This study explored the growing adoption of the Metaverse in the supply chain field, primarily focusing on topics discussed in news media and identifying the benefits of effective implementations. It further investigated whether disparities in these topics exist across various industries. Over 2,000 news articles, published in reputable global newspapers were collected using the LexisNexis online database to examine the applications of the Metaverse in supply chains. The study employed Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and BERTopic topic-modeling methodologies to identify prevalent topics within these articles. The results show that the BERTopic approach yields more coherent topics than the LDA approach. The most prominent topic identified was "global supply chain growth amplified by digital technologies", highlighting the potential of the Metaverse to enhance financial growth across supply chains. The analysis also revealed that the Metaverse is being utilized across diverse sectors, including manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, retail, media, and mining. This study provided multi-faceted implications, extending beyond academic insights to offer tangible guidance for policymakers and industry leaders on the advantages and challenges of Metaverse implementation. This research contributed a fresh perspective to the existing literature by identifying key topics and successful implementations.
The supply chain management (SCM) field has undergone profound transformations due to technological advancements. Emerging technologies such as the Metaverse, extended reality (ER), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) have gained significant attention in recent years (Piñeiro-Chousa et al., 2024). While AR and VR have been extensively studied, the Metaverse offers unique attributes that distinguish it from these technologies (Song et al., 2023). Unlike VR, which primarily emphasizes physical immersion, the Metaverse underscores service-oriented sustainability and social engagement, creating a scalable environment that fosters a heightened sense of community (Park & Kim, 2022).
The Metaverse is conceptualized as a virtual world where users interact through avatars, with the potential to enhance the physical world via ER, VR, and AR technologies (Dwivedi et al., 2022). Supply chain (SC) executives are increasingly recognizing its potential impact on operations, with around two-thirds anticipating it will positively influence their operations (Cui et al., 2022). According to Fortune Business Insights,1 the Metaverse market is projected to experience substantial growth, with estimates reaching $3409.29 billion by 2027 (Park & Kim, 2022).
As an essential component of the Metaverse, AR can deliver real-time information to workers, thereby enhancing productivity and accuracy in handling products (Rejeb et al., 2020). The Metaverse can create a virtual representation of the SC network, providing a unified view that enhances visibility, coordination, and collaboration among stakeholders (Analytica, 2022; Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020). Its capabilities encompass rapid bottleneck detection, real-time inventory tracking, and streamlined transport routes, all of which contribute to improved operational efficiency (Deveci et al., 2023). Additionally, the Metaverse fosters collaboration among SC partners, increasing transparency and trust (Mourtzis et al., 2022). Moreover, the Metaverse contributes to SC sustainability by enabling precise visualization of the product lifecycle and accurate assessment of environmental impacts (Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020).
The optimization of inventory levels and the enhancement of logistics efficiency are critical to SCM. Applications of the Metaverse and AR facilitate real-time inventory management, enabling informed decision-making and the identification of bottlenecks (Deveci et al., 2023). Similarly, logistics managers can leverage the Metaverse/AR to monitor the movement of goods and ensure accurate deliveries (Deveci et al., 2023; Han et al., 2022; Koohang et al., 2023). By simulating various delivery scenarios within the Metaverse, potential issues can be anticipated, and contingency plans formulated.
Despite the considerable promise these technologies hold for the future of SCM, the integration of the Metaverse and AR presents significant challenges. Implementing the Metaverse within the SC requires substantial financial investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Furthermore, technical expertise is essential for successful deployment, posing challenges, particularly for smaller organizations with limited resources. The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed vulnerabilities within the global SC, underscoring the necessity for greater transparency, innovation, and resilience. The Metaverse offers significant potential to address these issues across industries within the SC (Musamih et al., 2022).
However, despite the promising potential of the Metaverse, current research on its applications within SCM remains limited in several critical areas. First, there is a dearth of comprehensive studies employing secondary data to explore the adoption and impact of the Metaverse within SCM. Most existing research has predominantly focused on AR and VR applications, leaving a substantial gap in understanding the broader implications of the Metaverse (Piñeiro-Chousa et al., 2024; Rejeb et al., 2020; Tan et al., 2023). Moreover, previous studies have frequently concentrated on specific industries without providing a multi-industry perspective. Such a broader view is crucial for comprehending the varied benefits and challenges of Metaverse implementation across different sectors (Park & Kim, 2022). Additionally, there has been limited investigation into how the discussions surrounding Metaverse applications in SCM evolve over time and differ across industries (Cui et al., 2022; Dwivedi et al., 2022; Queiroz et al., 2023; Trivedi & Negi, 2023). The current literature primarily focuses on individual case studies or theoretical explorations (Cui et al., 2022; Deveci et al., 2023; Pamucar et al., 2022), lacking a comprehensive analysis of real-world implementations and industry-specific variations.
This study aims to bridge these gaps by systematically analyzing over 2000 news articles to identify prevalent topics, benefits, and challenges associated with Metaverse adoption in SCs. This provides a multi-industry perspective that is currently absent from the literature. The following research questions (RQs) have been formulated to guide this study and address the identified gaps:
RQ1: What topics related to the Metaverse in SCs are being discussed in news media?
RQ2: Which companies have successfully implemented the Metaverse in their SCs?
RQ3: Are there differences in topics across industries and how do they evolve over time?
To address these research questions, this study utilized the LexisNexis online database to collect news articles discussing Metaverse applications in SCs. Two topic-modeling approaches—Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERTopic)—were employed to identify prevalent topics and compile a list of companies that have successfully implemented Metaverse technologies in their SCs. This dual approach ensures a robust analysis, leveraging the strengths of both methodologies to provide detailed insights.
This study contributes to the academic literature by addressing these gaps and offers practical guidance for industry practitioners and policymakers. The findings are expected to shed light on the potential of the Metaverse to enhance SC performance across various dimensions, including planning, logistics, warehousing, and inventory management. Moreover, this research underscores the critical role of digital technologies in driving financial growth and operational efficiency within SCs, thereby providing a solid foundation for future studies in this burgeoning field.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews the relevant literature. Section 3 details the research methods and data collection, including data analyses using LDA and BERTopic techniques. Section 4 presents the study's results, comparing LDA and BERTopic topics and exploring Metaverse applications. Section 5 discusses the insights derived from the results. Section 6 outlines the theoretical and practical implications. Finally, Section 7 concludes the study and explores potential future research directions.
Literature reviewThe Metaverse, a virtual environment where users interact like in the real world, has gained significant attention in recent years (Piñeiro-Chousa et al., 2024; Ritterbusch & Teichmann, 2023). The integration of the Metaverse into SCM offers several advantages, including the ability to predict market trends, enhance risk management strategies, and improve overall business performance (Scaff, 2022). It presents a comprehensive outlook that integrates growth, sustainability, and diversity, thereby guiding businesses.
