Evidence on the long-term use of tolvaptan in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is limited. The aim was to evaluate the tolvaptan effectiveness and safety in real clinical setting.
Material and methodsA single-center observational study (2016–2022) involving ADPKD patients treated with tolvaptan was conducted. Annual change in serum creatinine (sCr) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) before and after treatment initiation were evaluated. Change in total kidney volume (TKV), blood pressure (BP) and urinary albuminuria at 12, 24 and 36 months after initiation were also determined. Adverse events (AEs) according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 were analyzed.
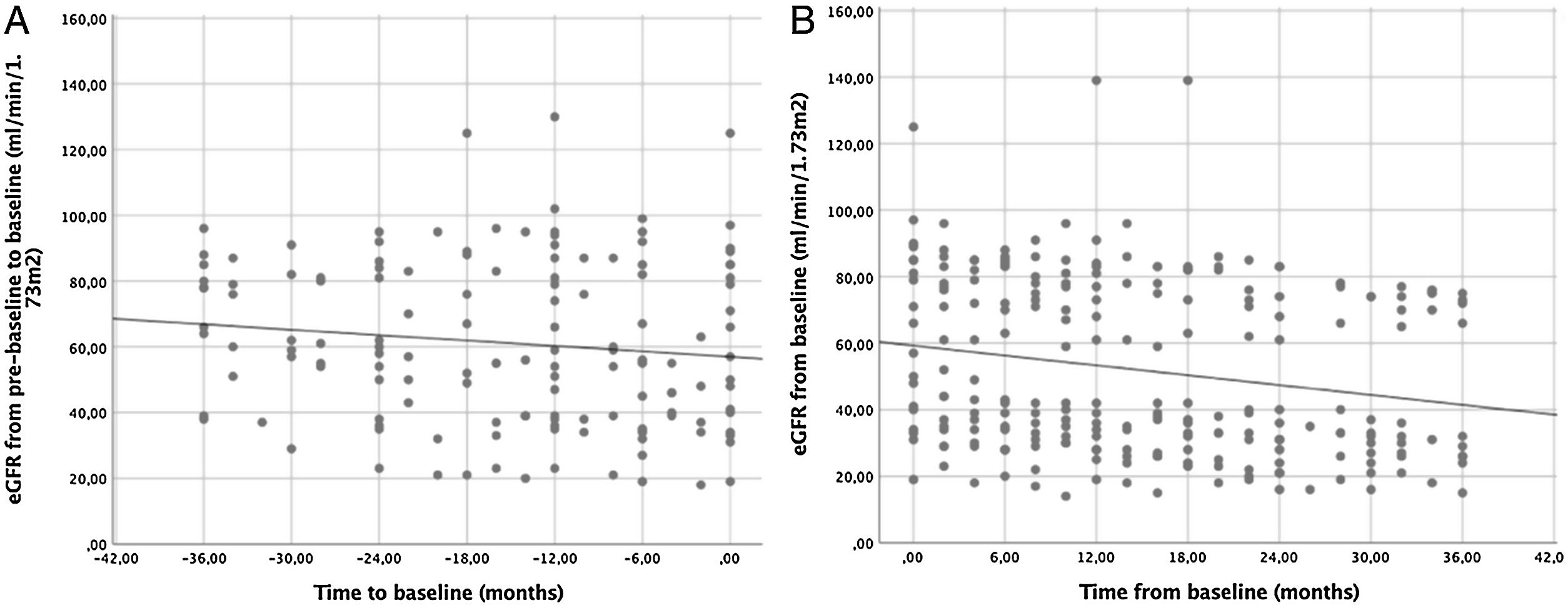
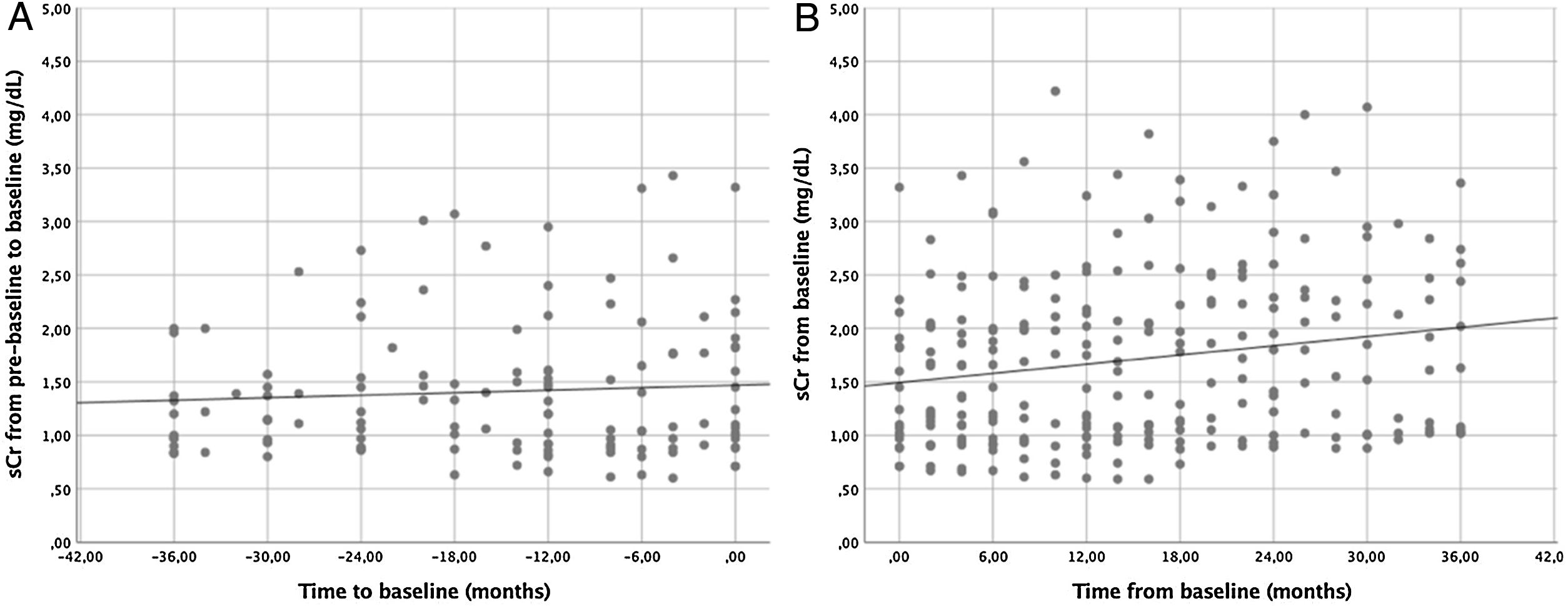
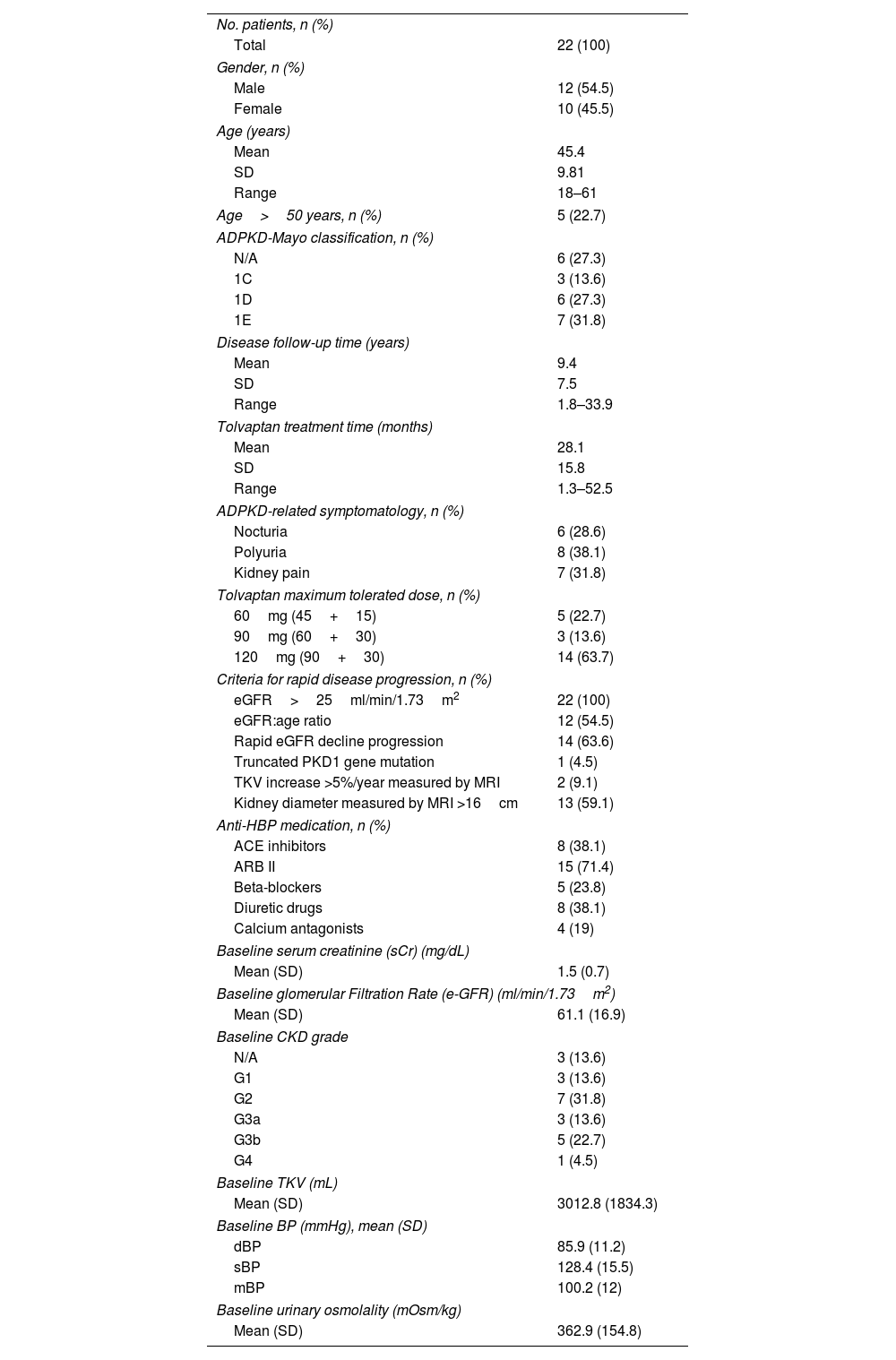
