Total hip arthroplasty (THA) and hemiarthroplasty are common treatments for severe hip joint disease. To predict the probability of re-admission after discharge when patients are hospitalized will support providing appropriate health education and guidance.
MethodsThe research aims to use logistic regression (LR), decision trees (DT), random forests (RF), and artificial neural networks (ANN) to establish predictive models and compare their performances on re-admissions within 30 days after THA or hemiarthroplasty. The data of this study includes patient demographics, physiological measurements, disease history, and clinical laboratory test results.
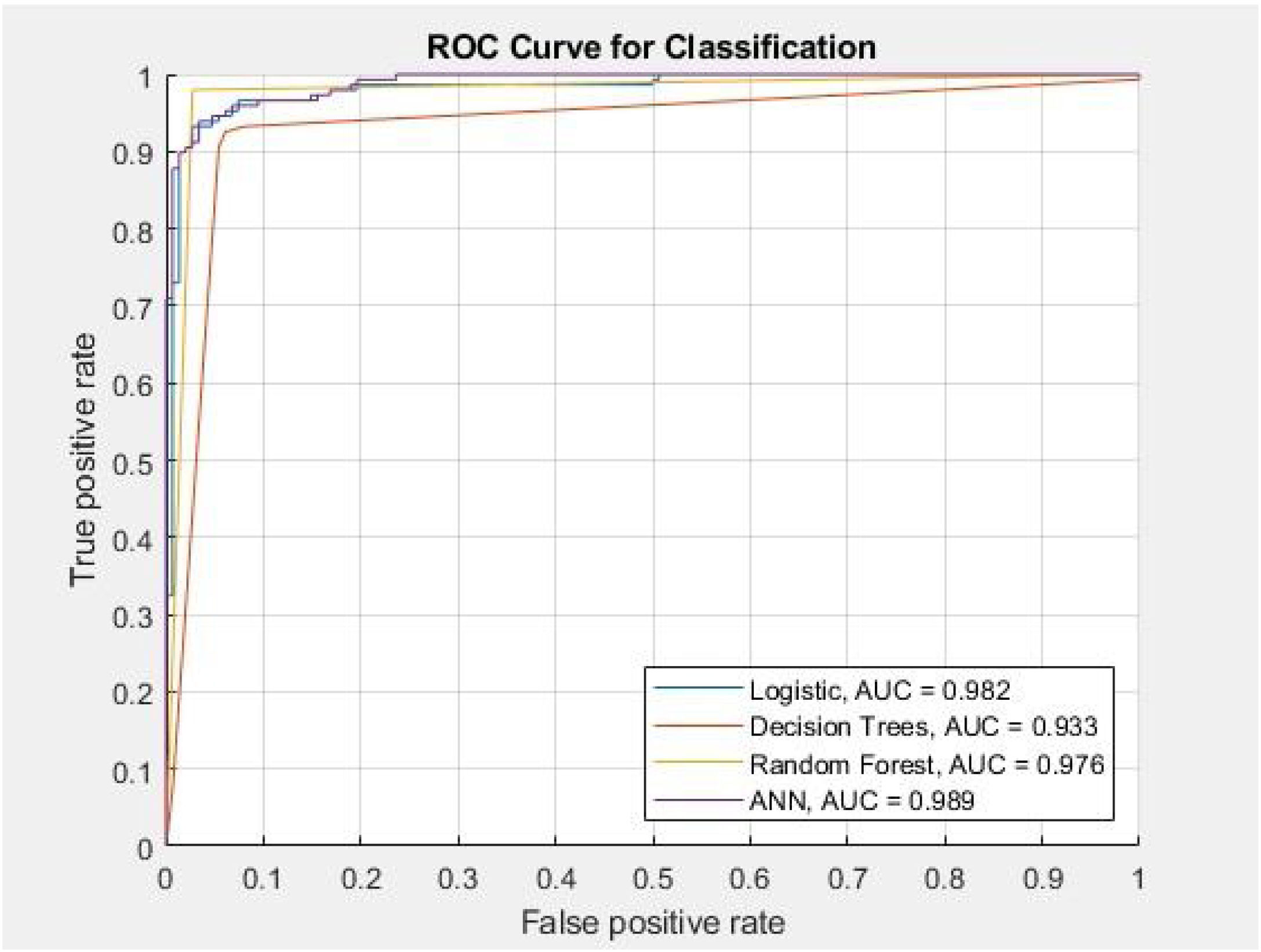
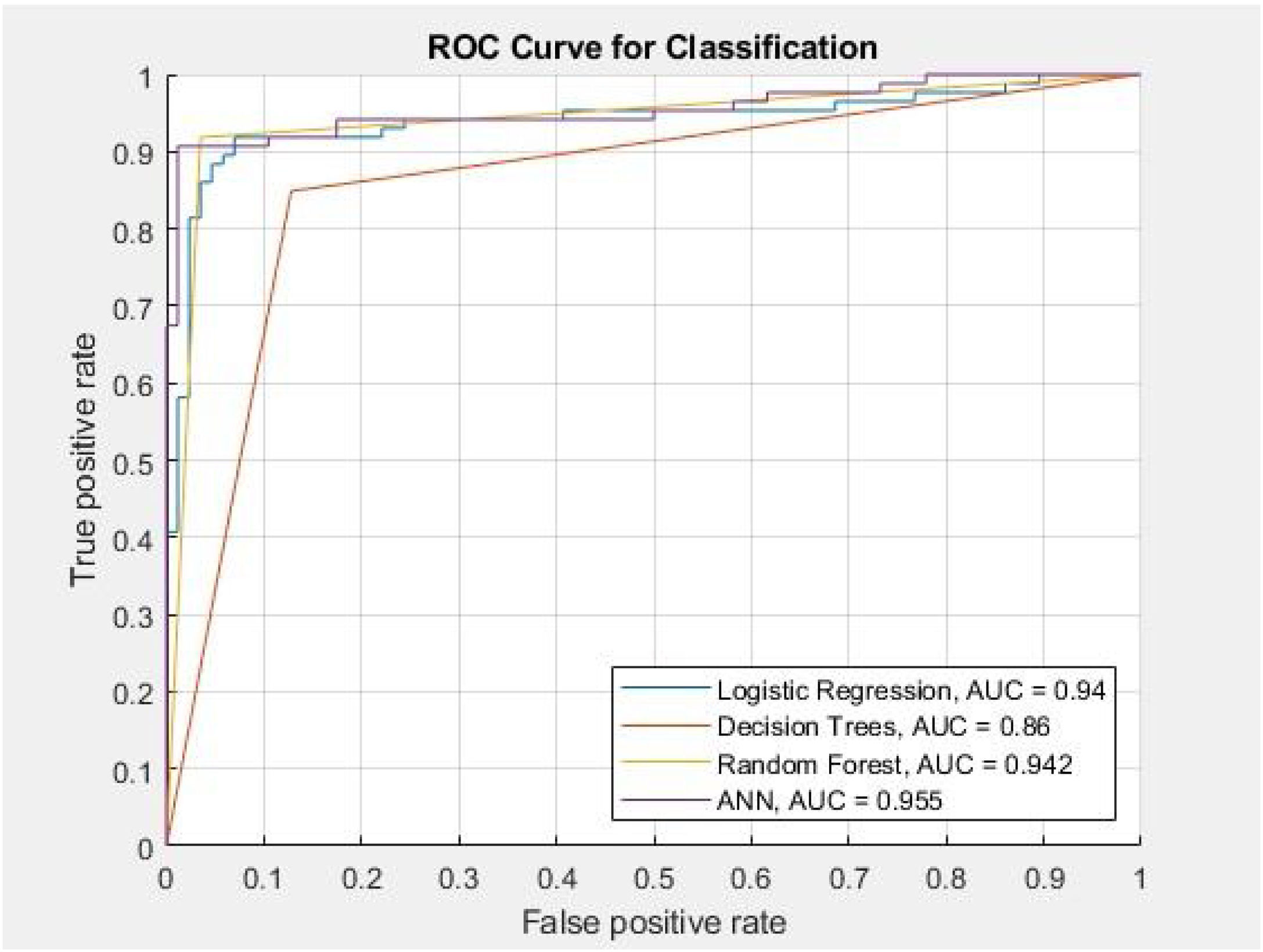
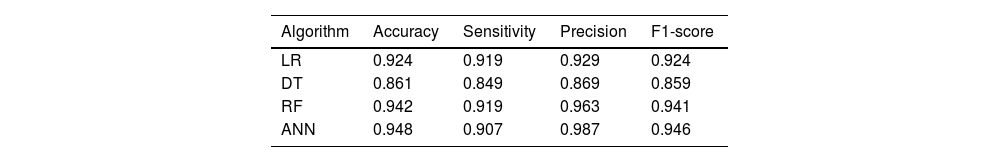
ResultsThere were 508 and 309 patients in the THA and hemiarthroplasty studies respectively from September 2016 to December 2018. The accuracies of the four models LR, DT, RF, and ANN in the THA experiment are 94.3%, 93.2%, 97.3%, and 93.9%, respectively. In the hemiarthroplasty experiment, the accuracies of the four models are 92.4%, 86.1%, 94.2%, and 94.8%, respectively. Among these, we found that the RF model has the best sensitivity and ANN model has the best area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) score in both experiments.