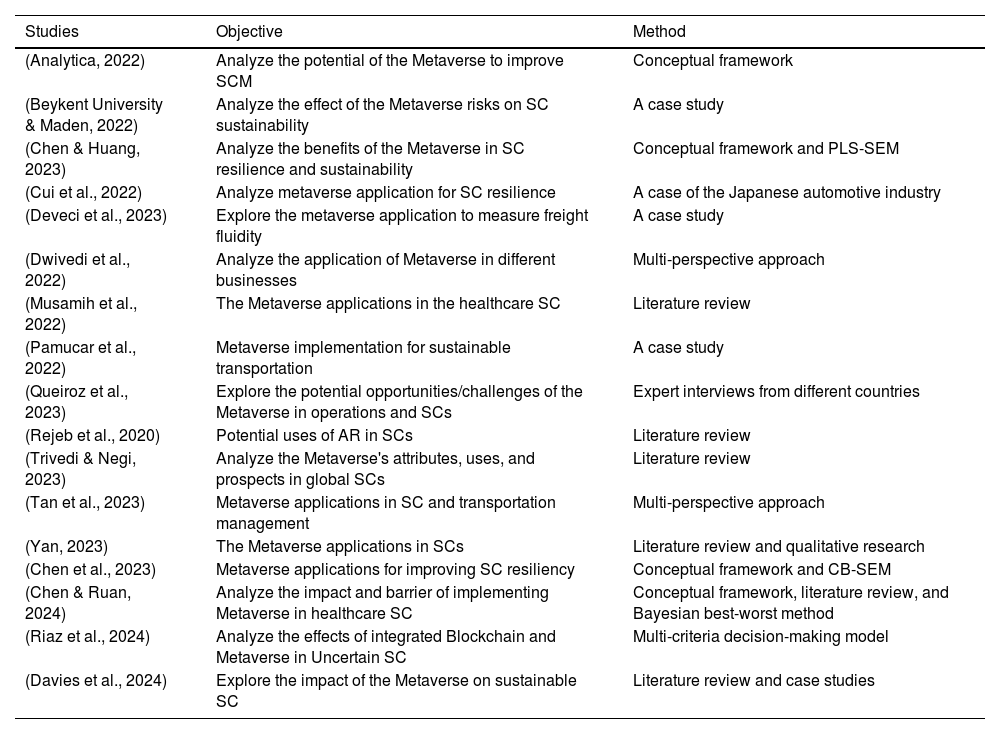
However, the literature review reveals a pressing need for further research on the applications of the Metaverse within SCM, logistics, and operations management. While existing studies have begun to explore the potential, opportunities, and challenges associated with the Metaverse in these areas, the body of knowledge remains fragmented and incomplete. Table 1 summarizes these studies, outlining their objectives and methodologies.
Summary of studies on Metaverse in SCs.
| Studies | Objective | Method |
|---|---|---|
| (Analytica, 2022) | Analyze the potential of the Metaverse to improve SCM | Conceptual framework |
| (Beykent University & Maden, 2022) | Analyze the effect of the Metaverse risks on SC sustainability | A case study |
| (Chen & Huang, 2023) | Analyze the benefits of the Metaverse in SC resilience and sustainability | Conceptual framework and PLS-SEM |
| (Cui et al., 2022) | Analyze metaverse application for SC resilience | A case of the Japanese automotive industry |
| (Deveci et al., 2023) | Explore the metaverse application to measure freight fluidity | A case study |
| (Dwivedi et al., 2022) | Analyze the application of Metaverse in different businesses | Multi-perspective approach |
| (Musamih et al., 2022) | The Metaverse applications in the healthcare SC | Literature review |
| (Pamucar et al., 2022) | Metaverse implementation for sustainable transportation | A case study |
| (Queiroz et al., 2023) | Explore the potential opportunities/challenges of the Metaverse in operations and SCs | Expert interviews from different countries |
| (Rejeb et al., 2020) | Potential uses of AR in SCs | Literature review |
| (Trivedi & Negi, 2023) | Analyze the Metaverse's attributes, uses, and prospects in global SCs | Literature review |
| (Tan et al., 2023) | Metaverse applications in SC and transportation management | Multi-perspective approach |
| (Yan, 2023) | The Metaverse applications in SCs | Literature review and qualitative research |
| (Chen et al., 2023) | Metaverse applications for improving SC resiliency | Conceptual framework and CB-SEM |
| (Chen & Ruan, 2024) | Analyze the impact and barrier of implementing Metaverse in healthcare SC | Conceptual framework, literature review, and Bayesian best-worst method |
| (Riaz et al., 2024) | Analyze the effects of integrated Blockchain and Metaverse in Uncertain SC | Multi-criteria decision-making model |
| (Davies et al., 2024) | Explore the impact of the Metaverse on sustainable SC | Literature review and case studies |
Previous research has highlighted the transformative influence of emerging technologies, including Blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI), on SCs and logistics operations (Chen & Yao, 2022; Lagorio et al., 2022; Riaz et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2023). While these studies do not explicitly address the Metaverse, they underscore the pivotal role of such innovative technologies in optimizing SC operations—a potential that the Metaverse is poised to harness. Rejeb et al. (2020) conducted a systematic review of 43 articles related to AR applications in SC and logistics activities. Their review revealed that AR contributes significant value to domains such as warehousing, manufacturing, sales, outdoor logistics, planning and design, and human resource management.
Tan et al. (2023) utilized a multi-perspective approach to evaluate the Metaverse's impact on marketing, SCM, and transportation, with a particular focus on its expanding applications in healthcare, retail, and infrastructure. Similarly, Trivedi and Negi (2023) investigated the Metaverse's attributes, uses, and prospects in global SCs, identifying its growing relevance in healthcare, retail, and infrastructure. Nevertheless, there remains a critical gap in the literature concerning SC security and traceability. Pamucar et al. (2022) presented a compelling case study evaluating Metaverse alternatives for sustainable transportation. They employed an integrated rough Aczel-Alsina function and ordinal priority approach to assess autonomous driving, public transit, and sharing economy applications for sustainable transport. Chen et al. (2023) demonstrated that the Metaverse enhances both emotional engagement and rational decision-making within SC firms, fostering mutual trust, promoting green knowledge sharing, and bolstering resilience and sustainable development.
Cui et al. (2022) explored how the Metaverse can enhance SC resilience, particularly in the context of the Japanese automotive industry. Their findings suggest that the Metaverse can facilitate efficient allocation of resources—including capital, labor, and technology—thereby enhancing SC resilience. Emphasizing the potential for enhanced transparency, Mourtzis et al. (2022) highlighted the potential of the Metaverse to enhance SC transparency by enabling 3D visualizations of the product lifecycle, from suppliers to end-users, thus fostering greater trust and collaboration within the SC (Analytica, 2022). Conversely, Maden (2022) highlighted the risks associated with the Metaverse regarding SC sustainability, using the spherical fuzzy AHP method to determine that social sustainability is the most critical dimension in addressing these risks. Davies et al. (2024) examined the impact of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on improving SC sustainability. Their findings indicate that NFTs significantly affect both digital and physical product offerings and sustainable practices, presenting a strong argument for their adoption.
Yan (2023) examined how the Metaverse could mitigate challenges in blockchain-enabled SC, particularly concerning regulatory barriers and information transparency issues. Through qualitative research, the study found that the Metaverse can significantly enhance the efficiency of SC operations. Deveci et al. (2023) demonstrated that integrating freight activities into the Metaverse yields superior fluidity measurement compared to other technologies.
Musamih et al. (2022) and Chen and Ruan (2024) investigated applications of the Metaverse in the healthcare SC, highlighting its ability to enable real-time monitoring and auditing of activities. The Metaverse also facilitates seamless virtual visits to healthcare stores, verifies product authenticity, improves sales forecasting accuracy, and allows for the simulation of new processes and operations before their implementation. Queiroz et al. (2023) provided a balanced assessment of the Metaverse in the context of operations and SCM, identifying 15 benefits and 15 challenges through a literature review and empirical testing. Their results suggest that the Metaverse has the potential to enhance customer engagement and improve SC collaboration. However, it also presents challenges, such as the need for new infrastructure and heightened security considerations. Recently, Chen et al. (2023) examined the factors influencing Metaverse adoption in knowledge-sharing contexts within SCs, gathering data from over 200 Chinese manufacturers. The study revealed that performance expectancy, facilitating conditions, and trust among SC partners are key determinants of behavioral intentions toward Metaverse adoption for knowledge sharing, which in turn enhances SC resilience.
