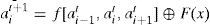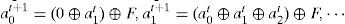A novel optical encryption method is proposed in this paper to achieve 3-D image encryption. This proposed encryption algorithm combines the use of computational integral imaging (CII) and linear-complemented maximum-length cellular automata (LC-MLCA) to encrypt a 3D image. In the encryption process, the 2-D elemental image array (EIA) recorded by light rays of the 3-D image are mapped inversely through the lenslet array according the ray tracing theory. Next, the 2-D EIA is encrypted by LC-MLCA algorithm. When decrypting the encrypted image, the 2-D EIA is recovered by the LC-MLCA. Using the computational integral imaging reconstruction (CIIR) technique and a 3-D object is subsequently reconstructed on the output plane from the 2-D recovered EIA. Because the 2-D EIA is composed of a number of elemental images having their own perspectives of a 3-D image, even if the encrypted image is seriously harmed, the 3-D image can be successfully reconstructed only with partial data. To verify the usefulness of the proposed algorithm, we perform computational experiments and present the experimental results for various attacks. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed encryption method is valid and exhibits strong robustness and security.
Information security is becoming more and more important with the progress in the exchange of information for electronic commerce. Many applications, such as military image databases and medical imaging systems [1] require a reliable and robust security system to store and transmit digital images. The new technologies of image encryption [2] and watermarking [3-4] have been advocated by many specialists as the best solution for such multimedia security problems. The security requirements of digital images have led to the development of effective encryption techniques. Conventional encryption methods such as DES algorithm, IDEA, Blowfish and RSA are not suitable for bulky data such as digital images, because they require long computation processes and have some other issues, such as an inability to handle various data formats [5].
In recent years, many researchers have discovered that 3-D image encryption techniques show great potential in the field of 3-D information processing [6]. 3-D image encryption has the virtues of an inherent parallel-processing capability and strong robustness. Some 3-D image encryption is performed by Fourier transform (FT) [7] or fractional Fourier transform (FRT) [8, 9]. However, the conventional hologram-based image encryption and deception method has been limited in practical applications because of its optical system is complex, it lacks flexibility and it requires high-performance optoelectronic devices and systems [10]. Furthermore, FT and FRT-based encryption requires higher computation power and special treatment to handle non-integer values or complex values.
To address the above-mentioned problems, in our work, we propose a novel 3-D image encryption algorithm that combines the use of computational integral imaging (CII) and MLCA.
Integral imaging was a 3-D imaging and display technique invented in 1908 by G. Lippmann [11]. Figure 1 shows the basic concept of the II system, composed of a pickup part and a display part. In the pickup part, a 3-D object is recorded on a charge-coupled device (CCD) in the form of a 2-D image array, called an elemental image array (EIA) [12-14], by means of a lens array. The lens array consists of a number of small identical lenses, called elemental lenses or lenslets. The recorded elemental images (EIA) contain parallax information, so each elemental image has a different view observed from a different viewing direction. In the display part, the EIA are reconstructed through the lenslet array. According to the principle of II, in 3-D encryption based on II, this hologram-like 3-D property of EIA could support a robust reconstruction of the 3-D image during attacks. Techniques based on II in the field of information security also have important benefits, as they enable the digital storage, transmission, and decryption of encrypted data.
However, images encryption based on the conventional optical II, the quality of the reconstructed image is degraded due to the diffraction and limitations of the physical devices. To overcome these problems, the computational integral imaging reconstruction (CIIR) [15] technique was proposed, In the CIIR, the elemental images are digitally processed by use of a computer where 3D images can be easily reconstructed at a desired reconstruction plane without optical devices.
Cellular automata (CA) [16-18] compose a dynamical system in which space and time are discrete. The linear maximum length CA (MLCA) [19-21] is n-bit CA, which can generate sequences having a period of 2n-1. MLCA is introduced into encrypting images because it has the following advantages:
- (i)
Error-free encrypting and decrypting interactions.
- (ii)
The number of CA evolution rules is very large. Hence, the key space is extremely large.
- (iii)
Recursive CA substitution only requires integer arithmetic (XOR) logic operations, which simplifies the computation burden.
