La hipertensión nocturna aislada se asocia a mayor cantidad de eventos cardiovasculares y daño de órgano blanco por hipertensión arterial. La prevalencia en poblaciones especiales no se encuentra del todo descrita. El objetivo del siguiente estudio es describir la prevalencia de hipertensión nocturna aislada en población conviviendo con el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana, y observar su relación con las categorías de presión arterial en el consultorio y los fenotipos de la medición ambulatoria de presión arterial de 24h.
MetodologíaSe realizó una cohorte retrospectiva en una población con el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana en un hospital público de España, se registraron características clínico epidemiológicas, mediciones de presión arterial en consultorio y medición ambulatoria de presión arterial de 24h (MAPA). Se realizó un análisis en función de los diferentes fenotipos de presión arterial por MAPA, así como también en función de las diferentes categorías de presión arterial de consultorio se calcularon los riesgos para la hipertensión nocturna aislada.
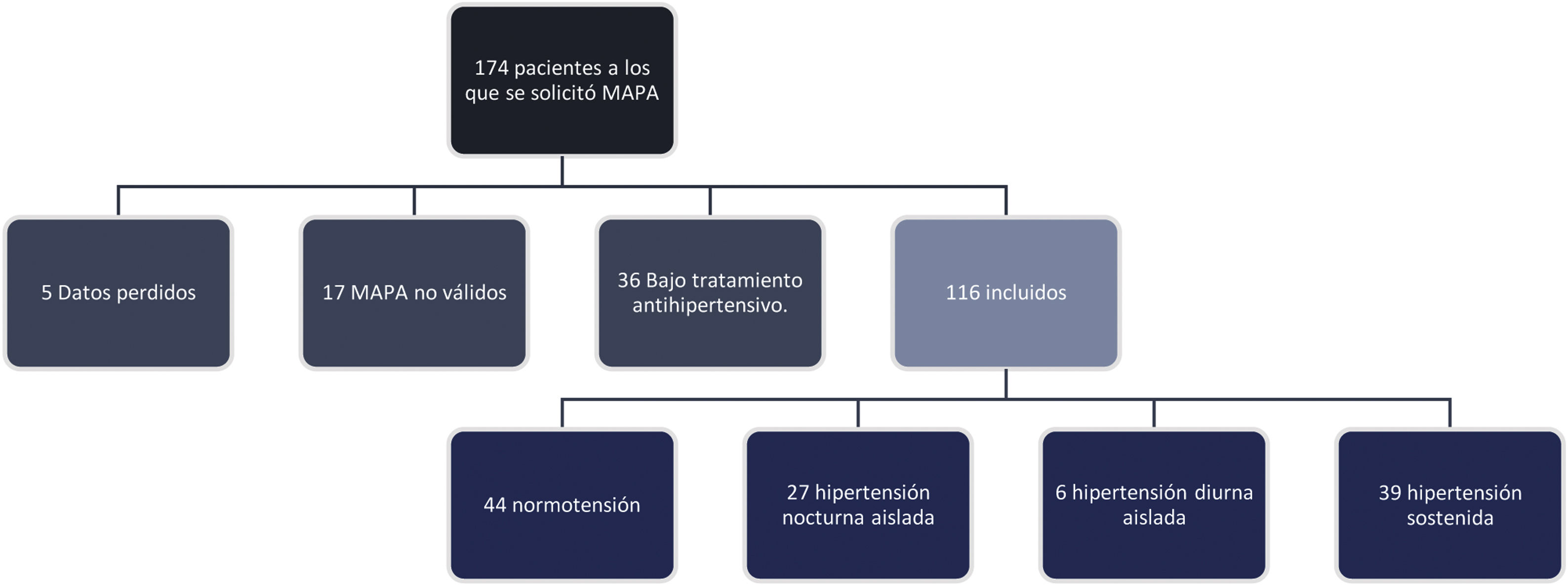
ResultadosSe incluyeron en el análisis 116 individuos, sin medicación antihipertensiva ni antecedentes de enfermedad cardiovascular establecida. Se describió una prevalencia de hipertensión nocturna del 23,3%. No se pudo demostrar diferencias significativas entre fenotipos por MAPA de ninguna variable propia del VIH.
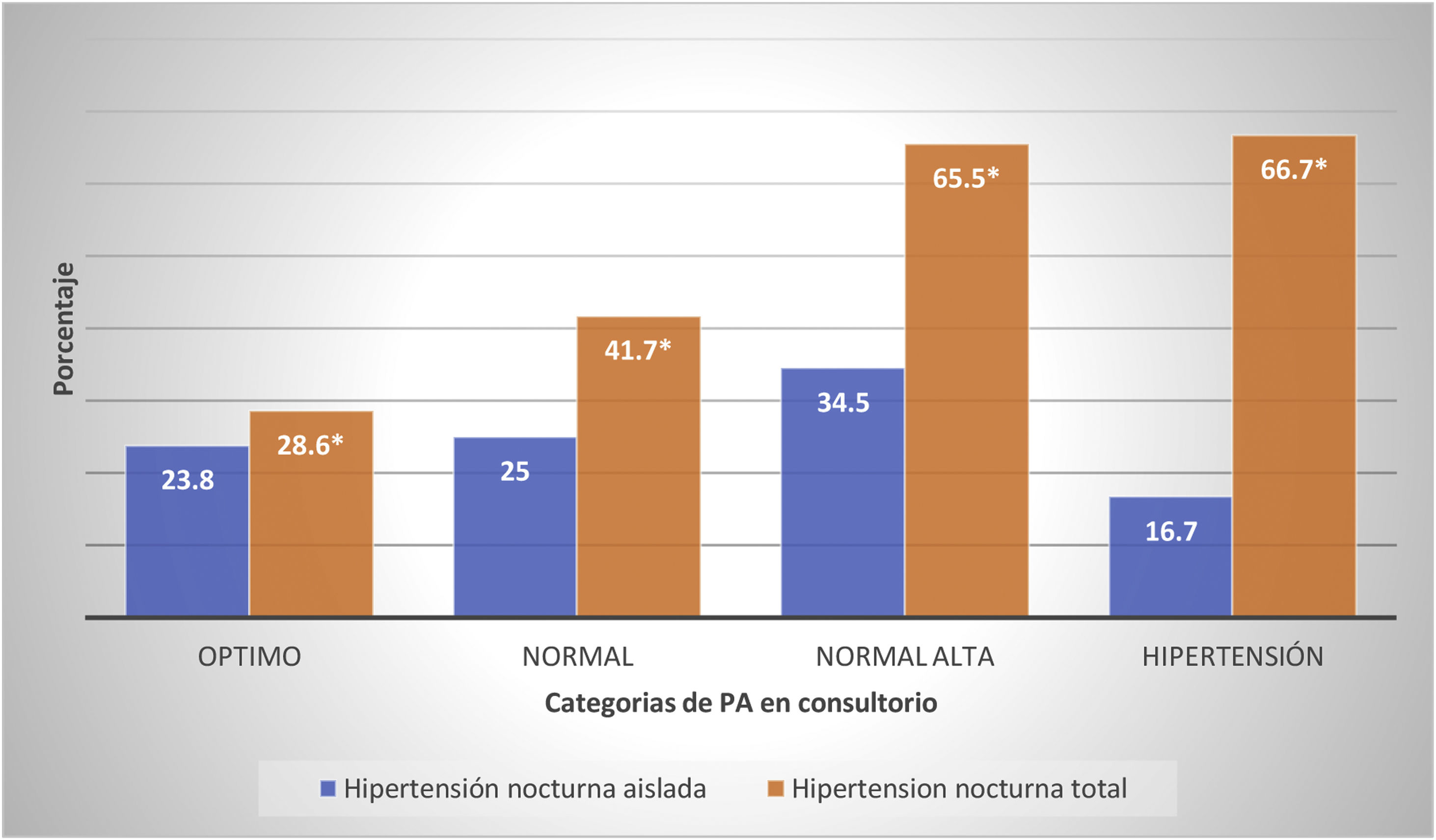
No hubo diferencias de riesgo ajustadas entre las diferentes categorías de normotensos en consultorio.
ConclusionesLa hipertensión nocturna aislada es más frecuente en pacientes con VIH, y los valores de presión arterial de consultorio en normotensos no son suficientes para predecir HTA nocturna aislada.
Isolated nocturnal hypertension is associated with a greater number of cardiovascular events and target organ damage due to arterial hypertension. It has been observed that patients in the general population with this entity do not have high blood pressure figures in the office; and it is necessary to perform an outpatient measurement to unmask it. The prevalence in special populations is not fully described. The objective of the following study is to describe the prevalence of isolated nocturnal hypertension in a population living with the human immunodeficiency virus and to observe its relationship with the categories of office blood pressure and the phenotypes of the 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure measurement.
MethodologyA retrospective cohort was carried out in a population with human immunodeficiency virus in a public hospital in Spain, clinical epidemiological characteristics, office blood pressure measurements and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure measurement (ABPM) were recorded. An analysis was performed based on the different ABPM blood pressure phenotypes, as well as based on the different office blood pressure categories, the risks for isolated nocturnal hypertension were calculated.
ResultsOne hundred and sixteen individuals, without antihypertensive medication or history of established cardiovascular disease, were included in the analysis. A prevalence of nocturnal hypertension of 23.3% was described. It was not possible to demonstrate significant differences between phenotypes by ABPM of any variable specific to HIV.
There were no adjusted risk differences between the different categories of office normotensives.
ConclusionsIsolated nocturnal hypertension is more frequent in patients with HIV and office blood pressure values in normotensive patients are not sufficient to predict isolated nocturnal hypertension.