Beyond the SC, the Metaverse has been studied in various other sectors, including education (Díaz et al., 2020; Hirsh-Pasek et al., 2022), smart cities, culture, healthcare (Ali et al., 2023; Moztarzadeh et al., 2023; Thomason, 2021), tourism (Monaco & Sacchi, 2023; Pencarelli, 2020), retail (Gadalla et al., 2013; Papagiannidis & Bourlakis, 2010), and manufacturing (Bian et al., 2021; Cui et al., 2022).
While the literature on Metaverse applications in SCM, logistics, and operations management is still nascent, there is a growing recognition of the transformative potential that the Metaverse, alongside other emerging technologies, holds for the future of SC operations. However, a significant gap exists in research that systematically analyzes the discourse surrounding Metaverse applications in SCs across various industries as reported in the news media. This study seeks to address this gap by collecting and analyzing over 2000 news articles from around the world through a text-mining approach.
Research methods and data collectionThis study collected news articles focusing on the application of Metaverse/AR/VR technologies in SCM to comprehensively evaluate the relevant topics. The data were primarily obtained from the widely recognized LexisNexis database, known for its extensive collection of articles, including newspapers, periodicals, magazines, and journals from diverse global sources. Using LexisNexis as a research data repository aligns with previous studies, such as Singh's (2020) work on sustainable SC risk management practices, which also utilized this database.
The query "metaverse" OR "virtual reality" OR "augmented reality" AND "atleast5(supply chain)" was carefully designed to ensure our search captured articles with a substantial focus on supply chain issues in the context of Metaverse, virtual reality, and augmented reality implementation. By setting a threshold of at least five occurrences of "supply chain," we aimed to exclude less relevant news articles and ensure that those included in our analysis provided comprehensive and meaningful discussions on the topic. This approach aligns with the literature (Weaver & Bimber, 2008), which highlights the effectiveness of keyword frequency thresholds in increasing the relevance and quality of search results from large databases like LexisNexis.
The keywords were carefully selected to ensure relevance to the research questions while capturing a broad range of related articles. Subsequently, the search results were further refined using the following set of criteria, as outlined in Table 2.
Search and filter criteria.
The specified timeline was determined based on the current development of Metaverse and AR technologies and their potential applications in SCM. This search yielded 2006 articles, which were then assessed for relevance primarily through their titles and abstracts. Duplicate entries were removed to minimize redundancy within the dataset. As the LexisNexis database imposes a downloading limit of 1000 articles per instance, to download all relevant articles, the timeframe was strategically divided into three segments: January 1999 – December 2021, January 2022 – August 2022, and November 2022 – February 2023.
To analyze the collected news articles and identify the pertinent topics, this study employed two topic modeling techniques: LDA, an unsupervised machine-learning algorithm (Blei et al., 2003), and BERTopic, a deep learning-based model (Grootendorst, 2022). The following sections systematically explain the processes employed to extract relevant information from these articles.
Data pre-processing and cleaningThe Python packages—Genism (Rehurek & Sojka, 2011) and NLTK (Bird, 2006)—were employed to clean and analyze all text data collected in PDF format. Crucial metadata, including news text, date, authors, and outlets, were meticulously extracted from the PDF files and exported to Microsoft Excel for easier manipulation and analysis. Prior to analyzing the news documents, comprehensive and rigorous pre-processing of the text data was conducted.
The pre-processing involved tokenization, whereby the text data were deconstructed into distinct words, and stemming, which reduced the text data to its base root by removing suffixes and prefixes. This process facilitated analysis by treating words as a single entity. Subsequently, lemmatization was applied to capture the core meaning of a term based on its context and morphological analysis. Commonly used terms or 'stopwords' were removed to improve the efficiency of subsequent analysis (Birjali et al., 2021). This pre-processing step significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as information retrieval, sentiment analysis, and topic modeling.
Moreover, a customized "dropwords" list was incorporated, consisting of frequently used words in news articles, such as "announcement", "report", "annual", and "fiscal year". The removal of these specific elements tailored the pre-processing to the study's specific context and mitigated potential overfitting issues.
LDA analysisLDA is a widely recognized unsupervised machine learning algorithm designed for extracting latent topic information from large documents (Blei et al., 2003). LDA modeling iteratively learns the underlying topic distribution by estimating the probability of words appearing in each topic and the probability of topics appearing in each document. Each document within the corpus is defined as having a multinomial distribution of T topics, represented by θ. Similarly, each topic is associated with a multinomial distribution of words from the vocabulary, denoted as φ. Both θ and φ are assigned a Dirichlet prior distribution with hyperparameters α and β, respectively.
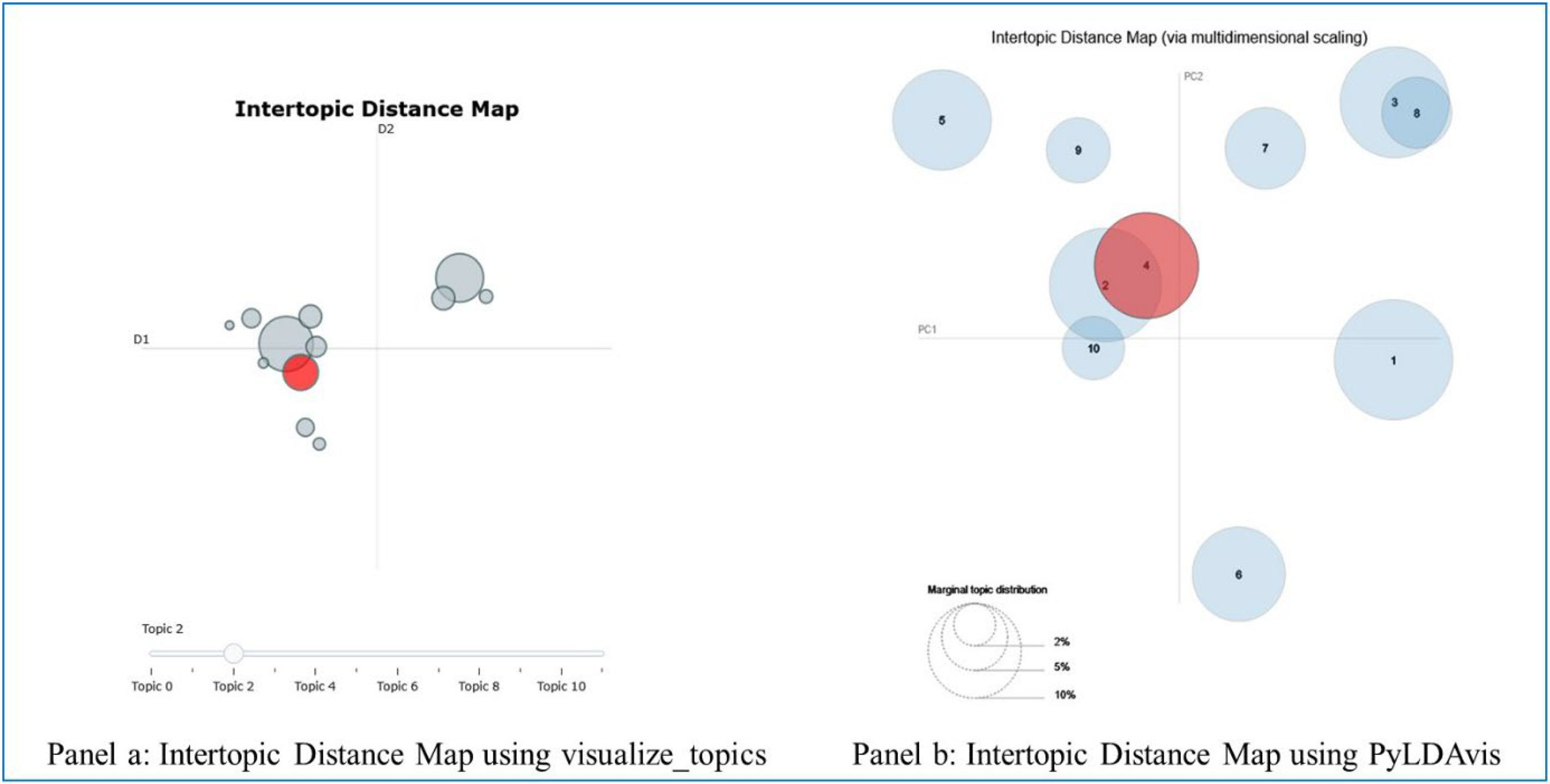
For each word in a document, a topic z is sampled from the multinomial distribution θ specific to that document. Subsequently, a word w is sampled from the multinomial distribution φ corresponding to the chosen topic z. This process is repeated N times, where N represents the total number of words in the document, resulting in the generation of the document. By iteratively sampling topics and words, LDA uncovers the latent topic structure present in the corpus, enabling further analysis and insights. This study utilized the coherence score technique to determine the optimal number of topics. Additionally, an intertopic distance map was employed to validate the optimal number of topics and reveal overlapping topics. While the LDA approach has been widely used in different sectors, its applications in operations and SCM remain limited (Saura et al., 2024).