In this paper, to improve the quality and security of reconstructed 3D image, we propose a new 3D image encryption algorithm using CII and MLCA. In the proposed algorithm, a 3-D image is recorded as a 2-D EIA by using a lenslet array, and the recorded 2-D EIA are enciphered by MLCA. The decryption process and the encryption process are exact opposites. The 2-D EIA are recovered by the inverse MLCA process, and the 3-D object is subsequently reconstructed using the recovered EIA via computational integral imaging reconstruction (CIIR). The quality of the reconstructed images using CIIR is better than that of the images reconstructed using all optical II. This is because CIIR is free of diffraction and device limitations. To show the usefulness of the proposed algorithm, preliminary experiments are performed, and the experimental results are analyzed.
2Proposed MethodIn this paper, we propose a 3-D image encryption algorithm that combines CII and MLCA. The algorithm is composed of four different processes, as shown in Figure 2.
2.1Pickup process of CIIIn the pickup process of CII, the information of the rays originating from a 3-D object are spatially sampled through use of a lenslet array and are recorded by a 2-D image sensor. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we have constructed an experimental system with a lenslet array consisting of 30×30 lens elements. The pitch of each of these array is 1.08×1.08mm, and the focal length of each lenslet is 3mm. We define g as the gap between the lenslet array and the pickup device and l as the distance between the object and the lenslet array. The pickup process is shown schematically in Figure 3. A 3-D object is located at a distance l and is recorded as elemental images by using a CCD camera. Here, g=3mm, l=27mm.
2.2Encryption algorithm using MLCA.An n-cell binary CA is an array of n registers. The CA state at time t is denoted as A(t)=[a0(t),a1(t),a2(t),…,an-1(t)]′, where ai(t)∈GF(2). The evolution operator Г performs the following operation:.A(t+1)=Г(At). Figure 4 shows an 8-cell hybrid CA and the transform Г={R90,R150,R90,R90,R150,R90,R150,R150}.
The states of a CA during each discrete time step can be successively sampled to form a pseudorandom n-cell sequence. We only consider CA with null boundary conditions where the leftmost and rightmost cell is zero (see Figure 4). The next state can be described by the matrix operation on the state of a CA at time t:
Here, T is called the state-transition matrix. A state A0 is called a cycle state if there exists an integer p such that
The smallest integer p that satisfies Eq. (2) is called the cycle length, and if the length of the n-cell CA is 2n−1, it is called a linear MLCA (LMLCA). Figure 4 is an L-MLCA. The state-transition matrix of the n-cell CA is a tri-diagonal matrix block described in Eq. (3).
Here, we only consider a 2-state, 3-site CA. When the i-th cell ai=0, the transition rule R90 is used, where i=(0, 1, 2,…, n-1). In contrast, when ai=1, the transition rule R150 is applied. The sequence {a0, a2,…, an-1} as the 90/150 CA transformation Г. The linear 90/150 CA rules are listed below:
The complemented MLCA (C-MLCA) is based on the L-MLCA and the evolution of C-MLCA can be expressed as:
Here, f represents the local transition function, and F is the complemented vector. For the above example 8-cell hybrid CA transformation rule Г={R90,R150,R90,R90,R150,R90,R150,R150} (see Figure 4), the next state of C-MLCA can be expressed as:
In this paper, we propose a cipher key CA from the combined use of L-MLCA and C-MLCA. The principle of the algorithm is performing the logic XOR operation on L-MLCA and C-MLCA. This CA is called LC-MLCA.
The proposed 3-D image encryption scheme using MLCA, which is illustrated in Figure 5, consists of two steps of operations:
Step1. Decompose the 3-D image to 2-D images. In the CII pickup process, the 3-D object is spatially sampled through the use of a lenslet array and recorded by a 2-D image CCD sensor. Here, the distances l and g are 27mm and 3mm, respectively.
Step2.2-D elemental images encryption process. Apply the MLCA basic image and obtain the 2-D encrypted image by performing the logic XOR operation on the 2-D elemental images.
2.3Decryption algorithm using MLCA.Image decryption is the inverse process of encryption. We can recover the elemental image by the MLCA key through the decryption process, as shown in Figure 6.
Because the MLCA-based encryption algorithm is a lossless cryptographic system, the performance of the proposed algorithm can be dramatically improved relative to the conventional transform DCT-based lossy data compression encryption technique.
