This quasi-experimental, non-randomized study described the process of implementing ISO 7101 subclause 8.10.5 Health literacy in specialty consultations, then determined the effects of implementation on patient general health literacy scores and perceptions of quality of care.
MethodImplementation steps were outlined, nurses were trained and used a standardized health literacy checklist with patients. The HLS19-Q12 was used to calculate patients’ general health literacy scores pre- and post-implementation of subclause 8.10.5. Paired samples t-test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test determined relationships between implementation, health literacy score, and quality of care perceived.
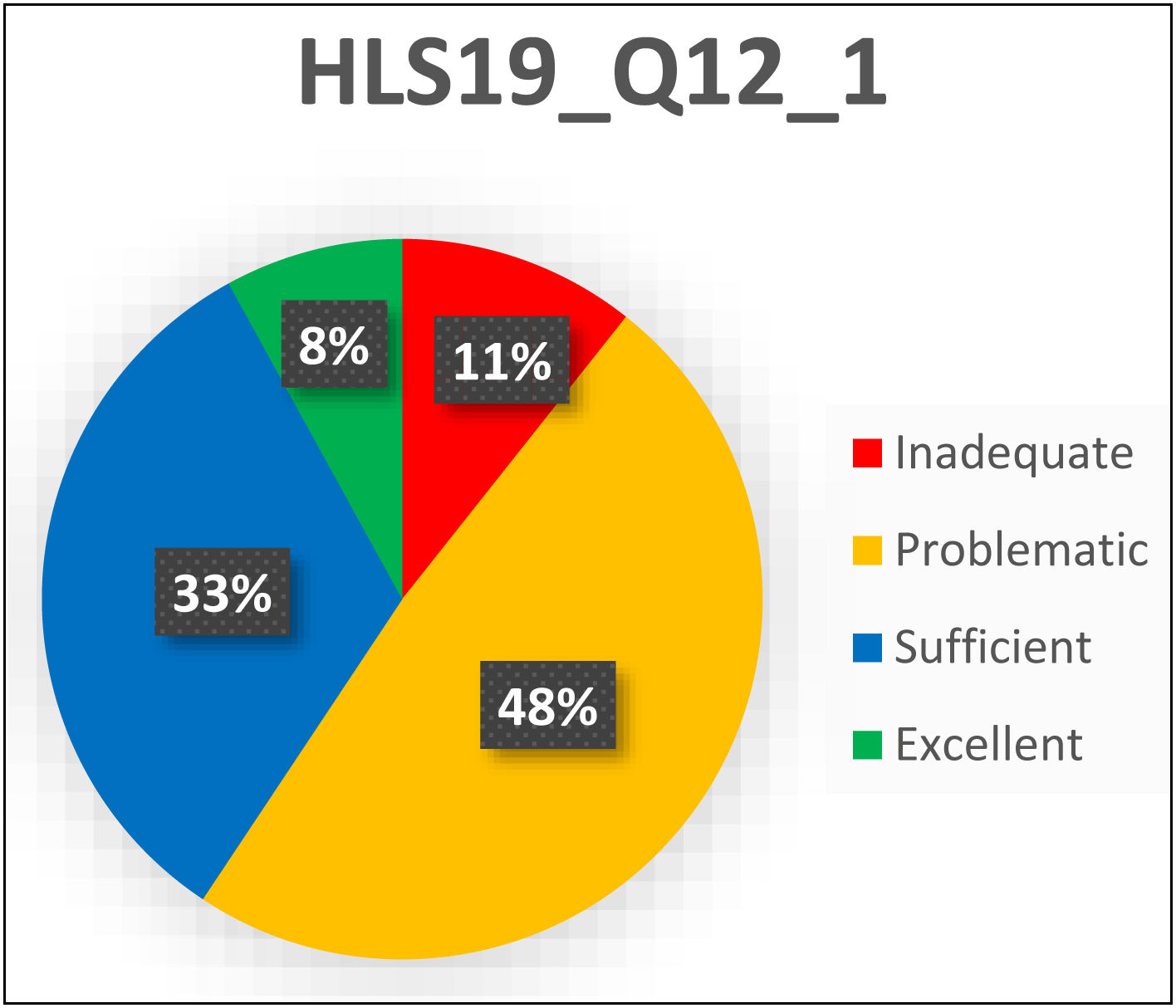
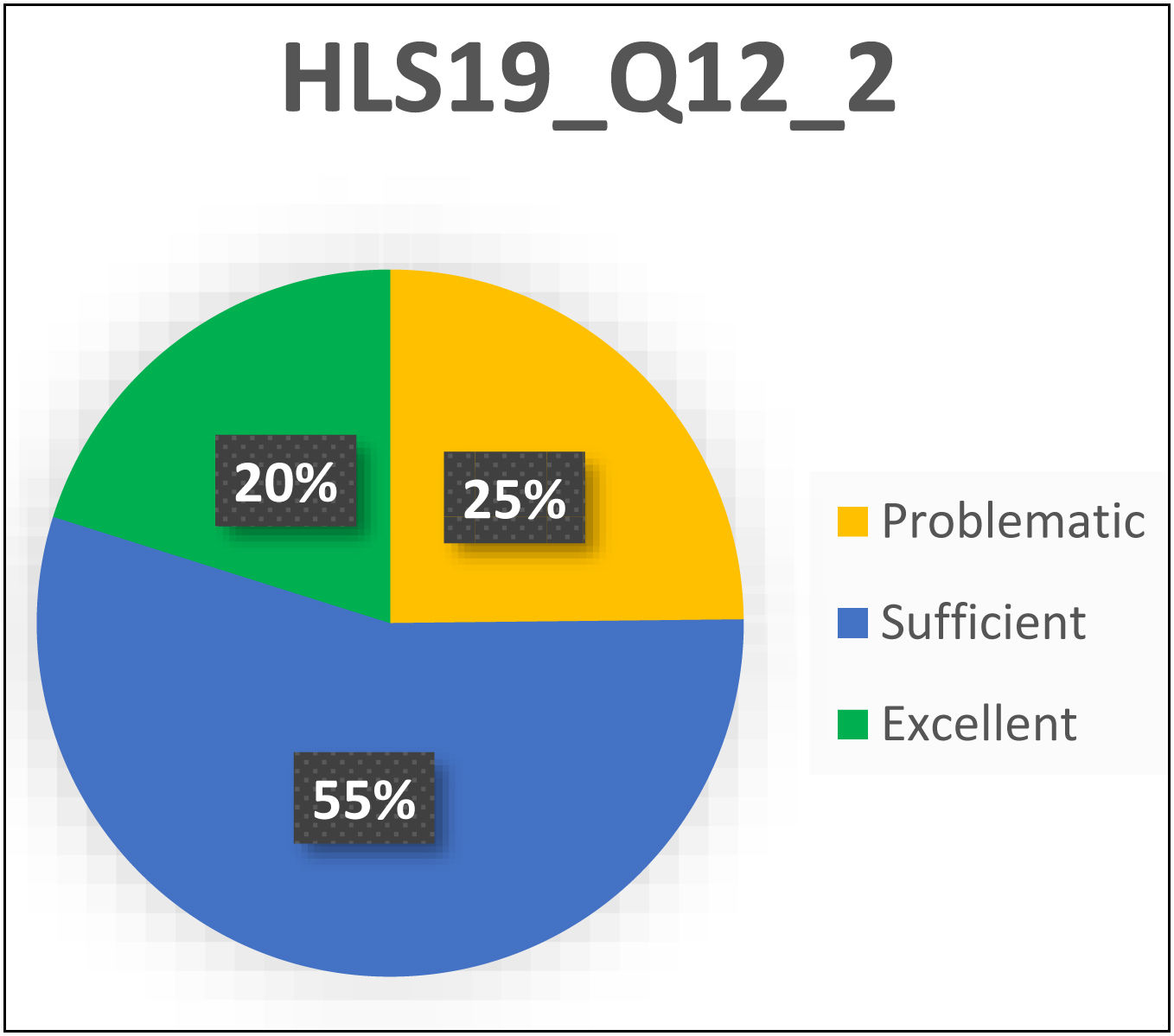
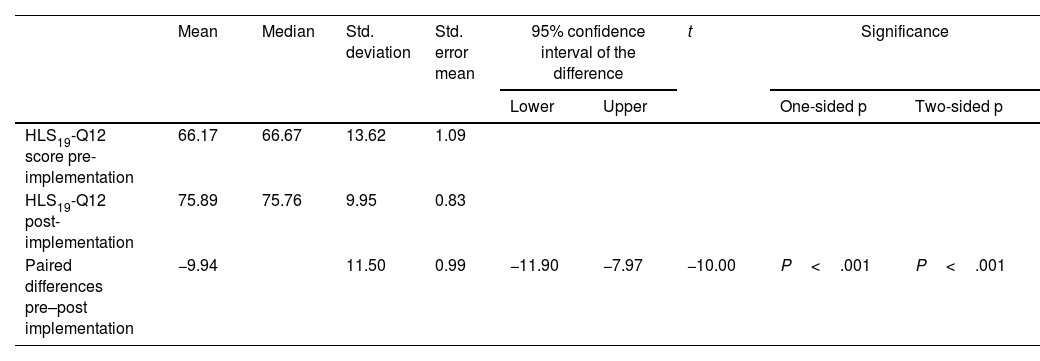
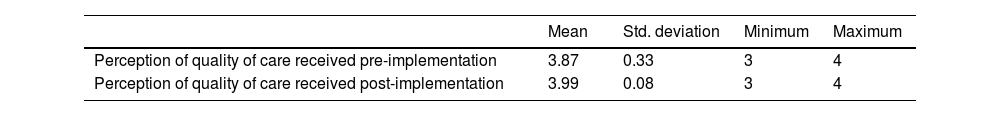