BERTopic analysisBERTopic (Grootendorst, 2022) represents an advanced topic modeling technique that leverages the BERT language model to extract meaningful topics from a collection of documents. BERTopic utilizes BERT and c-TF-IDF (contextual Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) to comprehensively capture the semantic meaning and contextual understanding of words within a given corpus.
Unlike LDA, which relies on a bag-of-words representation—treating each word in isolation without considering its context—BERTopic employs BERT's contextual word embeddings, which capture the nuanced meaning of words based on their context within a sentence or document. The BERTopic model is capable of automatically determining the optimal number of topics and incorporates a hierarchical reduction mechanism to merge similar topics, thereby reducing redundancy and enhancing topic coherence. Furthermore, an intertopic distance map was integrated into the BERTopic model to illustrate overlapping topics and validate the optimal number of topics.
Data analysis and resultsComparison of LDA and BERTopic topicsTo assess the effectiveness of the topic models—LDA and BERTopic—we calculated the 'C_v' and 'U_Mass' coherence scores, as presented in Table 3. The 'C_v' score measures the similarity between topics, while the 'U_Mass' score evaluates the word distance within topics. An efficient topic model is characterized by minimal internal distance within topics and maximal distance between clusters.
The results indicate that the LDA model achieves its highest 'C_v' value of 0.5952 with four topics, whereas BERTopic obtains a value of 0.5912 with 12 topics. However, we posit that considering more topics within the LDA model could offer more insightful information. Therefore, we chose to extract topics based on the next highest 'C_v' score of 0.5469, resulting in ten topics. For our subsequent analyses, we determined that the optimal number of topics to be considered would be 10 for the LDA model and 12 for the BERTopic model, respectively.
Numerous studies have thoroughly examined and compared the outcomes of LDA and BERTopic models. The prevailing consensus among researchers is that the BERTopic model often outperforms LDA (Egger & Yu, 2022). To further assess the models, we employed the PyLDAvis tool to visualize the topics. By selecting ten topics for LDA and 12 topics for BERTopic, we observed minimal inter-topic distance and overlapping terms, as depicted in Fig. 1. This outcome corroborates our decision to use ten topics for LDA and 12 topics for BERTopic in our analysis.
Additionally, we employed hierarchical clustering for the BERTopic model to group similar topics based on semantic similarity. This approach aimed to enhance coherence measurement and improve the interpretability of the generated topics. By grouping related topics together, we aimed to reveal the underlying themes and make the topics more meaningful and coherent. As illustrated in Fig. 2, by applying hierarchical clustering and setting a distance threshold of 0.8, we identified 11 topics (excluding topic −1, which was not considered in the hierarchical clustering analysis). This outcome aligns with our coherence score analysis, confirming the consistency of the two methods.
Combining these methods allowed us to leverage their complementary strengths. The LDA model provides a broad understanding of thematic structures through its probabilistic approach and captures various topics. This broad spectrum is essential for our foundational analysis, where we selected ten topics based on the highest 'C_v' score for meaningful specificity. Conversely, BERTopic, with its advanced embedding and clustering techniques, offers more contextually rich and semantically coherent topics (Egger & Yu, 2022; Hristova et al., 2022). The model's ability to dynamically adapt and detect emerging trends makes it especially suitable for analyzing evolving news content related to the Metaverse. Given that BERTopic consistently generated more coherent and meaningful topics than LDA, we decided to focus on the BERTopic results in our detailed analysis. This dual approach, supported by coherence scores and visual tools like PyLDAvis, provides a robust and comprehensive analysis of our dataset, effectively meeting our research objectives.
Topic identificationThis section comprehensively analyzes the most prominent topics extracted through text mining related to Metaverse applications in SCs. Table 4 presents the identified topics in both the LDA and the BERTopic models, along with the weights assigned to each keyword concerning its affiliated topic. A keyword's weight indicates its relative significance within the topic. The following sections provide a detailed exploration of these topic names.
Identified topics in the LDA and BERTopic models.
While the identified keywords offer substantial insights, assigning accurate labels using precise terminology is equally important. Experts conducted a meticulous examination of each keyword, referencing original documents to extract relevant information, thereby enabling informed determinations regarding the topic labeling. To further validate the topic identification process, enhance the reliability of topic extraction, and provide a comprehensive assessment of both the LDA and the BERTopic models, the similarity scores of topics were calculated and visualized in Fig. 3 as a heatmap. Interestingly, topic 4 in the LDA model exhibits the lowest similarity score with any of the topics in the BERTopic model.
Fig. 4 illustrates the popularity of different topics over time. It is important to underscore that the topics have been renamed manually based on the most frequently occurring terms within each topic. The graph visually represents the trends and fluctuations in interest or discussion surrounding each topic during the specified period. For instance, topic 1, "Global supply chain growth amplified by digital technologies", has been a longstanding subject with extensive discussions on the impact of innovative technologies and the digital industry on revenue growth in the SC. However, in recent years, there has been a notable surge in the number of news articles related to this topic. Conversely, topics 3, 6, 9, and 10 are relatively new and encompass news articles discussing the utilization of the Metaverse in SCM across industries. These topics have gained traction and are receiving increased attention, as evidenced by the growing number of news articles dedicated to them.
