In the U.S., sepsis afflicts 1.7 million adults, causing 270,000 deaths each year. Early detection of sepsis could decrease the number of deaths by 92,000 annually and decrease hospital expenditures by 1.5 billion USD. Few prior studies and reviews have presented a holistic understanding of the relationship between machine learning and existing process improvement measures. This study, in addition to discussing machine learning and existing process improvements measures, elaborates on the disadvantages and the barriers to integrating machine learning into the clinic. This article synthesizes previous studies to educate healthcare professionals on effectively managing sepsis by leveraging the benefits of machine learning.
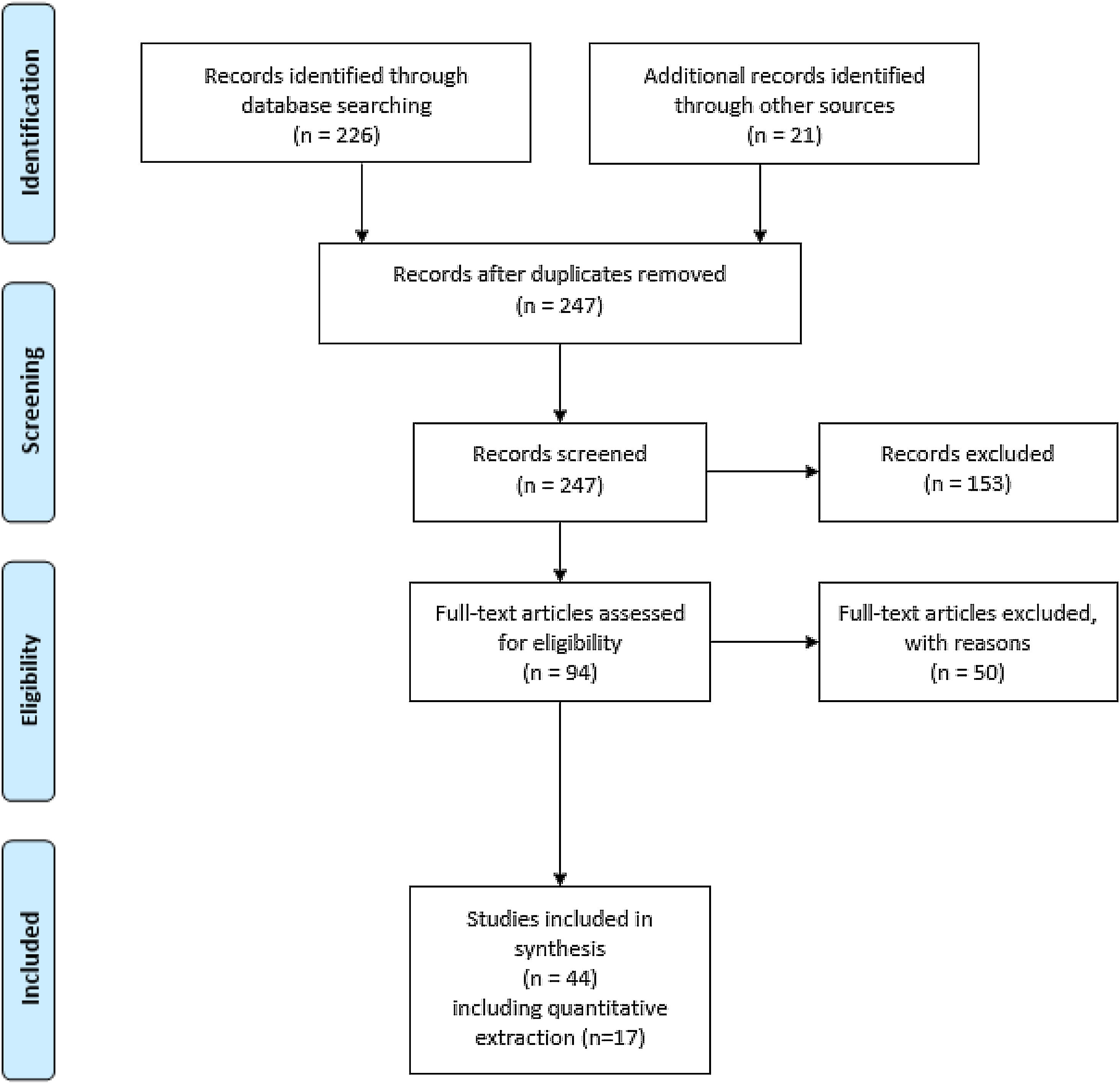
MethodsThis study used the PubMed database. Search terms include sepsis antibiotics, sepsis process improvement, sepsis machine learning. Our search criteria included previous studies published between January 1, 2017, and February 1, 2022.
