The aim of this research was to investigate the relationship between disease activity and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) considering the increased interest in the management of this disease.
Materials and methodsHRQoL was measured at clinic visits during a 12-month follow-up period using questionnaires on fatigue (FACIT-FATIGUE); quality of life, EuroQol 5-dimension (EQ-5D-5L) health questionnaire with 5 levels; disability, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), and a Global Health Status (GHS) scale. Disease activity, organ damage and other clinical factors that could affect HRQoL were recorded. The association between disease activity and HRQoL was assessed using Bayesian linear regression models with monotonic effects.
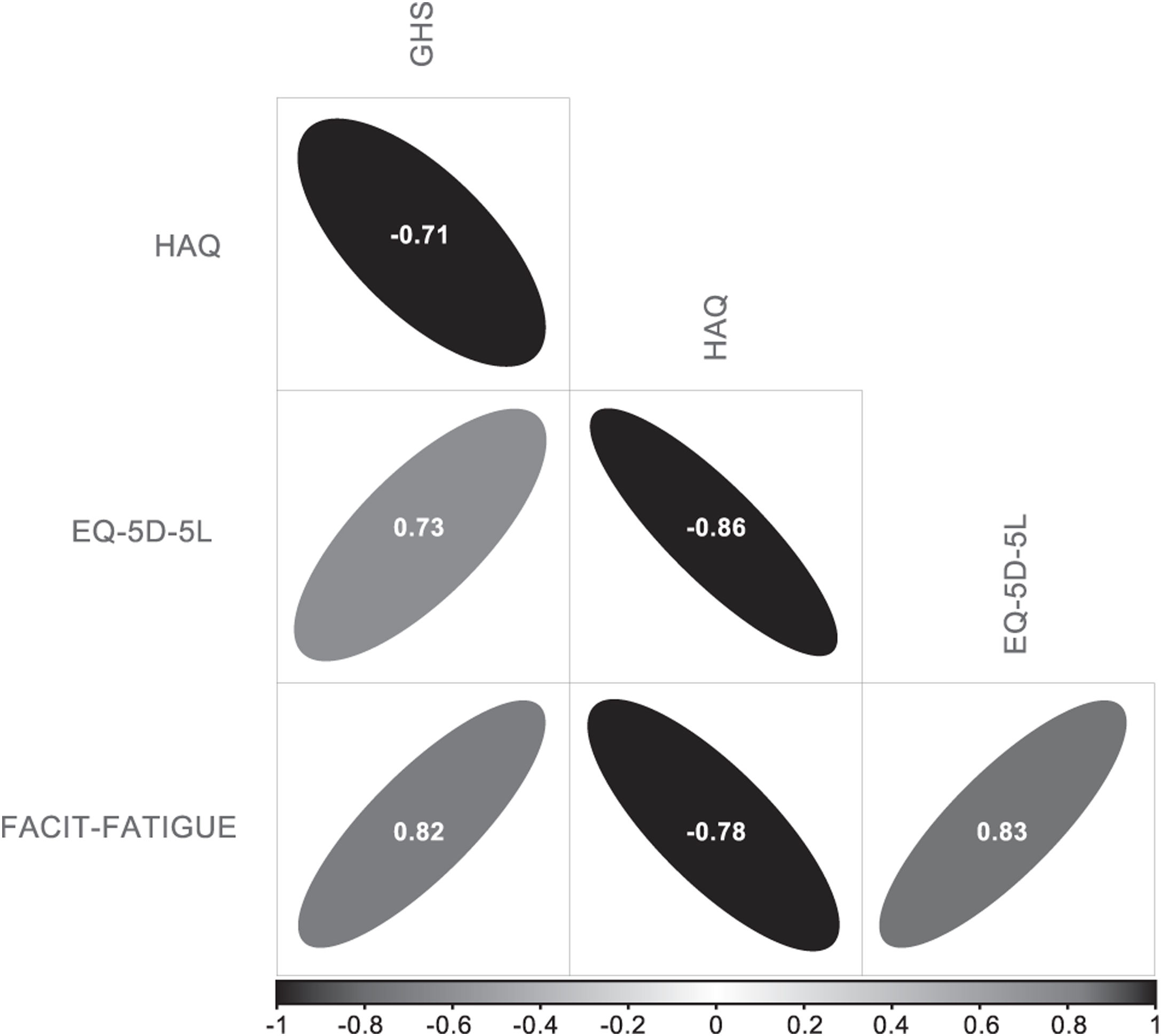
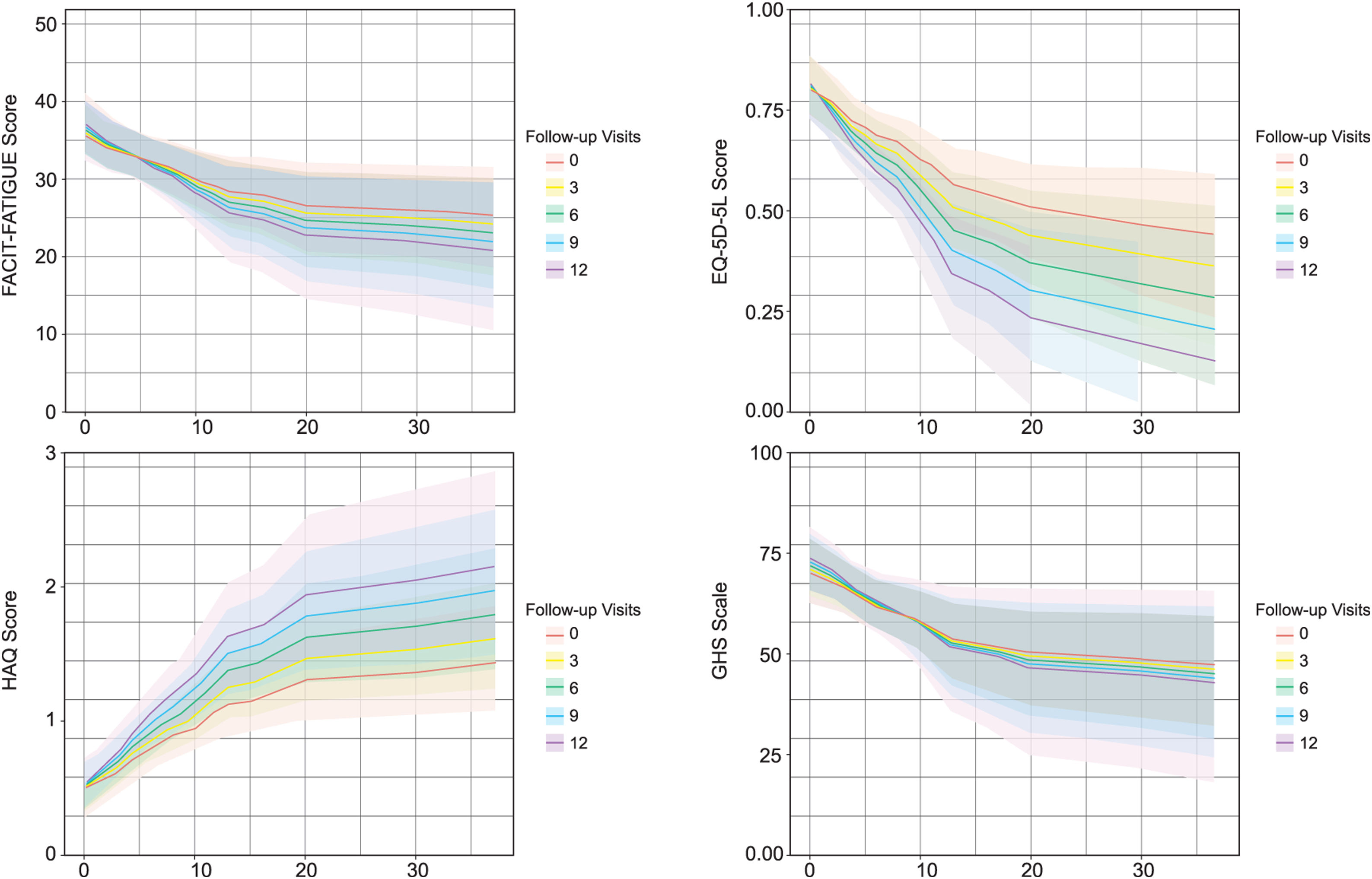
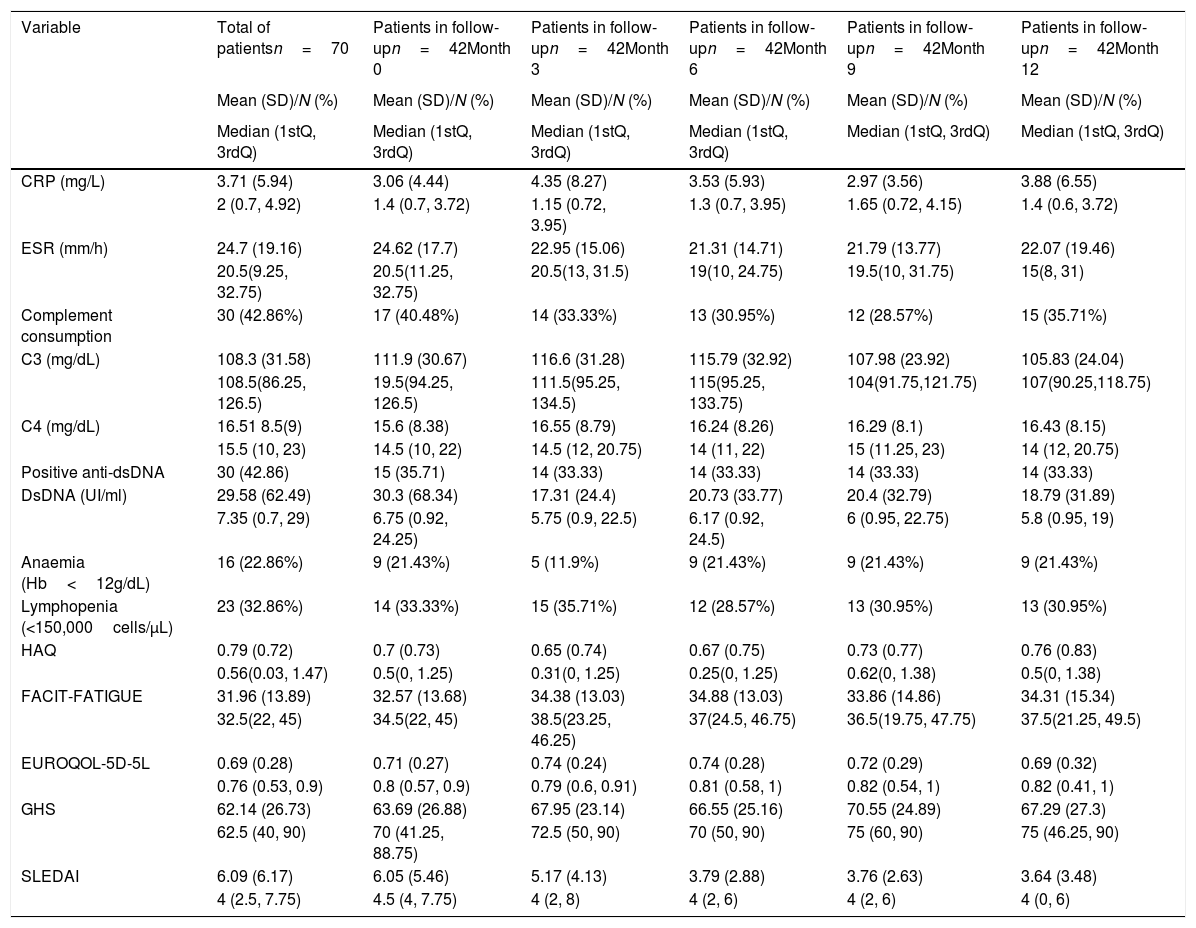
ResultsData from 70 patients at the baseline visit and 42 patients with 1 year of follow-up were analyzed. At baseline, 28.57% of patients presented Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)>6. In the 70 baseline patients, disease activity was