The emphasis on BERTopic-derived topics in our analysis, as depicted in Fig. 4, stems from its superior performance compared to LDA. While both models were initially applied to identify topics, BERTopic provided more coherent and contextually rich topics. This superiority is evidenced by higher coherence scores shown in Table 3 and qualitative assessments that demonstrate better alignment with the core themes of our study. BERTopic utilizes advanced embeddings from transformer models and hierarchical clustering to create semantically meaningful topics that capture nuanced themes, which traditional models like LDA often overlook (Egger & Yu, 2022; Hristova & Netov, 2022). This advanced methodology allows BERTopic to adapt to new data and detect emerging trends dynamically, making it particularly suitable for analyzing the evolving discourse in news articles.
Therefore, the topics generated by BERTopic provide deeper insights and a more accurate representation of the subject matter. Focusing on the more robust BERTopic results ensured clarity and consistency in our analysis and discussions, leading to stronger and more actionable insights. This approach justifies our decision to focus on BERTopic results in the subsequent analysis and discussion.
Comparative analysis of identified themesIn this section, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the themes identified using LDA and BERTopic, highlighting their significance for SCM. This comparison yields several critical insights for SCM practices. LDA captures broad themes, providing a foundational understanding of Metaverse applications across different sectors. This broad spectrum is essential for identifying general trends and thematic structures. Conversely, BERTopic delves deeper (Abuzayed & Al-Khalifa, 2021), providing contextually nuanced insights that elucidate the subtle impacts of Metaverse technologies on SCM. For example, while LDA broadly identifies "Metaverse Applications in Mining SC", BERTopic explores specifics such as "Cost Reduction in US Mining Industry through Metaverse". BERTopics more effectively identify emerging trends and evolving themes, which is crucial for SCM practitioners who aim to stay ahead of technological advancements. For instance, the theme "Surge in Demand for Display Panels with Metaverse Adoption" identified by BERTopic signals an emerging market trend that is less evident in LDA results.
While LDA provides an overarching view of sectors utilizing the Metaverse, BERTopic delves into specific sectoral impacts. For example, the theme "Rapid Net Operating Revenue Growth in Chinese Technology Companies" underscores the significant financial impact and rapid adoption of Metaverse technologies in the Chinese tech sector. Similarly, themes like "Enhanced Retail SC and Warehouse Operations" offer actionable insights for retail and logistics managers looking to implement Metaverse solutions for operational efficiency.
Both models highlight the Metaverse's potential to enhance operational efficiency. LDA captures this broadly, while BERTopic offers more detailed scenarios like real-time tracking and IoT integration. For instance, the themes "Expanding IoT Software for Metaverse Accessibility" and "Enhanced Retail SC and Warehouse Operations" identified by BERTopic suggest specific technological integrations that can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve accuracy in SC processes. The combined insights from both models can significantly aid SCM executives in strategic planning by offering a comprehensive perspective on leveraging Metaverse technologies for competitive advantage. LDA provides a macro view of potential applications across various sectors, helping to identify areas of strategic interest. Conversely, BERTopic's detailed insights enable the formulation of targeted strategies, such as investing in specific technologies or partnerships that align with identified trends and sector-specific needs.
BERTopic's detailed thematic insights can guide R&D efforts by pinpointing high-potential areas for innovation and growth. For example, the theme "Surge in Demand for Display Panels with Metaverse Adoption" indicates a growing market segment that companies can focus on for developing or enhancing new products. Understanding the thematic landscape provided by both LDA and BERTopic can inform policymakers about the areas where regulatory frameworks might need to be updated or created. For instance, the theme "Government Support for Battery Manufacturing and Semiconductor Innovation" highlights the need for supportive policies to foster innovation and growth in these critical areas for Metaverse development.
Finally, leveraging both LDA and BERTopic provides a dual perspective combining breadth and depth, ensuring a robust and comprehensive analysis. This approach enables stakeholders to fully grasp the Metaverse's impact on SCM, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning. By integrating these findings into our analysis, this study offers a well-rounded understanding of the Metaverse's impact on SCM, addressing the critical gaps identified in the literature. This dual approach ensures that both broad thematic trends and detailed contextual insights are considered, providing a solid foundation for future research and practical applications in SCM.
Metaverse applicationsTable 5 presents a comprehensive overview of industries identified through the BERTopic model, highlighting each sector's top four similar/related topics. Additionally, we extracted company names using the LDA model to gain further insights into organizational involvement. The LDA model demonstrates particular effectiveness in extracting company names due to its design for uncovering latent topics and identifying distinct keywords associated with those topics. Conversely, BERTopic excels in identifying semantic similarities and clustering related topics, focusing less on the explicit extraction of named entities (Churchill & Singh, 2022). The results indicate that numerous organizations have already integrated the Metaverse into their SCs. Topic 1 emerges as a predominant theme across all industries, underscoring the imperative of digitizing SCs for effective Metaverse implementation. Leading public companies such as Amazon, Google, Apple, Nvidia, and Tencent are proactively restructuring their products and operations to fully capitalize on the capabilities of the Metaverse (Ball, 2022).
Adopting companies and top four similar topics across industries.
Table 5 lists these companies along with their corresponding geographical regions. Several companies, including AWS, Rackspace Technology, Inc., Vimeo, HKEx, ChinaNet, and Qualcomm, have emerged as key players within the consulting and service industries. These companies primarily focus on providing services for Metaverse implementation and have established a significant presence in the USA and China. The findings also indicate that automotive and manufacturing companies across various regions are swiftly adopting Metaverse technologies. Similarly, Boeing and Lockheed Martin are leveraging the Metaverse to drive innovation within the aerospace and defense sectors.
It is important to note that the adoption of Metaverse technologies within the logistics sector, remains remarkably limited, with only one company, DP World, spearheading the implementation of this technology. This observation highlights a significant gap that must be addressed to fully integrate the Metaverse into the logistics industry. Considerable efforts and advancements are still required to achieve successful Metaverse integration within logistics and transport operations.
Results discussions and insightsThis section provides a detailed discussion of each identified topic and offers managerial insights based on the findings.
Topic 1: Global Supply Chain Growth Amplified by Digital Technologies
Digital technologies, encompassing the Metaverse, AR, VR, IoT, blockchain, digital twins, and data analytics, significantly impact SC performance. These technologies enable companies to optimize their global SCs, enhance efficiency, and respond to market demands more effectively (Gezgin et al., 2017). The implementation of advanced digital technologies also serves to minimize SC risks (Chen & Huang, 2023; Chen et al., 2023; Chowdhury et al., 2023; Cui et al., 2022; Ivanov & Dolgui, 2021). SC leaders acknowledge the potential of the Metaverse in improving SC visibility, planning, decision-making, collaboration, and sustainability (Analytica, 2022; Queiroz et al., 2023; Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020). The digital SC is capable of significantly improving performance across various dimensions, such as planning, lost sales, logistics, warehousing, and inventories (Analytica, 2022; Queiroz et al., 2023; Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020).
Topic 2: Rapid Net Operating Revenue Growth in Chinese Technology Companies/Groups Providing Metaverse Services for Supply Chain
By embracing the Metaverse and leveraging the power of cloud technology, digital transformation can fundamentally revolutionize SC across various industries. Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure and scalability to successfully implement the Metaverse (Trivedi & Negi, 2023). These technologies offer enhanced connectivity, scalability, and accessibility to large data, benefiting SCs at all stages (Periyasami & Periyasamy, 2022). Over the next five years, China's largest city, Shanghai, is expected to actively adopt the Metaverse in areas such as public services, business offices, social entertainment, industrial manufacturing, production safety, and electronic gaming (Cheng, 2021).