2.4Reconstruction of the 3-D image in computational integral imaging.To reconstruct 3-D images in II, we use a computational integral imaging reconstruction (CIIR) technique as shown in Figure 7 (a). A commonly used technique, CIIR computationally reconstructs 3-D images by inversely mapping EIA through a virtual pinhole array. The quality of the synthesized image using CIIR is superior to the images reconstructed using all optical II. This improved performance of the CIIR is the lack of diffraction effects and device limitations. Figure 7 illustrates the operational principle of the CIIR technique. First, the EIA are projected inversely through each virtual pinhole, and the projected elemental images are magnified by a factor of δ=l/g. The enlarged EIA are then overlapped and summed at the corresponding pixels of the reconstructed image plane. A set of depth-dependent 3-D images can be reconstructed along the output plane, as shown in Figure 7 (b). The reconstructed 3-D images are different at different distances l. As shown in Figure 7 (b), the 3-D image is reconstructed clearly at distance l=27mm, where the object was originally located. However, the 3-D images are not clearly reconstructed at the other distances. This principle provides the proposed algorithm with a function for the 3-D image encryption.
3Simulation and discussionIn the experiment, ‘die’ and ‘foot’ toys are used as 3-D objects, as shown in Figure 8 (a). The sizes of the ‘die’ and ‘foot’ were 1×1×1cm3 and 0.5×0.5×0.2cm3, respectively. The objects are located at l=27mm. For these 3-D objects, we performed the experiments and analyzed the performance of the encryption to verify the functionality of the proposed encryption algorithm.
3.1Statistical analysisAn image-histogram illustrates how the pixels in an image are distributed by graphing the number of pixels at each gray intensity level. We have calculated and analyzed the histograms of several ciphered images as well as their original images. One example of such histogram analysis is shown in Figure 8. As shown in Figure 8, the horizontal patterns of the ciphered images based on LMLCA and C-MLCA, provide hints that can be used to attack the system. However, the ciphered image based on LC-MLCA is invisible and secure, as the histogram of the ciphered image is nearly uniformly distributed and significantly different from that of the original EIA.
Histograms and ciphered images using MLCA: (a) the original 3-D image, the EIA and the histogram of the EIA, (b) the LC-MLCA basic image, the encrypted image using LC-MLCA and the histogram of the encrypted image, (c) and (d) the L-MLCA and C-MLCA, respectively, of the basic images and the corresponding encrypted images and histograms.
To demonstrate the performance of the scheme, we also use the peak peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and bit-correct ratio (BCR) to evaluate the quality of the original EIA and the recovered EIA. If the PSNR and BCR have a high values, then there is significant similarity between the decrypted image and the original image. In contrast, if the PSNR and BCR have low values, then the encrypted image is significantly dissimilar to the original image.
Here, in the reconstructed process through computer simulations, the ciphered image based on LC-MLCA is used as the test image. Figure 9 (b) shows the EIA recovered from the ciphered image, which is decrypted by using the correct key of the LC-MLCA basic image. Figure 9 (c) indicates that no loss of data occurred between the original EIA and the recovered EIA. In the CIIR process, Figure 9 (d) shows the reconstructed 3-D image using the correct key. Figure 9 (e) and (f) show the reconstructed 3-D images using an incorrect key for L-MLCA and C-MLCA basic images, respectively.
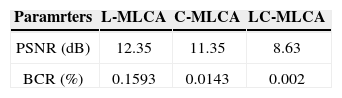
From Table 1, the calculated PSNR and BCR of the LC-MLCA encryption method are found to be 8.63 dB and 0.0002%. This performance analysis confirms that the LC-MLCA encryption method significantly more secure than the other two MLCA methods.
To further prove feasibility of the proposed scheme, we comparatively analyze the qualities of the reconstructed 3D images for two kinds of 3D imaging method based II, under the same conditions, the 3D image is reconstructed from the recovered EIA which produced by the proposed scheme and the conventional optical II-based scheme. Figure 10 shows the reconstructed 3D images based the two methods. By visually comparing the proposed reconstructed 3D image against the conventional methods, it is obviously that the reconstructed object plane of our scheme is more clearly reconstructed. Because CIIR is free diffraction and no optical devices needed.
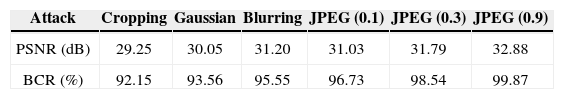
3.2Robustness AnalysisVariable attacks by image processing operations, including cropping, Gaussian noise, blurring and JPEG compression, have been performed on the proposed scheme. We only use the ciphered image based on LC-MLCA as the test image to determine the robustness against common noise attacks.
