Hypertension (HTN) is the most frequent cause of subcortical vascular brain injury (VBI) and its cognitive consequences. The aims were to show the usefulness of the Clock Drawing Test (CDT) to detect cognitive impairment in hypertensive patients and to compare it with the Mini-Mental Test (MMSE).
MethodsA subset of hypertensive patients of the Heart-Brain Study in Argentina was included. Demographic characteristics, vascular risk factors, blood pressure (BP) and schooling level were recorded. The MMSE and CDT tests were used for neurocognitive assessment and Hospital Anxiety Depression scale (HAD) for mood disorder evaluation.
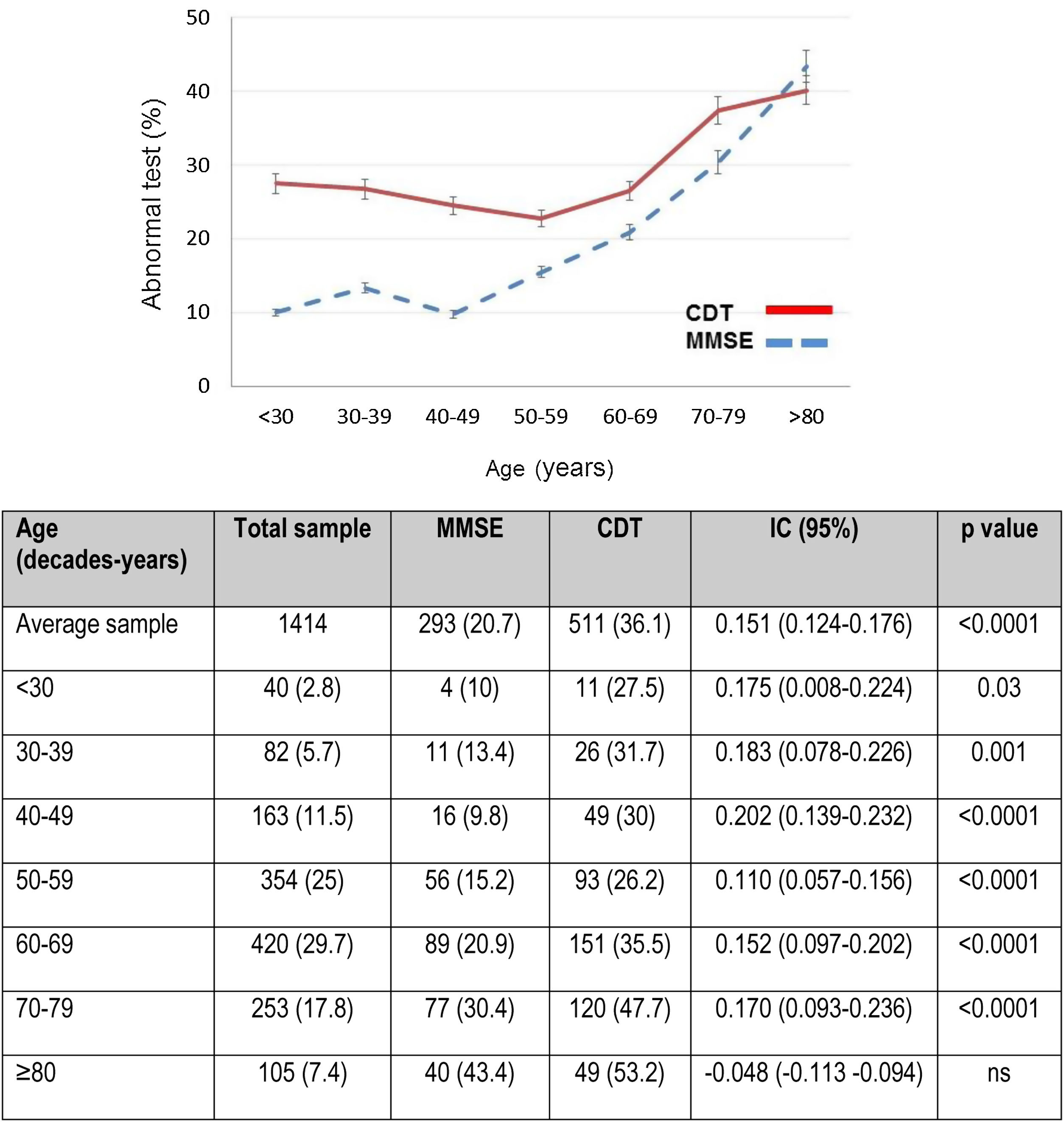
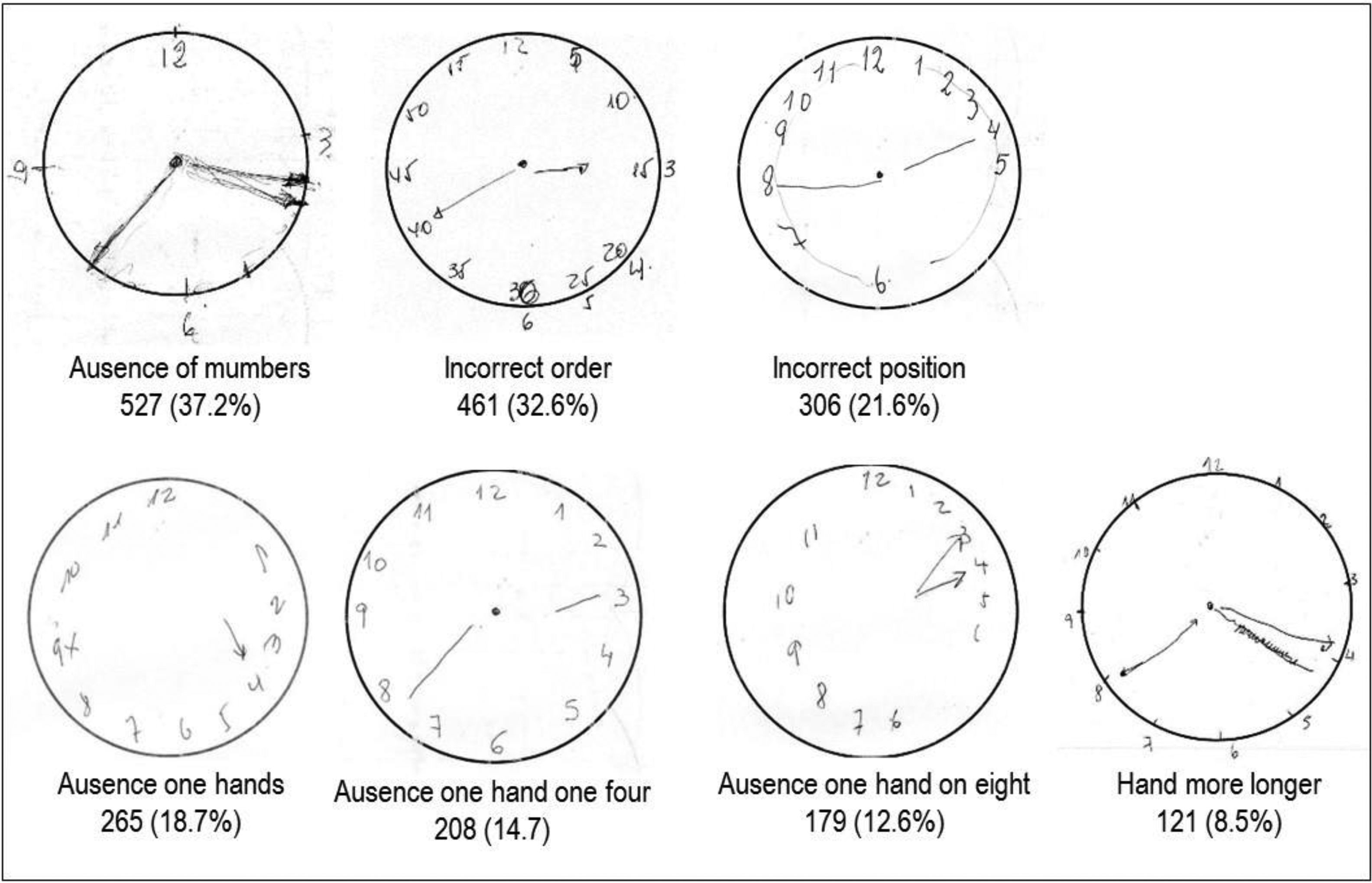
Results1414 hypertensive patients (age 59.7±13.8 years, female (62.3%). The prevalence of cognitive impairment was 20.7% (using MMSE) and 36.1% (using CDT). Among hypertensive patients with normal MMSE (>24) 29.3% had cognitive impairment (abnormal CDT). The CDT was associated with level of education but not with age or mood status.
ConclusionsThe CDT is a useful screening tool to detect hypertension-mediated brain damage earlier (especially in midlife) and is more sensitive than MMSE.
