This study aimed to examine the effects of a six-week of concurrent training using high-intensity interval plus resistance training on flow-mediated dilation and pulse wave velocity in hypertensive, elevated blood pressure, or normotensive. A secondary goal was to analyze the inter-individual variability.
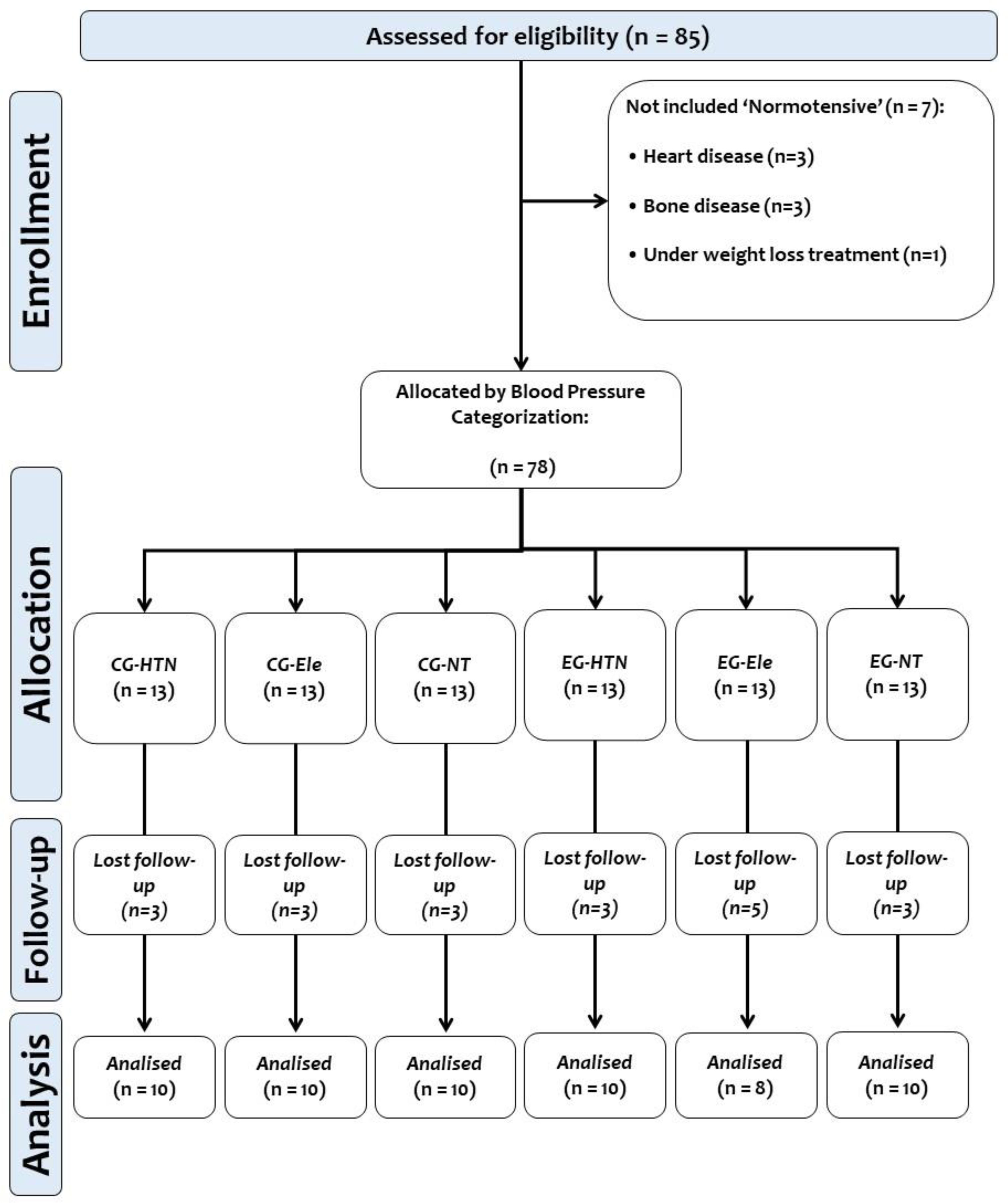
MethodsA randomized controlled clinical trial was executed with 60 adult participants distributed across six groups: three control groups of hypertensive, elevated blood pressure, or normotensive and other three experimental hypertensive, elevated blood pressure, and normotensive groups, each comprising n=10 individuals. Participants underwent a six-week intervention of concurrent exercise using high-intensity interval plus resistance training three-weekly. Flow mediated dilation and pulse wave velocity and secondary vascular assessments were conducted before and after the intervention.