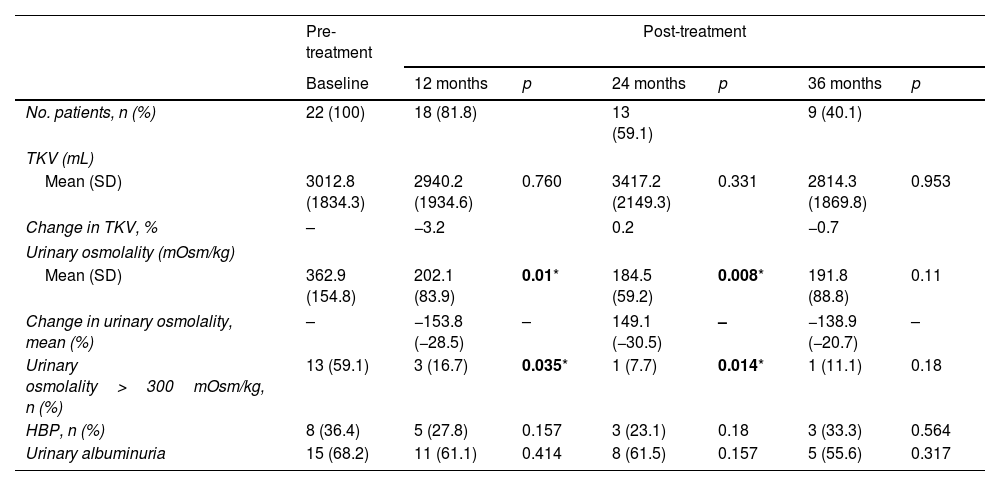
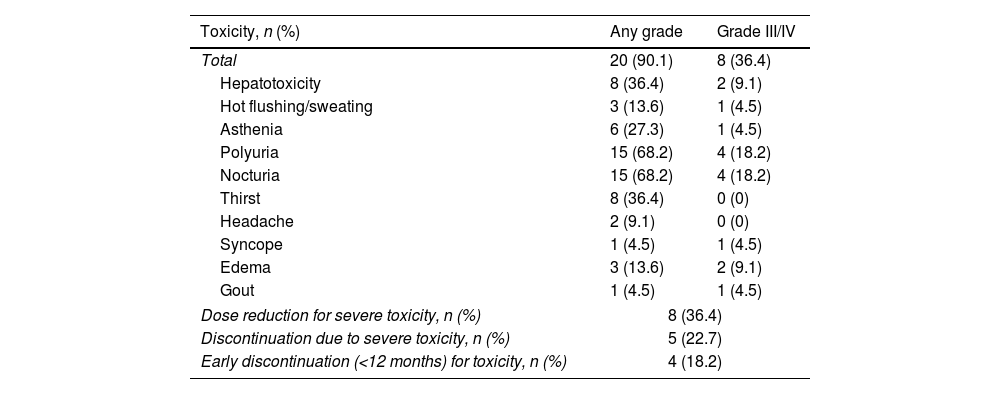
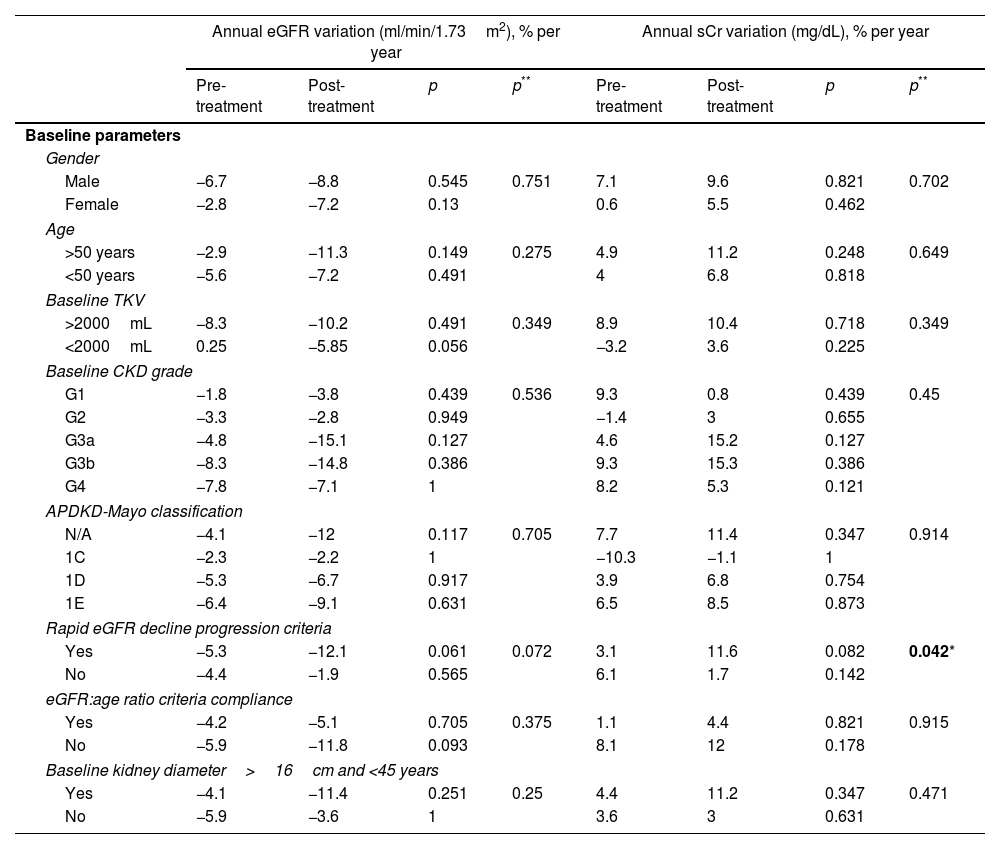
ResultsA total of 22 patients were included. No significant differences pre- vs post tolvaptan treatment in annual rate of change in eGFR (−3.52ml/min/1.73m2 [−4.98%] vs −3.98ml/min/1.73m2 [−8.48%], p=0.121) and sCr (+0.06mg/dL [4.22%] vs +0.15mg/dL [7.77%], p=0.429) were observed. Tolvaptan improved urinary osmolality at 12 (p=0.019) and 24 months (p=0.008), but not at 36 months (p=0.11). There were no changes in TKV, BP control and urinary albuminuria at 12, 24 or 36 months. A worse response was shown in patients with rapid kidney function decline (p=0.042). A 36.4% of the patients developed grade III/IV AEs. A 22.7% discontinued treatment due to unacceptable toxicity.