La hipertensión es la causa más frecuente de lesión cerebral vascular subcortical y de sus consecuencias cognitivas. El objetivo de este estudio fue mostrar la utilidad del Test del dibujo del reloj (TDR) para detectar el deterioro cognitivo en pacientes hipertensos y compararlo con el test Mini-mental statement examination (MMSE).
MétodosSe incluyó a un subconjunto de pacientes hipertensos del Estudio Corazón-Cerebro de Argentina. Se registraron las características demográficas, los factores de riesgo vasculares, la presión arterial y el nivel educativo. Se utilizaron TDR y MMSE para la evaluación neurocognitiva, y la escala Hospital Anxiety Depression (HAD) para evaluar los trastornos emocionales.
ResultadosSe evaluaron 1.414 pacientes hipertensos (edad 59,7±13,8años; mujeres, 62,3%). La prevalencia de deterioro cognitivo fue del 20,7% (utilizando MMSE) y del 36,1% (utilizando TDR). Entre los pacientes hipertensos con MMSE normal (>24) el 29,3% tenían deterioro cognitivo (TDR anormal). Se asoció el TDR al nivel de formación, pero no a la edad ni al estado emocional.
ConclusionesEl TDR constituye una herramienta de cribado útil para detectar tempranamente el daño cerebral mediado por hipertensión (especialmente en la mediana edad), con mayor sensibilidad que el MMSE.