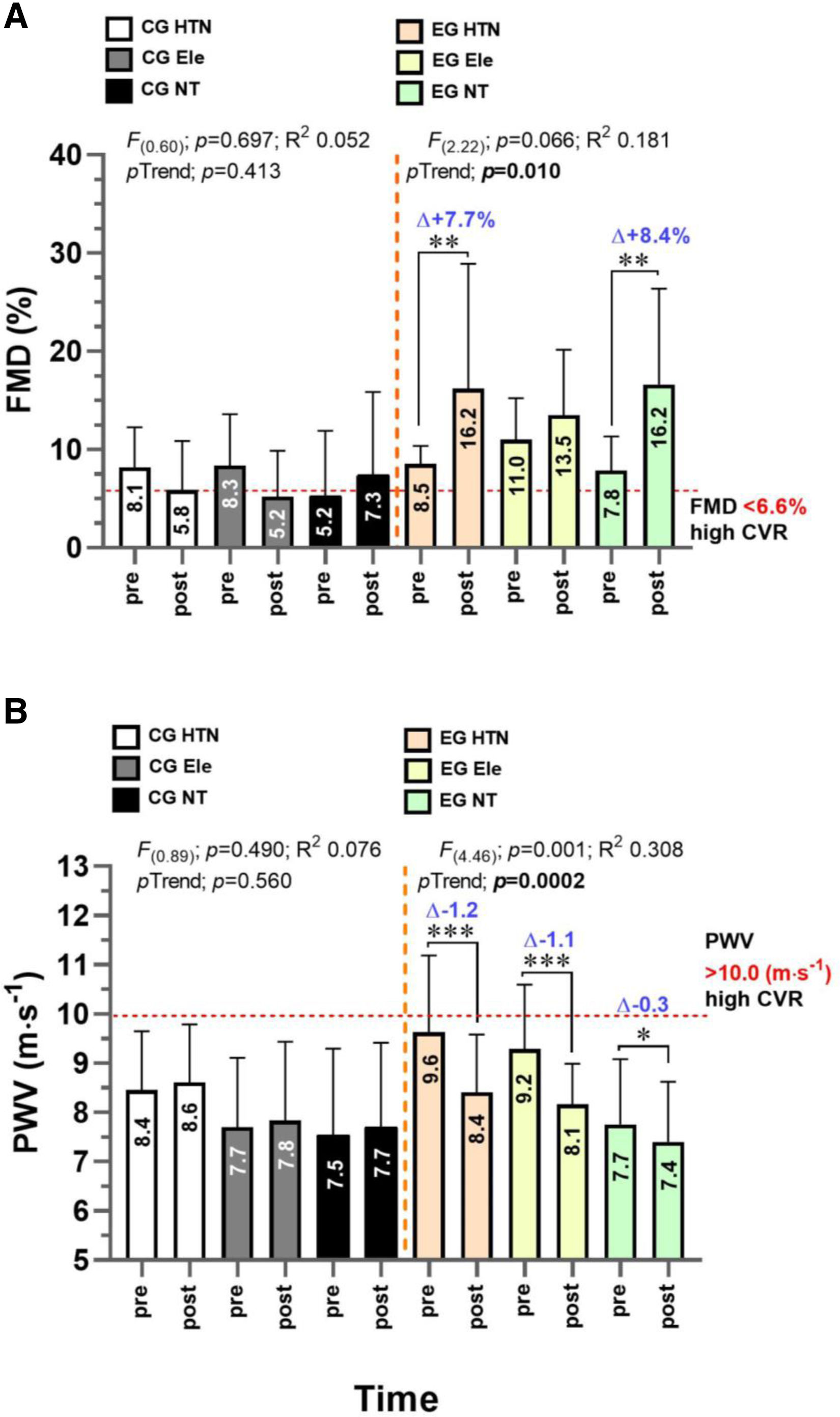
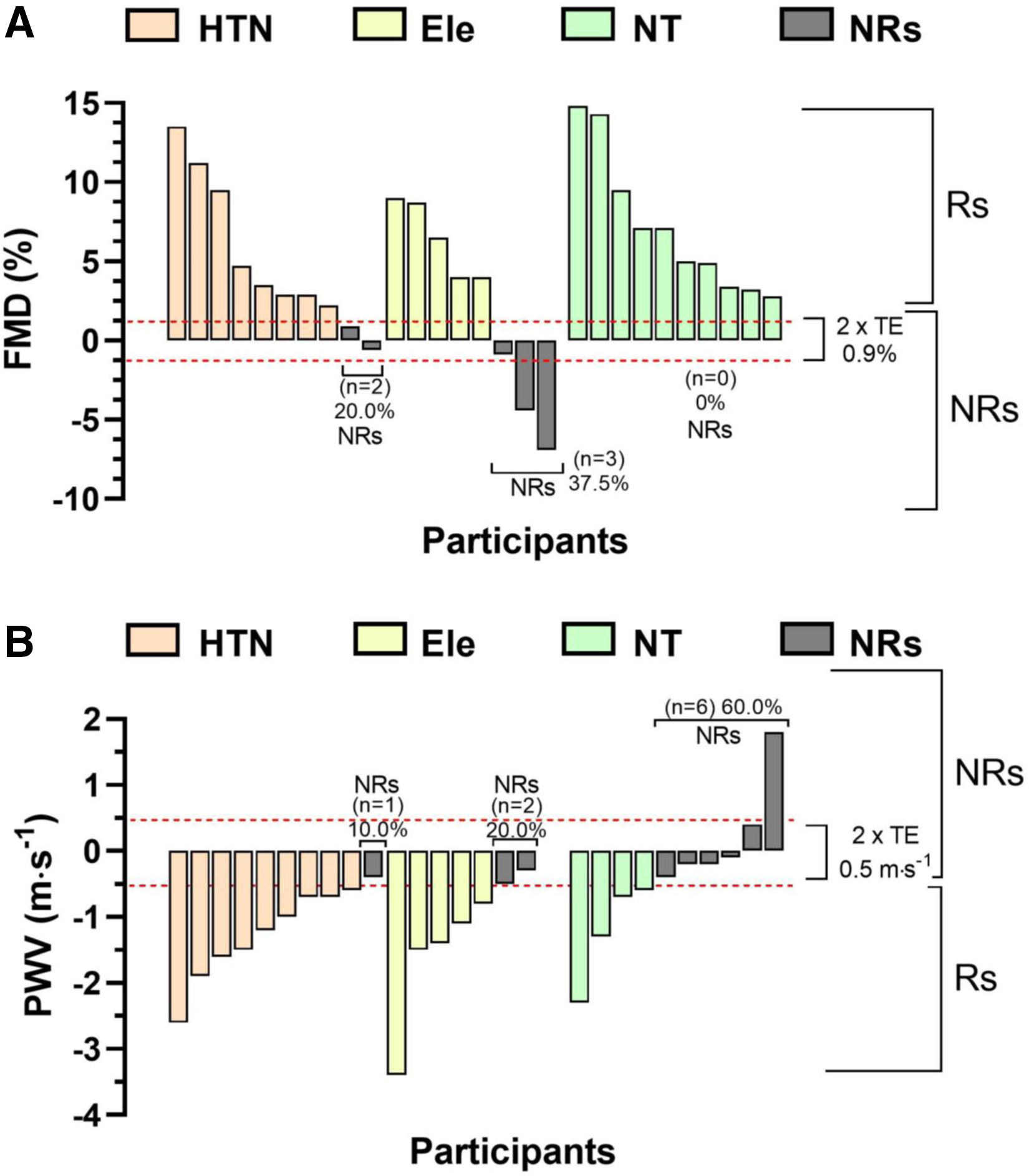
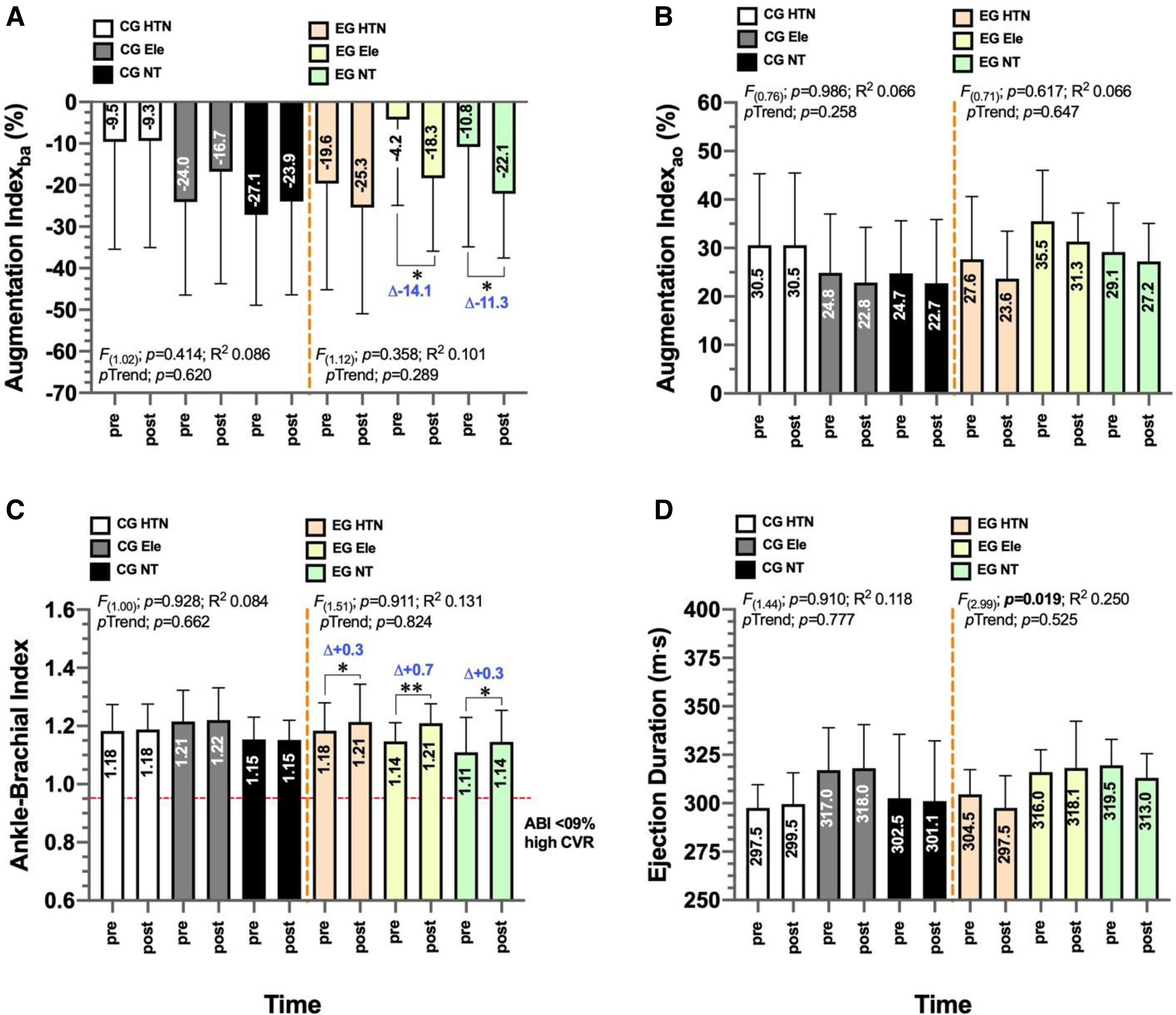
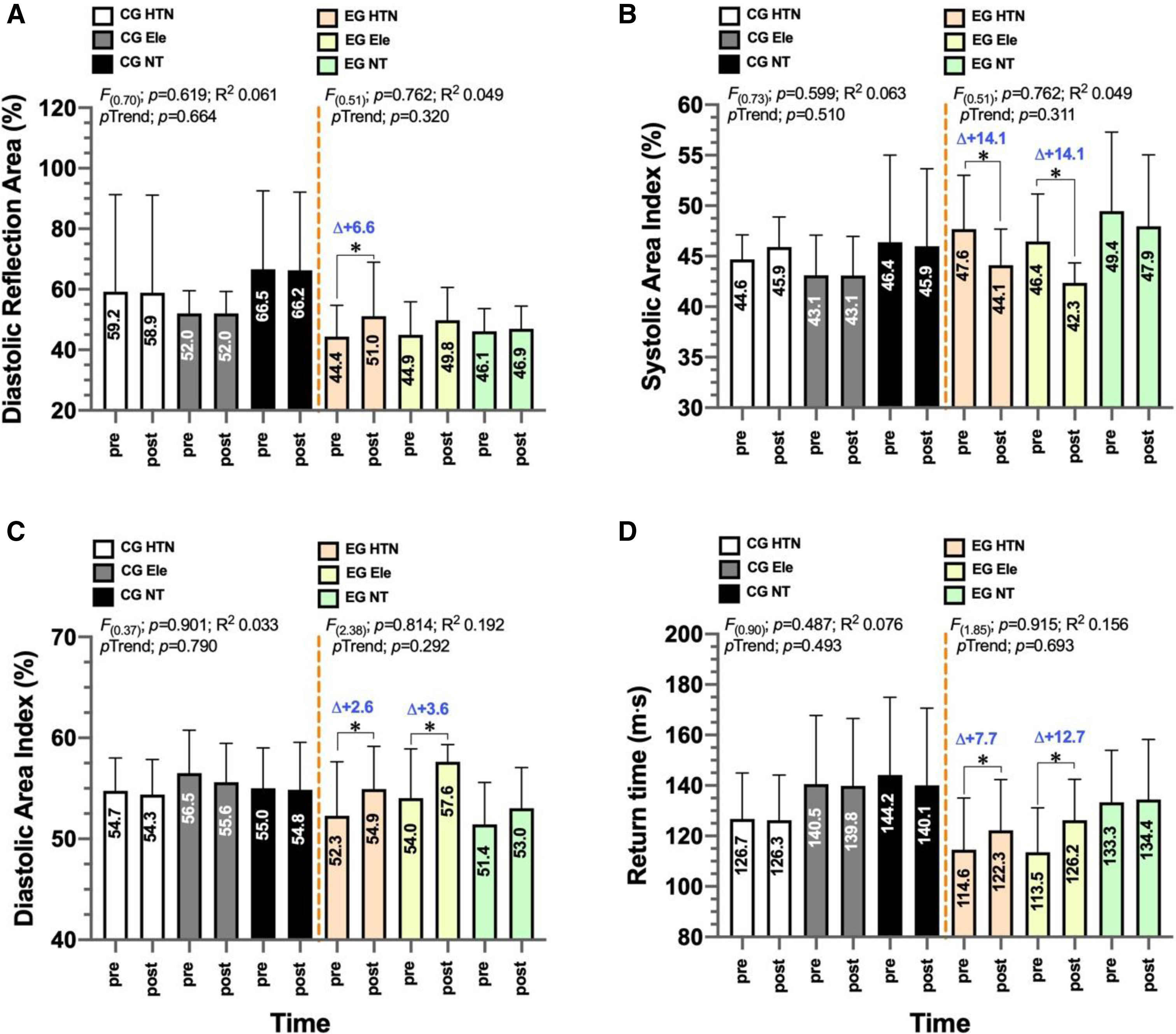
ResultsThe hypertensive exercise group exhibited a significant increase in flow mediated dilation (Δ+7.7%; p=0.003) and a reduction in pulse wave velocity (Δ−1.2ms−1; p<0.0001). The normotensive exercise group also showed a significant increase in flow mediated dilation (Δ+8.4%, p=0.002).
ConclusionThe six-week concurrent exercise using high-intensity interval plus resistance training protocol, characterized