ConclusionsThis study shows a modest benefit of tolvaptan in ADPKD patients, as well as safety concerns.
El objetivo fue evaluar la eficacia y la seguridad del tolvaptán en los pacientes con poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante (PQRAD) en la práctica clínica real.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional unicéntrico (2016-2022) que incluyó pacientes con PQRAD tratados con tolvaptán. Se evaluó el cambio anual en creatinina sérica (sCr) y la tasa de filtración glomerular estimada (eGFR) antes y después del inicio del tratamiento. Se determinaron los cambios en el volumen renal total (VTR), en la tensión arterial (TA) y en la albuminuria urinaria a los 12, 24 y 36 meses tras el inicio. Se registraron los acontecimientos adversos (EA) según la Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v.5.0.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 22 pacientes. No se observaron diferencias en la variación de FGe (−3,52ml/min/1,73m2 [−4,98%] vs. −3,98ml/min/1,73m2 [−8,48%]; p=0,121) y sCr (+0,06mg/dl [4,22%] vs. + 0,15mg/dl [7,77%]; p=0,429). Tolvaptán mejoró la osmolalidad urinaria a los 12 (p=0,019) y 24 meses (p=0,008), pero no a los 36 meses (p=0,11). No hubo cambios en el VTR, en la TA ni en la albuminuria urinaria a los 12, 24 o 36 meses. Se observó una peor respuesta en pacientes con un rápido deterioro de la función renal (p=0,042). Un 36,4% de los pacientes desarrolló EA severos. Un 22,7% interrumpió el tratamiento por toxicidad inaceptable.
ConclusionesEste estudio muestra un modesto beneficio del tolvaptán en los pacientes con PQRAD, así como limitaciones en el perfil de seguridad.