Topic 3: Metaverse is Digitalizing Global Supply Chain Operations such as Logistics, Manufacturing, Retailing, and Customer Engagement
The Metaverse, in conjunction with digitalization, enables organizations to gather real-time data from both the supply and market sides. It facilitates enhanced visibility of products at each stage, thereby reducing product lead times, logistics expenses, and delivery delays (Mourtzis et al., 2022). The Metaverse's capability to provide real-time tracking of goods and simulate delivery scenarios offers logistics managers the insights needed to anticipate potential issues and formulate contingency plans, thereby improving logistics and manufacturing processes. For instance, the global logistics leader DP World utilizes Metaverse services, such as simulating warehouse and port operations, conducting container and vessel maintenance inspections, and providing safety training (Sharma, 2022). The company implements fully immersive online training for its staff, replacing physical training and reducing training time by 50 percent.
Companies can digitally simulate product designs, manufacturing processes, and factory operations in the Metaverse, leading to data-driven decisions, waste reduction, and cost savings (Trivedi & Negi, 2023). For example, Unilever uses digital twins to create a virtual representation of its manufacturing facilities. At the same time, Volvo has developed a model that enables the company to conduct ethnographic research in a simulated environment. The Metaverse also eliminates downtime during product-type switchovers, facilitating the cost-effective production of customized products.
Topic 4: Utilizing the Metaverse in Defense and Aerospace Supply Chains to Boost Net Income
Defense and aerospace are highly complex and capital-intensive industries. These industries are actively developing the Metaverse to enhance troubleshooting, inspections, maintenance, and training (Rawat & El Alami, 2023). The Metaverse offers personalized training experiences for pilots and astronauts, improves operational efficiency, reduces engine downtime, and accurately predicts asset lifespan (Patel, 2019). Aerospace and defense companies like Boeing, Lufthansa, and GE Aviation leverage digital technologies and the Metaverse to optimize maintenance, enhance component performance, and improve asset reliability.
For example, Boeing employs digital twins to enhance aircraft manufacturing and maintenance within its commercial and defense sectors. The US Air Force utilizes Boeing's digital twin to assess airplane performance without physical interaction. Lufthansa Technik's AVIATOR platform uses digital tools to notify customers of potential issues in advance, reducing manual efforts by up to 80 percent and defect resolution time by 50 percent (Can & Turkmen, 2023). Similarly, the Metaverse enables real-time tracking of products, identifies bottlenecks, and facilitates preemptive actions, ultimately increasing efficiency and reducing costs in the aerospace SC.
Topic 5: Pharmaceutical Companies Leveraging the Metaverse for Pre-Release Clinical Trial Information to Mitigate Financial Risks
The Metaverse has gained significant attention in medicine in recent years. It plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical industry by accelerating the drug discovery process, facilitating communication, and reducing the cost of clinical trials (Oh et al., 2023). The Metaverse enables risk identification, improves diagnosis accuracy, predicts treatment responses, and enhances the effectiveness of medical facilities. In healthcare and medicine, it is often studied within the medical Internet of Things (MIoT) framework, supported by AR/VR, and notably, with China, India, and the US leading advancements in this area (Yang et al., 2022). Applications include radiology, plastic surgery, physiotherapy, virtual biopsies, counseling, and alert response (Chengoden et al., 2023). Notably, several leading hospitals have already adopted Metaverse technology. For instance, Kankakee's Riverside Healthcare became the first hospital to offer AR spine surgery in March 2021. Similarly, Medtronic and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center have employed AR to reduce training costs and treat chronic pain.
The Metaverse holds significant potential to revolutionize clinical education. Students can rapidly acquire therapeutic skills using the Metaverse to simulate clinical scenarios (Yang et al., 2022). Through high-quality immersive content and gamification features, clinicians can use the Metaverse to enhance patient engagement, provide personalized training experiences, and offer virtual tours of medical facilities (Chengoden et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022). Clinical trials are expensive and time-consuming, accounting for 60 % of drug development costs. By utilizing digital twin models and simulation experiments, the Metaverse can significantly reduce both costs and duration of clinical trials (Shetty et al., 2023). However, implementing the Metaverse in healthcare presents challenges, including high costs, privacy concerns, ethics, and the need for agreements with healthcare administrations.
Topic 6: Metaverse Driving Financial Growth for Media Companies
The Metaverse is a transformative force in the media and entertainment industry, offering vast potential. The media SC encompasses creating, managing, and delivering various types of content (e.g., videos, images, and games) from producers to consumers. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated the growth of the Metaverse in media and entertainment companies, primarily due to the rising demand for remote working tools and work-from-home options, which are poised to drive substantial revenue growth (Park & Kim, 2022). The Metaverse is gaining unprecedented traction as it facilitates the creation of virtual environments for interviews and meetings, broadcasting news, organizing online events, and fostering interactive experiences through 3D rooms (Babu & Mohan, 2022). A Gartner study reveals that 25 % of people are projected to spend at least one hour daily engaging in work, shopping, learning, socializing, and entertainment activities within the Metaverse (Rimol, 2022). During the COVID-19 pandemic, renowned artists like Imagine Dragons, Travis Scott, Muse, BTS, and Post Malone successfully hosted virtual concerts and generated substantial revenue.
Media companies have invested heavily in developing Metaverse capabilities, collaborating with technology partners, and establishing a presence within the virtual world. For example, the NHL's LA Kings collaborated with Tetavi to leverage volumetric technology to create immersive content and experiences for its fans (Lemire, 2022; Wyshynski, 2022). Qualcomm recently committed $100 million to implement Metaverse technologies (Ghatke & Kumar, 2022). Additionally, Disney has obtained a patent for incorporating Metaverse functionality into its theme parks (Babu & Mohan, 2022). However, privacy and security concerns, legal complexities, and the high costs of AR and VR devices remain challenges for the Metaverse in the media and entertainment industry (Wang et al., 2023).
Topic 7: Global demand for LCD and OLED display panels companies surges with Metaverse adoption
The Metaverse's success depends on next-generation display panels, such as micro-OLED and microLED. These display panels are used in various electronic devices, including smart TVs, notebooks, tablets, and wearables, as well as in near-eye displays like VR/AR devices (The Global Market, 2023). The demand for high-resolution microdisplays has surged due to the increased adoption of the Metaverse across various sectors (Ha et al., 2023).
Leading companies, including Samsung and LG, are heavily investing in developing and producing next-generation displays to meet the recent surge in demand driven by the Metaverse. However, the development of user-friendly near-eye display systems remains a challenge. Despite significant strides made thus far, developing a user-friendly near-eye display system that can emulate the human vision system and meet high user expectations remains a formidable challenge.
Topic 8: Expanding IoT Software and Service Offerings for Enhanced Metaverse Accessibility
Implementing the Metaverse requires specialized technologies, skills, and expert guidance. Metaverse consulting firms provide expert advice and support to organizations in developing strategies, products, and transformative experiences. According to a PwC survey2 involving 5000 US consumers and 1000 business leaders, the primary challenges in implementing the Metaverse are cybersecurity, privacy, and technology costs or constraints (Hernandez, 2022). Technologies such as blockchain and IoT offer solutions to these challenges (Charles et al., 2023). Additionally, independent consultancy services and audits of smart contract codes can further enhance security.