ResultsMean general health literacy scores increased post-implementation from 66.35 to 76.29, as did the mean score of perception of quality of care received (M=3.87 to M=3.99). Wilcoxon test for both variables was significant (P<.001), and effect size was large (d≥0.8).
ConclusionsImplementation of ISO 7101, subclause 8.10.5 Health literacy had a positive, statistically significant impact on patient general health literacy scores and perceptions of quality of care. This is valuable information for healthcare management decision makers as they implement new standards and seek to improve patient health outcomes.
Describir el proceso de implementación de la subcláusula 8.10.5 de la norma ISO 7101 en consultas especializadas, determinar sus efectos en las puntuaciones de alfabetización sanitaria del paciente y en las percepciones de la calidad de la atención.
MétodoSe diseñó la implementación, se capacitó a las enfermeras y se utilizó una lista de verificación estandarizada. Se empleó el HLS19-Q12 para cuantificar el efecto de la norma antes y después de la implementación. Se utilizaron muestras pareadas: la prueba t y la prueba de rangos con signo de Wilcoxon para determinar las relaciones entre la implementación, la puntuación de alfabetización sanitaria y la calidad de la atención percibida.
ResultadosLas puntuaciones medias de alfabetización general sanitaria aumentaron de 66,35 a 76,29, al igual que la puntuación media de la percepción de la calidad de la atención recibida (M=3,87 a M=3,99). La prueba de Wilcoxon para ambas variables fue significativa (p<.001) y el tamaño del efecto fue grande (d≥0,8).
ConclusionesLa norma tuvo un impacto positivo y estadísticamente significativo en las puntuaciones de alfabetización sanitaria y en las percepciones de la calidad de la atención. Esta información sirve en la toma de decisiones en la gestión de la atención médica al implementar nuevos estándares para mejorar los resultados de salud de los pacientes.