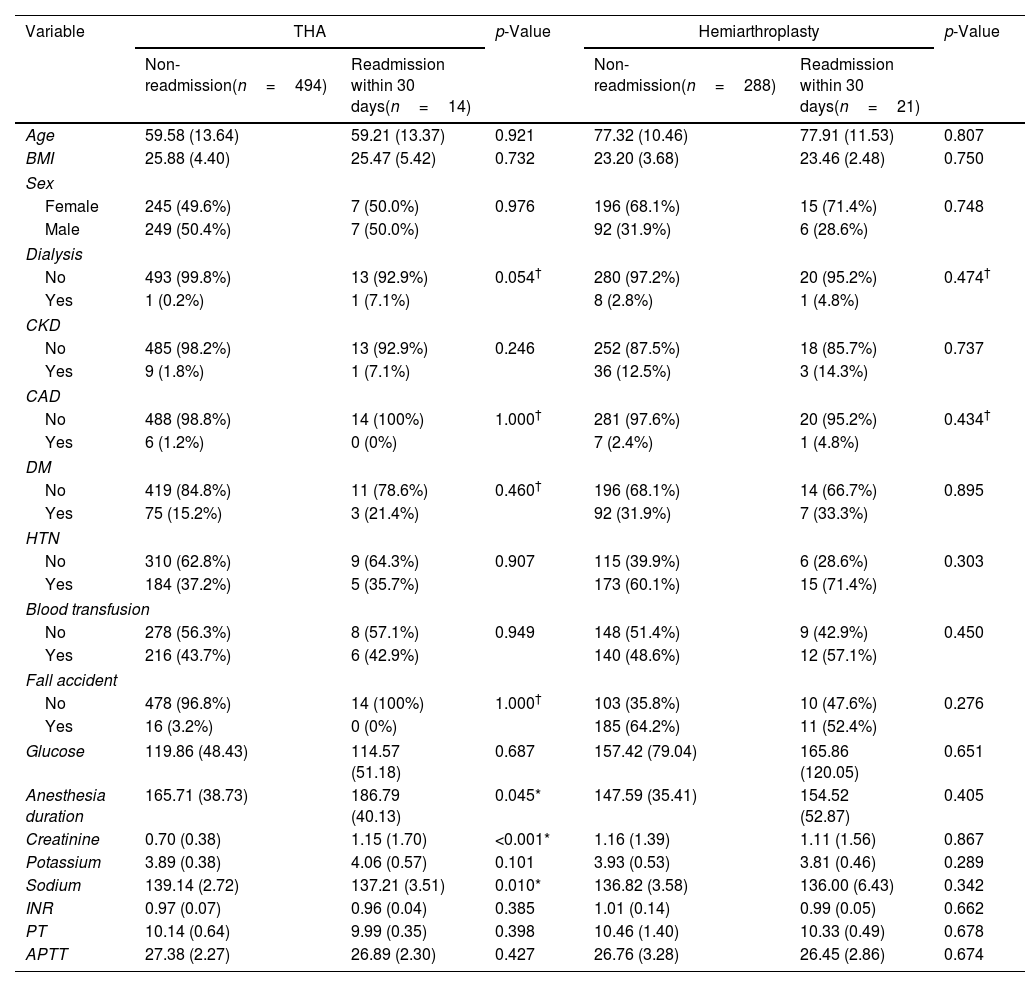
ConclusionsThe THA experiment confirmed that the performance of the RF model is better than the other models. The key factors affecting the prognosis after THA surgery are creatinine, sodium, anesthesia duration, and dialysis. In the hemiarthroplasty experiment, the ANN model showed more accurate results. Poor kidney function increases the risk of hospital re-admission. This research highlights that RF and ANN model perform well on the hip replacement surgery outcome prediction.
La artroplastia total de cadera (total hip arthroplasty [THA]) y la hemiartroplastia son tratamientos comunes para tratar problemas graves de la articulación de la cadera. El poder predecir la posibilidad de reingreso de un paciente contribuirá a poder ofrecerle una adecuada educación y orientación sanitaria durante su hospitalización.
MétodosEsta investigación llevó a cabo Regresiones Logísticas (Logistic Regression [LR]), Árboles de Decisión (Decision Trees [DT]), Bosques Aleatorios (Random Forests [RF]) y Redes Neuronales Artificiales (Artificial Neural Networks [ANN]) a fin de establecer modelos predictivos y comparar su eficacia en los reingresos durante los 30 días posteriores a la THA o la hemiartroplastia. El presente estudio engloba los datos demográficos, las mediciones fisiológicas, los antecedentes clínicos y los resultados de los análisis clínicos de los pacientes.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 508 pacientes de THA y 309 de hemiartroplastia desde septiembre de 2016 hasta diciembre de 2018. El índice de precisión mostrado por los cuatro modelos LR, DT, RF y ANN en el experimento de THA alcanzó respectivamente el 94,3%, el 93,2%, el 97,3% y el 93,9%. En el experimento de hemiartroplastia, el índice de precisión de los cuatro modelos fueron del 92,4%, del 86,1%, del 94,2% y del 94,8%, respectivamente. Entre estos, descubrimos que el modelo RF mostró la mejor sensibilidad y el modelo ANN mostró la mejor puntuación acerca del área bajo la característica operativa del receptor (area under the receiver operating characteristic [AUROC]) en ambos experimentos.
ConclusionesNuestra experiencia de THA confirmó que el rendimiento de RF era mejor que el de los demás modelos. Los factores clave que inciden en el pronóstico tras la cirugía de THA son la creatinina, el sodio, la duración de la anestesia y la diálisis. En los resultados en la hemiartroplastia, el modelo ANN mostró resultados más precisos. La alteración del funcionamiento renal incrementa el riesgo de reingreso en el hospital. La presente investigación subraya que los modelos RF y ANN funcionan bien con respecto a la predicción del resultado de la cirugía de reemplazo de cadera.