Figure 11 shows the recovered images are decrypted from the encrypted EIAs against the attack types of cropping, Gaussian noise, blurring, and Figure 12 shows the recovered images are decrypted from the encrypted EIAs against JPEG compression. In Table 2, the calculated PSNR and BCR values for the decrypted EIAs of Figure 11 and Figure 12 are presented. Our proposed method exhibits a high values of PSNR and BCR.
The reconstructed 3-D images are shown in Figure 13. The high image quality of reconstructed 3-D images confirmed that the proposed method exhibits strong robustness against cropping, Gaussian noise, blurring, and JPEG compression attacks.
Next, we comparatively analyze the characteristics of the robustness against some common attacks for three types of optical image encryption algorithms.
(1) Our proposed algorithm
We proposed a novel CII-based image encryption algorithm combined with linear-complemented MLCA. In the encryption procedure, a lenslet array first decomposes the image into an elemental image array (EIA) via the pick-up process of the II system. We encrypt the EIA with an encryption method based on linear-complemented MLCA.
(2) FT-based optical image encryption algorithm
Lin and Shen (2012) proposed a new FT-based encryption method. In the encryption procedure, different random amplitude masks (RAMs), which are placed into the reference arm, vertically admit the multiplexing capability. When decrypting one of the original images, a reference wave with the same incident angle as the wave encrypting the target image is used to illuminate the encrypted hologram with the insertion of a random amplitude mask, whose transmissivity is the reciprocal of that of the encrypting random amplitude mask in the reference arm.
(3) FRT-based optical image encryption algorithm
Jin and Yan (2006) proposed an optical image encryption based on a multichannel fractional Fourier-transform (FRT) and a double random-phase encoding technique. One can implement the fractional domain encoding for different parts of input images through the corresponding channels.
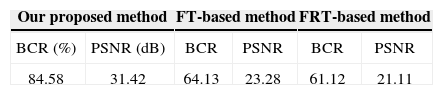
The gray image, Lena, with 256×256 pixels that is used as the test image, is shown in Figure 14 (a). Figure 14 (b)-(d) shows the Lena image encrypted by our proposed algorithm, the FT-based algorithm and the FRT-based algorithm; after 70% of pixels were cropped, the corresponding reconstructed images are shown in Figure 15 (a)-(c). The values of BCR and PSNR are listed in Table 3. The BCR and PSNR of our proposed method is 84.58% and 31.42 dB, respectively. The BCR and PSNR are 64.13% and 23.28 dB, respectively, for the FT-based method and 61.12% and 21.11 dB, respectively, for the FRT-based method. In other words, the BCR and PSNR of our proposed method exhibit an improvement of 31.25% and 37.70%, 35.82% and 48.94% compared to that of the FT-based and the FRT-based methods, respectively.
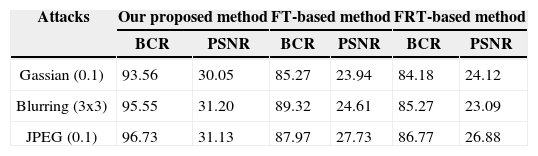
According to the analysis of the data in Table 4, the proposed method has a higher robustness against some of the most common attacks because the EIA array has multiple parallel elemental images, even if some of the EIA array data is lost by some data loss attacks, images can still be reconstructed with the remaining partial data. On the basis of the above data, we conclude that the proposed method exhibits higher robustness to attacks compared to conventional methods.
BCR, PSNR of The Decrypted Lena Image with Gaussian, Blurring, and JPEG Compression Attacks
| Attacks | Our proposed method | FT-based method | FRT-based method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCR | PSNR | BCR | PSNR | BCR | PSNR | |
| Gassian (0.1) | 93.56 | 30.05 | 85.27 | 23.94 | 84.18 | 24.12 |
| Blurring (3x3) | 95.55 | 31.20 | 89.32 | 24.61 | 85.27 | 23.09 |
| JPEG (0.1) | 96.73 | 31.13 | 87.97 | 27.73 | 86.77 | 26.88 |
In conclusion, a 3-D image encryption algorithm based on a combination of the CII and MLCA has been proposed. Compared with existing 3-D image encryption schemes, the new scheme exhibits high quality of reconstructed image because of CIIR is free of diffraction and device limitations. Furthermore, our proposed method is based on MLCA method; it exhibits no image information loss. These positive aspects make our proposed method a very good candidate for 3-D image encryption applications. Experiments and analysis have both demonstrated the feasibility and efficiency of the new algorithm.