associated with HRQoL in all four parameters. In the 42 patients with 12 months of follow-up, the positive association of disease activity with GHS, FACIT-FATIGUE and EQ-5D-5L and the negative association with HAQ was maintained.
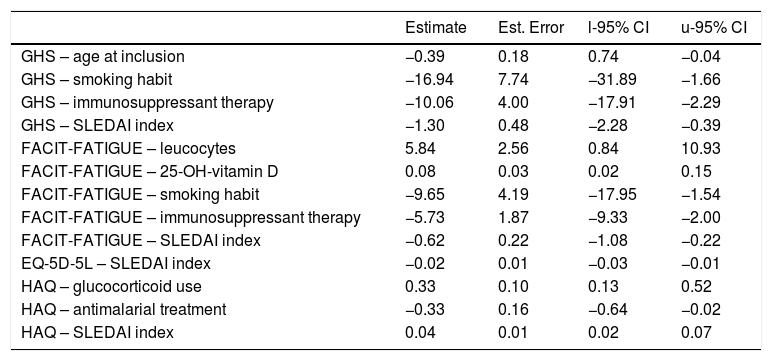
Patients who are smokers and those receiving immunosuppressant therapy presented low GHS and FACIT-FATIGUE scores. Moreover, older age at inclusion was significantly associated to low GHS, while low leucocyte and 25-OH-vitamin D levels were associated to fatigue perception in SLE patients.
ConclusionOur results showed a statistically significant association between disease activity and HRQoL parameters.
El objetivo del estudio fue analizar la relación entre la actividad clínica y la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) en pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES).
Material y métodosLa CVRS se evaluó en la visita basal y durante 12 meses de seguimiento mediante un cuestionario de fatiga (FACIT-FATIGUE), calidad de vida (EQ-5D-5L), discapacidad (HAQ) y una escala analógica visual de estado general de salud (EVA). La actividad clínica, el daño acumulado y otros factores clínicos que pudieran afectar a la CVRS se analizaron mediante un modelo de regresión lineal bayesiano con efectos monotónicos.
ResultadosSe analizaron los datos de 70 pacientes incluidos en la visita basal y los 42 con 12 meses de seguimiento seleccionados aleatoriamente. En la visita basal el 28,57% de los pacientes presentaban un índice SLEDAI>6. La actividad clínica medida mediante el índice SLEDAI se asociaba de forma estadísticamente significativa a los 4 parámetros de CVRS. En los 42 pacientes con un año de seguimiento la relación directa entre la actividad clínica y el FACIT-FATIGUE, EVA y EQ-5D-5L, así como la relación indirecta con el HAQ, se mantuvieron.
Los pacientes fumadores y aquellos bajo tratamiento inmunosupresor presentaban valores disminuidos de EVA y FACIT-FATIGUE. Además, los pacientes con edades más avanzadas presentaban valores disminuidos de EVA, y aquellos con niveles bajos de vitamina D o leucopenia presentaban mayor percepción de fatiga.
ConclusiónLa actividad clínica se asocia a diferentes dominios de la CVRS, apoyando la evaluación de la CVRS como complemento en el manejo del LES.