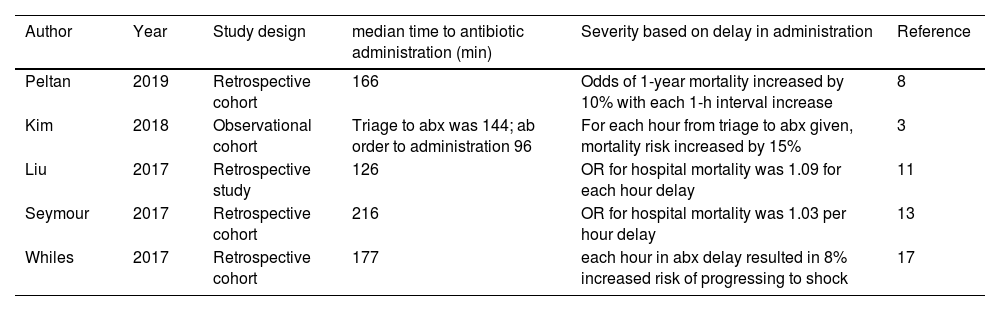
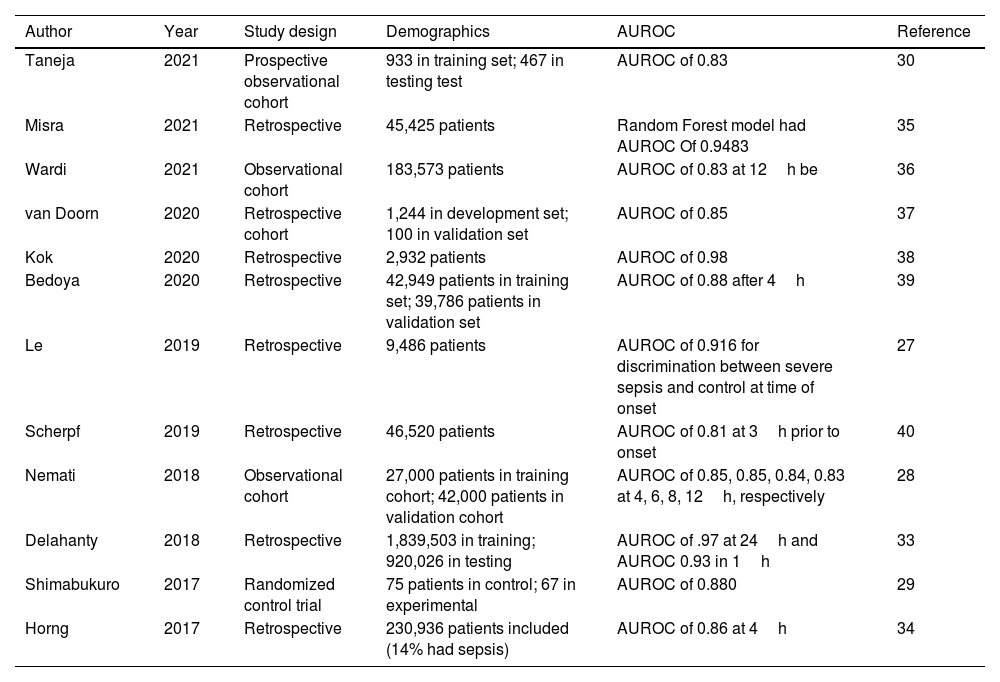
Results/discussionAlthough machine learning algorithms have better predictive capabilities, their effectiveness in the clinical setting is limited as studies show mixed results because the medical staff often fails to intervene. To overcome poor interventional response, clinicians need to work with the facility's IT department to ensure integration into clinical workflow and minimize alert-fatigue. Algorithms should enhance the productivity of clinical teams, not attempt to replace them entirely.
ConclusionHospitals can employ process improvement measures that effectively utilize machine learning algorithms to ensure integration into clinical workflows. Healthcare professionals can utilize workflow tools in addition to the predictive capabilities of machine learning to enhance clinical decisions in sepsis.
Pocos estudios y revisiones anteriores han presentado una comprensión holística de la relación entre el aprendizaje automático y las medidas de mejora de procesos existentes. Este estudio, además de discutir el aprendizaje automático y las medidas de mejora de procesos existentes, profundiza en las desventajas y las barreras para integrar el aprendizaje automático en la clínica. Este artículo sintetiza estudios previos para educar a los profesionales de la salud sobre el manejo efectivo de la sepsis aprovechando los beneficios del aprendizaje automático.
MétodosNuestro estudio utilizó la base de datos PubMed. Los términos de búsqueda incluyen antibióticos para sepsis, mejora de procesos para sepsis, aprendizaje automático para sepsis.
Resultados/discusiónAunque los algoritmos de aprendizaje automático tienen mejores capacidades predictivas, su efectividad en el entorno clínico es limitada ya que los estudios muestran resultados mixtos porque el personal médico a menudo no interviene. Para superar una respuesta intervencionista deficiente, los médicos deben trabajar con el departamento de TI de la instalación para garantizar la integración en el flujo de trabajo clínico y minimizar la fatiga por alertas. Los algoritmos deben mejorar la productividad de los equipos clínicos, no intentar reemplazarlos por completo.
ConclusiónLos hospitales pueden emplear medidas de mejora de procesos que utilizan de manera efectiva algoritmos de aprendizaje automático para garantizar la integración en los flujos de trabajo clínicos. Los profesionales de la salud pueden utilizar herramientas de flujo de trabajo además de las capacidades predictivas del aprendizaje automático para mejorar las decisiones clínicas en sepsis.