by its clinical time-efficiency, was effective in improving endothelial function, as demonstrated by increased flow mediated dilation, and in reducing arterial stiffness, indicated by decreased pulse wave velocity.
Examinar los efectos de seis semanas de ejercicio combinado usando ejercicio interválico y de fuerza en el flujo mediado por dilatación y velocidad de onda de pulso en sujetos hipertensos, con presión elevada y normotensos. Secundariamente, analizar la variabilidad interindividual al ejercicio.
MétodosEstudio clínico aleatorizado y controlado desarrollado en 60 adultos distribuidos en seis grupos: tres grupos control de hipertensos, presión elevada y normotensos, y otros tres grupos experimentales de hipertensos, presión elevada y normotensos, cada uno incluyendo n=10 sujetos. Los participantes desarrollaron seis semanas de ejercicio combinado usando ejercicio interválico y de fuerza. Las mediciones vasculares de flujo mediado por dilatación, velocidad de onda de pulso y otras evaluaciones vasculares secundarias se desarrollaron antes y después de la intervención.
ResultadosEl grupo ejercicio de hipertensos mostró un incremento significativo del flujo mediado por dilatación (Δ+7.7%; p=0,003) y una reducción significativa de la velocidad de onda de pulso (Δ−1.2 m s-1; p<0,0001). El grupo ejercicio de normotensos también mostró un incremento significativo en el flujo mediado por dilatación (Δ+8.4%, p=0,002).
ConclusiónSeis semanas de un programa tiempo-eficiente de ejercicio combinado usando ejercicio interválico y de fuerza mejoran la función endotelial mediante el incremento del flujo mediado por dilatación y reducen la rigidez arterial mediante la velocidad de onda de pulso.