Topic 9: Improved Experience in Retail Supply Chain and Warehouse Operations
The Metaverse has significantly enhanced experiences across diverse SCs (Kozinets, 2023). Companies can implement the Metaverse by creating a simulated virtual version of manufacturing processes, cargo ships, warehouses, distribution centers, and retail outlets (Gadalla et al., 2013; Papagiannidis & Bourlakis, 2010). This enables efficient warehouse planning, optimization of shelf space, and staff scheduling, thereby providing a superior overall retail experience. Companies such as Forever 21 and Walmart are leveraging the Metaverse for virtual storefronts, demand forecasting, and SC optimization. The Metaverse also facilitates shelf optimization, staff location, and scheduling (Deveci et al., 2023; Han et al., 2022; Koohang et al., 2023).
Topic 10: Cost Reduction in Production, Operations, and Sales in the US Mining Industry
The Metaverse has the potential to significantly revolutionize the production of various minerals, including copper, gold, and coal. Worker safety remains a paramount concern in the mining industry. Breakdowns in communication can lead to operational disruptions, halts, and even endanger lives. The mining industry faced significant challenges during the COVID-19 lockdowns, as it had limited opportunities for remote work due to a lack of technology adoption.
The Metaverse, AR/VR glasses, and 5 G networks hold significant potential to transform the mining industry by enhancing safety, improving communication, enabling remote operations, and providing real-time information and training to workers without requiring their physical presence for on-site field maintenance (Carrión, 2022). Leading mining companies have conducted trials of 5 G networks for mission-critical communications and monitoring. For instance, Nokia and AngloGold Ashanti conducted underground mining trials of 5 G networks in Chile for mission-critical communications, vehicle teleoperation, and monitoring (O'Halloran, 2022). Similarly, Russian producer Nornickel successfully tested 5 G technology at Skalisty, the deepest mine in Eurasia, enabling high-precision machine guidance, continuous worker condition monitoring, and advanced push-to-talk solutions (Guthrie, 2022). However, successfully implementing the Metaverse within the mining industry requires significant advancements in communication infrastructure and a comprehensive approach to addressing safety concerns.
Topic 11: Metaverse in Advertising and Rental Services
The Metaverse is positioned to fundamentally reshape numerous aspects of marketing, including advertising, promotions, public relations, and online consumer behavior (Tan et al., 2023). It introduces unprecedented possibilities for advertising and marketing by creating immersive environments and virtual tours. The Metaverse can facilitate innovative opportunities for showcasing virtual tours and mirroring physical stores, thereby providing customers with an unparalleled shopping experience (Branca et al., 2023; Mourtzis et al., 2022). Prominent fashion brands such as Gucci and Balenciaga have established a presence in the Metaverse, offering virtual products for purchase. For example, Gucci has introduced Virtual 25, an exclusive collection of digital sneakers that can be bought and worn on Metaverse platforms. Similarly, Balenciaga offers virtual apparel, accessories, and weaponry for avatars.
Moreover, the Metaverse provides a unique platform for companies to showcase virtual properties for rent, host virtual events, conduct meetings, and display products. Rental spaces within the virtual world offer increased flexibility and dynamic engagement opportunities, allowing businesses to reach broader audiences and create more personalized customer experiences.
Topic 12: Government Support for Battery Manufacturing and Semiconductor Innovation
The Metaverse's computing power and data processing demands require advanced semiconductor and battery capabilities. Only a limited number of companies, such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, possess the capacity to produce such high-performance semiconductors. The AR/VR devices necessary for implementing the Metaverse consume significant power, and their prolonged use is challenging as they primarily rely on batteries. Cloud computing can alleviate the burden of complex real-time application processing, thereby reducing power consumption and the size of battery packs.
Governments worldwide, including those of South Korea, Dubai, El Salvador, and the USA, have invested in Metaverse projects and semiconductor manufacturing to drive economic growth and innovation. For example, the US Congress passed a bill allocating over $200 billion over the next five years to boost semiconductor chip manufacturing and providing $50 billion in incentives for top chip makers to set up factories in the US (Ramani et al., 2022). Governments and chip manufacturers recognize the critical need to increase semiconductor production to meet the Metaverse's demands. Initiatives to bolster battery production and provide incentives for chip manufacturers to establish factories are essential. Early data indicate much higher Metaverse adoption rates in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), and European countries compared to the USA (Piscione & Drean, 2023).
Theoretical and practical implicationsThis section delineates our study's theoretical and practical implications for integrating Metaverse technologies in SCM. It offers a comprehensive perspective on how our findings contribute to both academic scholarship and practical applications in SCM.
Theoretical implicationsThis study significantly advances the theoretical understanding of the Metaverse's application within SCM. Although the practical implications of Metaverse technologies are increasingly being recognized, the theoretical framework remains underdeveloped. Our research addresses this gap by contributing to several key areas:
Firstly, it extends the understanding of digital transformation in SCM by integrating Metaverse technologies with existing frameworks. Previous studies primarily focused on AR and VR applications (Piñeiro-Chousa et al., 2024; Rejeb et al., 2020), frequently overlooking the broader implications of the Metaverse. By collecting and analyzing over 2000 news articles, this study provides empirical evidence of the Metaverse's potential to revolutionize SCM through enhanced visibility, coordination, and collaboration. This study contributes to the body of knowledge on digital SCM, aligning with the dynamic capabilities framework (Teece et al., 1997) by demonstrating how Metaverse technologies can enhance the adaptability and resilience of SCs.
Secondly, this study provides a comprehensive multi-industry analysis, highlighting the varied impacts of Metaverse technologies across different sectors. While existing studies often focus on specific industries (Cui et al., 2022; Deveci et al., 2023), our study expands this scope by offering insights into the unique benefits and challenges associated with Metaverse implementation across sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, retail, and mining. This research critically addresses a notable gap in the literature and contributes to the development of sector-specific theoretical models in SCM (Queiroz et al., 2023).
Thirdly, by employing advanced topic modeling techniques, including BERTopic and LDA, this study not only identifies prevalent themes but also traces the temporal evolution of discussions surrounding Metaverse applications in SCM. This longitudinal analysis contributes to the theoretical discourse on the adoption and diffusion of emerging technologies (Queiroz et al., 2023). It provides a comprehensive understanding of how Metaverse technologies are progressively reshaping SCM practices, thereby informing theories related to technological innovation and change management (Dwivedi et al., 2022).
Moreover, applying BERTopic and LDA to analyze large datasets of news articles represents a methodological advancement in SCM research. This study demonstrates these techniques' effectiveness in capturing broad thematic structures and nuanced insights. The rigorous comparative analysis between LDA and BERTopic underscores the respective strengths and limitations of each method, thereby contributing to the literature on text mining and machine learning applications in SCM (Egger & Yu, 2022). This methodological contribution establishes a robust framework for future research exploring emerging technologies in SCM through large-scale text analysis.
Finally, the study identifies actionable insights for industry practitioners and policymakers, bridging the gap between theory and practice. It proposes that theoretical advancements in understanding the Metaverse can directly inform strategic decision-making, policy formulation, and innovation management in SCM. This synthesis of theoretical and practical implications reinforces the relevance of this article in addressing real-world challenges and opportunities in the digital age.
Practical implicationsThis study offers important practical implications for government policymakers, industry practitioners, and researchers. From a pragmatic standpoint, the findings highlight the transformative potential of the Metaverse in improving operational efficiency within SCs. For instance, Amazon has leveraged digital twin technologies to simulate and optimize warehouse operations, thereby reducing errors and substantially improving productivity (Travers & Baeuml, 2024). Similarly, Boeing employs digital twins to optimize aircraft maintenance and enhance operational efficiency, demonstrating how real-time data integration can streamline complex processes (Xiong & Wang, 2022). By embracing Metaverse technologies, companies can simulate logistics and manufacturing processes, enabling more effective planning and decision-making. This can lead to significant cost reductions and improved service levels across the SC.
