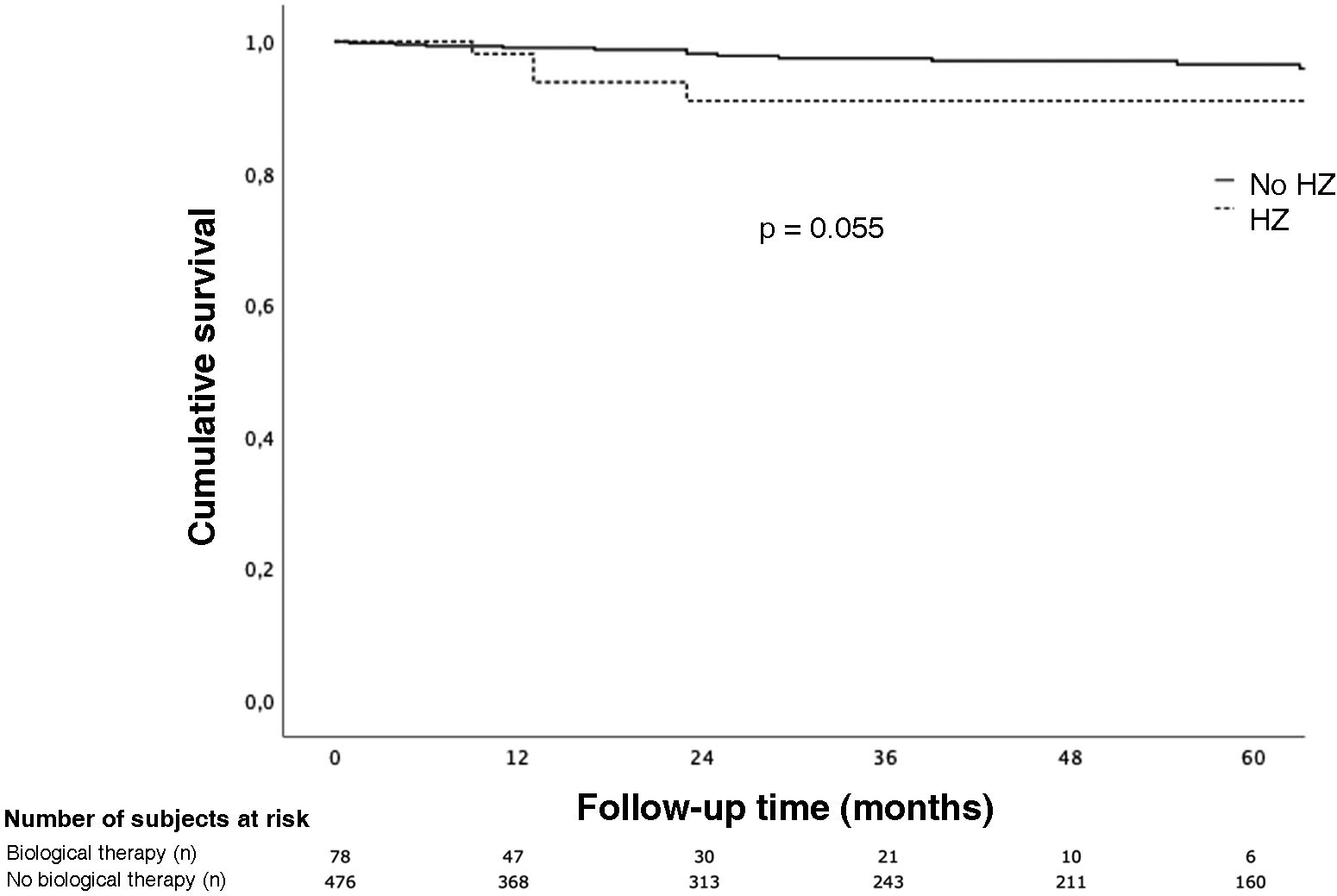
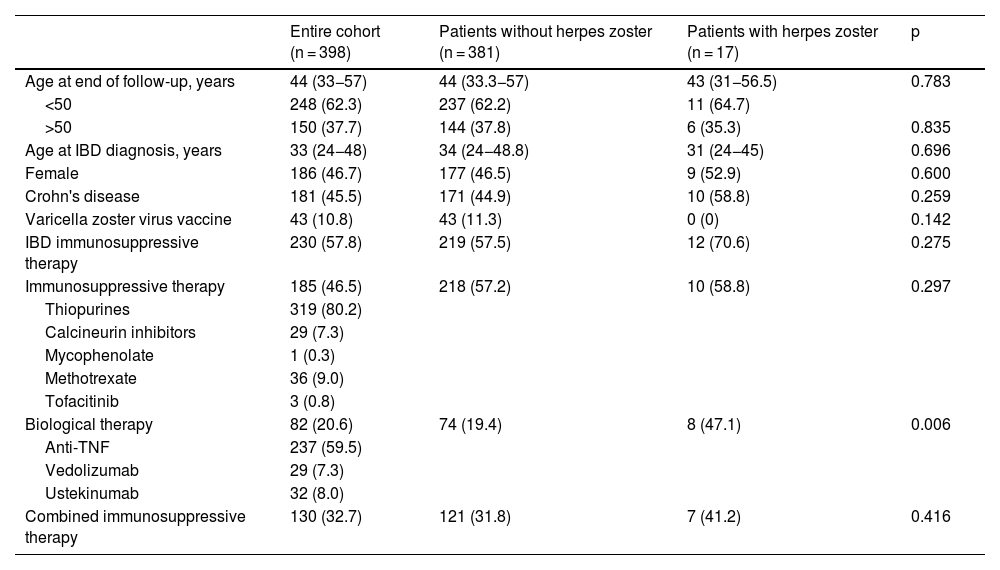
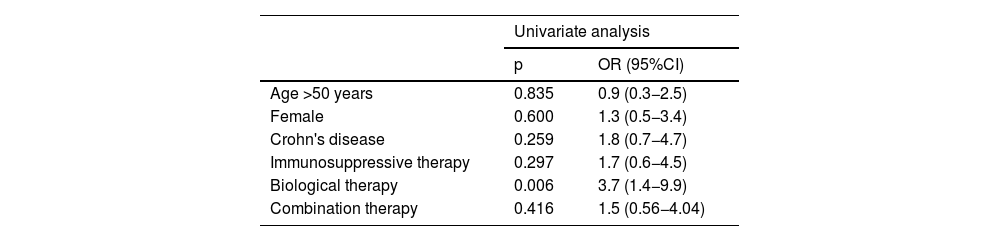
ResultsA total of 398 IBD patients with a positive IgG-VVZ serology were identified. Fifty-eight percent of the patients received IMT (46.5% immunosuppressants monotherapy, 20.6% biologics monotherapy and, 32.7% combination therapy). After a median follow-up of 71 months (IQR 41.5–138.0), 17 (4.3%) patients developed HZ (cumulative incidence of 5.2 per 1000 person-year), 12 of them (70.6%) while receiving IMT. Median age at HZ episode was 38 years (IQR 27.5–52.5). Two (11%) developed PHN. Biological therapy was the only risk factor for developing HZ (OR 3.8 IC95% 1.3–11.5; p = 0.018).
ConclusionsHZ is quite prevalent in IBD, occurring at early ages and particularly among patients using IMT. NPH appears to occur in a notable proportion of cases.
El herpes zóster (HZ) es una enfermedad prevalente causada por la reactivación del virus varicela-zóster (VVZ) y asociada a morbilidad crónica, particularmente la neuralgia postherpética (NPH). La enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) se ha asociado un mayor riesgo de HZ, especialmente en pacientes con terapia inmunosupresora (TIMS). Sin embargo, los estudios que evalúan el riesgo de HZ en la EII son escasos.
ObjetivosEvaluar la tasa de incidencia y factores de riesgo relacionados con HZ en la EII.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo en pacientes con EII y serología VVZ positiva de dos hospitales de referencia del área de Barcelona. Se registraron los casos de HZ y su evolución.
ResultadosSe identificaron 398 pacientes con EII y serología positiva para VVZ. El 58% de los pacientes recibieron TIMS en algún momento del seguimiento (46,5% monoterapia con inmunosupresores, 20,6% monoterapia con biológicos y 32,7% terapia combinada). Tras una mediana de seguimiento de 71 meses (RIC 41,5–138,0), 17 (4,3%) pacientes desarrollaron HZ (incidencia acumulada de 5,2/1.000 personas-año), doce de ellos (70,6%) durante TIMS. Dos pacientes (11%) desarrollaron NPH. La mediana de edad en el episodio de HZ fue de 38 años (RIC 27,5–52,5). El tratamiento biológico fue el único factor asociado al desarrollo de HZ (OR 3,8 IC 95% 1,3–11,5; p = 0,018).
ConclusiónEl HZ es relativamente prevalente en la EII, ocurre a edades tempranas y particularmente entre pacientes que utilizan TIMS. La NPH parece ocurrir en una notable proporción de casos.