Metaverse technologies also offer the potential to substantially enhance SC transparency and collaboration. Unilever, for instance, has implemented digital twins to create a holistic view of its SC, thereby improving visibility and coordination among stakeholders (Unilever, 2022). This initiative resonates and aligns with the study's findings that Metaverse applications can provide a unified view of the entire SC network, fostering enhanced collaboration and trust among partners. Enhanced transparency can lead to improved compliance, reduced risk of fraud, and more accurate forecasting and inventory management (Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020).
The Metaverse can serve as a potent catalyst for innovation within SCs. Companies like DP World have utilized Metaverse technologies for training and operational simulations, reducing training times and improving operational readiness (Sharma, 2022). This technological innovation extends to new product development, where companies can use virtual environments to prototype and test products before physical production, thus reducing time-to-market and increasing adaptability to market changes. The insights derived from this study underscore the potential for Metaverse technologies to drive such innovation, offering companies a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
Furthermore, the Metaverse reinforces sustainability objectives by enabling precise visualization of the product lifecycle and facilitating comprehensive environmental impact assessments. Companies like Nokia and AngloGold Ashanti have conducted trials of 5 G networks in mining operations, enhancing safety and reducing environmental impact through improved monitoring and management (O'Halloran, 2022). These endeavors align with the study's results, which indicate that Metaverse technologies can contribute to SC sustainability by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste.
For policymakers, the study emphasizes the necessity of supportive regulatory frameworks to catalyze the widespread adoption of Metaverse technologies. Governments can facilitate this adoption by incentivizing digital innovation and investing in the requisite infrastructure, such as 5 G networks and cloud computing capabilities. For example, the US government's substantial investment in semiconductor manufacturing to support digital transformation initiatives stands as a model for other regions (Ramani et al., 2022).
In synergy with other advanced technologies, the Metaverse has already found applications across diverse sectors, fulfilling multiple functions such as sales forecasting, higher education, employee training, medical and military training, and immersive shopping experience (Musamih et al., 2022). Moreover, it fosters social connectivity, mobility, and collaboration, thereby accelerating learning and skill acquisition through virtualization and gamification (Analytica, 2022; Rodríguez-Espíndola et al., 2020). This transformative technology also possesses the potential to disrupt traditional SC roles and structures as new businesses and job roles emerge within the Metaverse economy.
Nevertheless, it is imperative to acknowledge the complexities and challenges inherent in the Metaverse in operations and SCM. This study provides critical insights into identifying and addressing these challenges, equipping decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to make informed investment decisions regarding this technology. Developing and implementing the Metaverse requires a robust, secure, and sophisticated technological infrastructure, including high-speed internet connections, advanced AR/VR systems, robust cloud computing solutions, and powerful computational resources (Dionisio et al., 2013). Transitioning to a metaverse-enabled SC demands significant hardware, software, and infrastructure investments.
Additionally, this transition introduces various legal, regulatory, data privacy, security, digital assets, accessibility, and ethical issues that demand immediate attention from practitioners (Dwivedi et al., 2022). Managing the massive volumes of data generated within the Metaverse and ensuring data compatibility across different platforms presents another set of challenges. The complexity of the Metaverse technology itself necessitates a high level of technical expertise, which can pose substantial hurdles for organizations, particularly smaller ones that may struggle with resource allocation for its implementation. Therefore, organizations must adopt a long-term perspective and consider key performance indicators related to consumer and employee engagement when pursuing metaverse adoption.
Conclusions and future scopesThe COVID-19 pandemic has exposed critical vulnerabilities in traditional SCs, such as limited visibility, inaccurate inventory data, and a lack of resilience. These issues underscore the urgent need for innovative solutions like the Metaverse, which holds significant potential to revolutionize SCM (Musamih et al., 2022). Despite its promise, the literature on Metaverse applications in SCs remains limited, primarily consisting of a few case studies. Notably, there is a dearth of studies leveraging secondary data to explore the broader scope of Metaverse adoption in SCs.
To bridge this gap, our study analyzed over 2000 news articles from various global sources collected via the LexisNexis online database, focusing on Metaverse applications in SCs. We analyzed the data using the Genism and NLTK packages and employed BERTopic and LDA topic modeling approaches for an in-depth analysis. By evaluating the models using 'C_v' and 'U_Mass' scores, we identified ten optimal topics for LDA and 12 for BERTopic. Given the stronger performance of BERTopic in generating coherent and contextually rich topics, we prioritized its 12 topics for detailed analysis.
Our study further explored the evolution of the Metaverse in the SC field by tracking the popularity of different topics over time. The analysis revealed that "global supply chain growth amplified by digital technologies" was the most prevalent topic, highlighting the pivotal role of digitalization in driving financial growth and enabling Metaverse adoption in SCs. Additionally, emerging topics related to manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, retail, advertising, rental, media, and mining demonstrate a broadening interest in Metaverse applications across various sectors.
The comparative analysis across industries highlighted the unique advantages and challenges of Metaverse implementation. For instance, the mining sector faces specific challenges due to its operational nature, which necessitates physical interactions that are less conducive to digital transformation. Our research provides actionable, sector-specific recommendations to help companies effectively harness the Metaverse's potential within their SC strategies.
From a practical standpoint, the implications of this research are substantial. For example, Amazon's use of digital twins to optimize warehouse operations and Boeing's application of digital twins to enhance aircraft maintenance demonstrate the potential for operational efficiency improvements. Similarly, Unilever's implementation of digital twins for SC visibility underscores the importance of improved transparency and collaboration among SC stakeholders. These real-world examples illustrate how Metaverse technologies can drive efficiency, innovation, and sustainability within SCs. For policymakers, the study emphasizes the need for supportive regulatory frameworks to foster the adoption of Metaverse technologies. Governments can facilitate this by incentivizing digital innovation and investing in necessary infrastructure, such as 5 G networks and cloud computing capabilities. The U.S. government's investment in semiconductor manufacturing to support digital transformation initiatives serves as a benchmark for other regions.
The utility of this research extends beyond academia, offering practical insights for practitioners and policymakers. For researchers, this study contributes to the emerging field of digital SCM by providing a comprehensive analysis of the Metaverse's transformative potential. It also offers practical guidance for practitioners on integrating these technologies into SC operations. Policymakers can use these insights to develop supportive regulatory frameworks and digital infrastructure.
While this study provides valuable insights into the Metaverse's impact on SCM, some areas warrant further investigation. Future research should explore integrating other advanced technologies, such as Blockchain, 5 G, and IoT, within the context of the Metaverse in SCM. These technologies could further enhance the efficiency and security of SC operations. Moreover, incorporating primary data from specific company case studies can provide a more nuanced understanding of the Metaverse's broader implications. A mixed-method research approach could enhance the generalizability and applicability of the findings, offering a comprehensive view of how these technologies are implemented and their impact on SCM.
Additionally, investigating sector-specific applications of Metaverse technologies, focusing on unique challenges and opportunities within industries such as healthcare, automotive, and retail, can help develop targeted strategies for Metaverse adoption. Assessing the long-term impacts of Metaverse technologies on SCM, including their effects on organizational structure, employee roles, and customer relationships, can inform strategic planning and policy development. Furthermore, exploring regulatory and ethical considerations associated with Metaverse adoption in SCM presents another promising research topic.
CRediT authorship contribution statementMaryam Mahdikhani: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation. Purushottam Meena: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization.