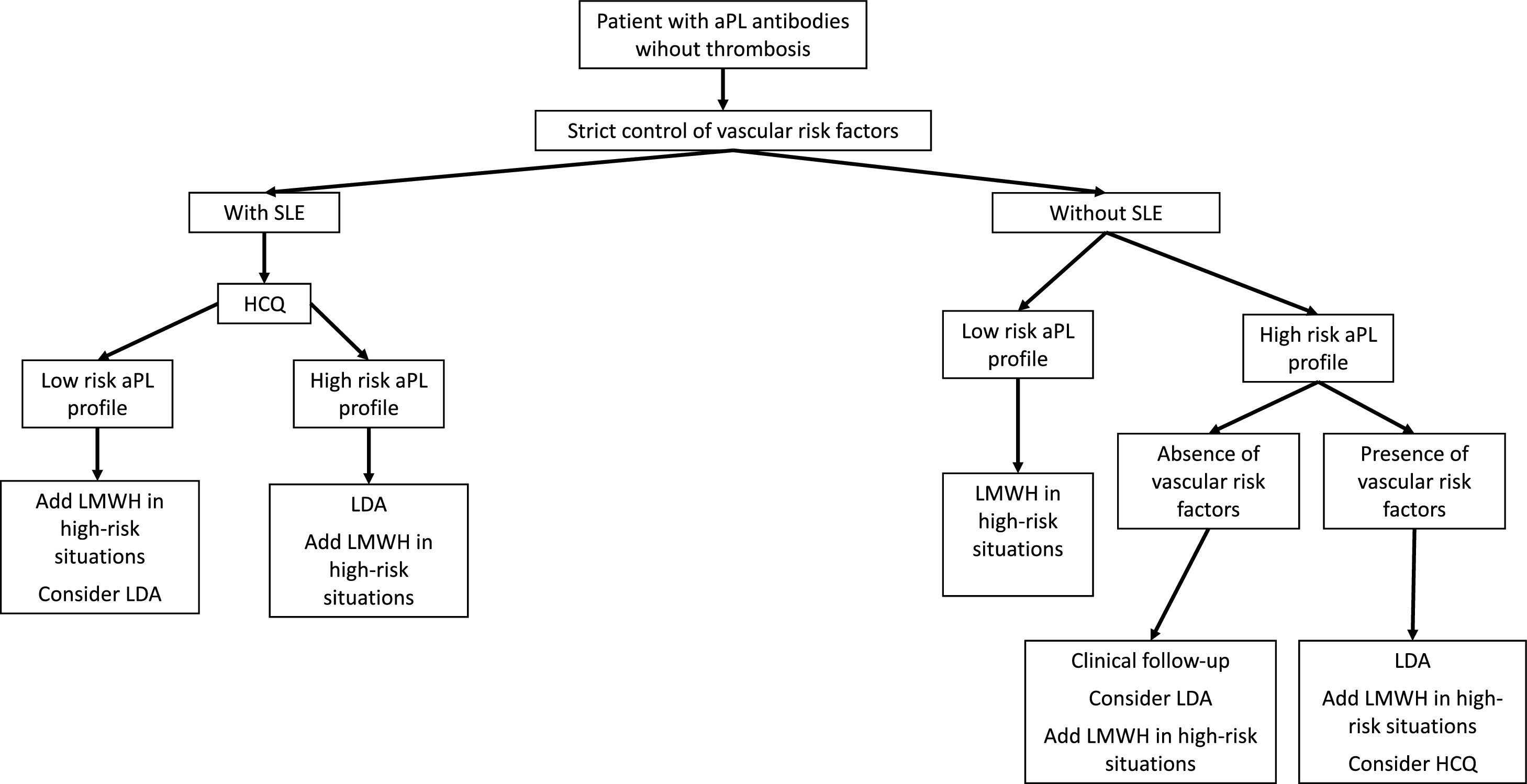
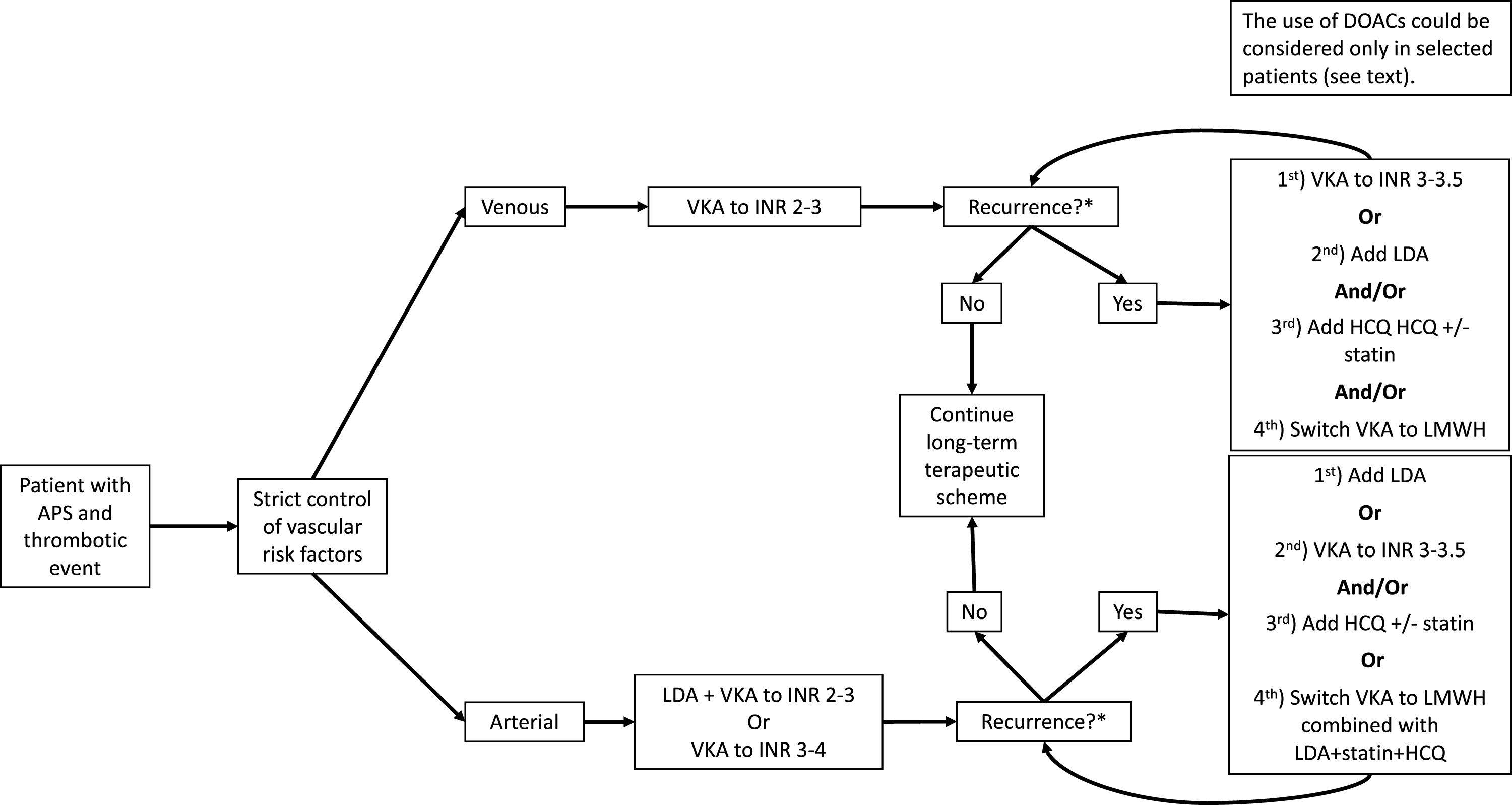
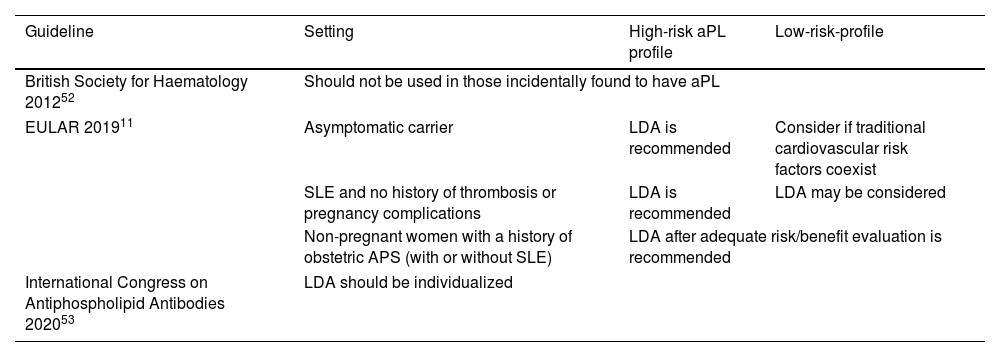
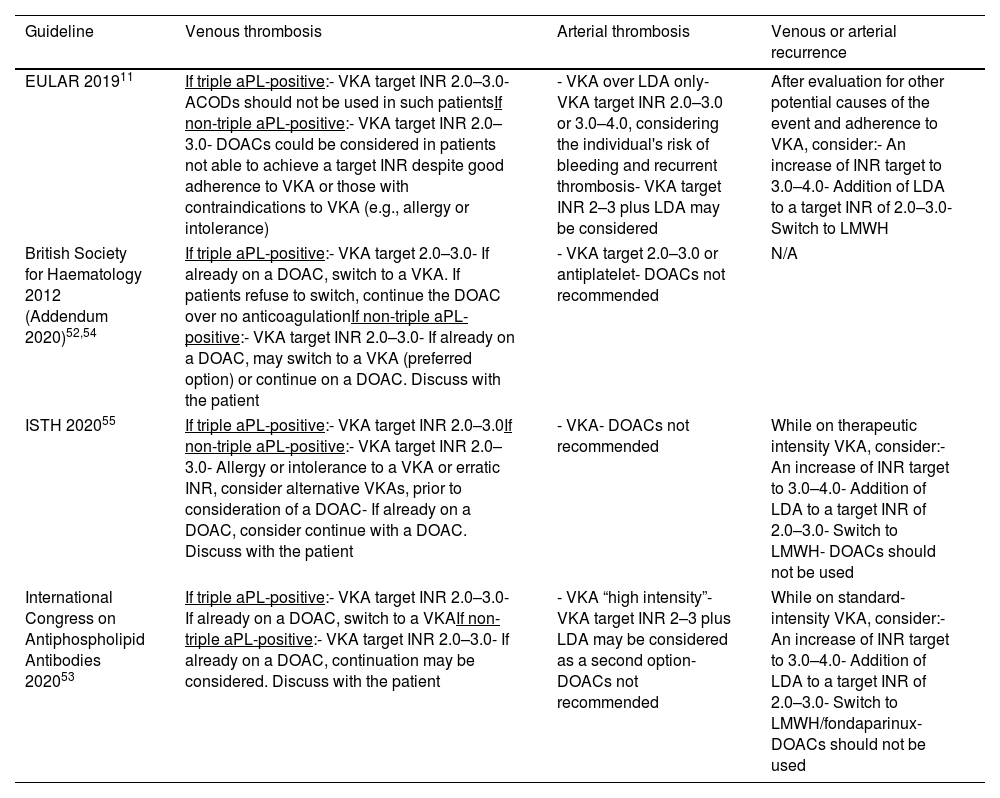
Thrombotic manifestations, mainly venous thromboembolism (VTE) and stroke, are the most common and potentially life-threatening presentations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). The management of APS requires the assessment of the antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) profile, of concurrent systemic lupus erythematosus or other systemic autoimmune diseases and the presence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease and bleeding. Anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) remains the cornerstone of therapy for thrombotic APS. As platelets play a central role in APS, low-dose aspirin is the first option for primary thromboprophylaxis in asymptomatic aPL carriers, and also plays a role as combination therapy with VKAs in arterial thrombosis. Treatment with direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) could be considered in certain low-risk situations, although they are not recommended in patients with arterial thrombosis or triple positive aPL. Adjuvant therapies such as hydroxychloroquine and statins may be useful in complex settings such as thrombotic recurrences or high risk of bleeding. In this article, we review the evidence and the recommendations of the guidelines for the treatment of APS, and provide a critical and practical approach of its management from our clinical perspective.
Las manifestaciones trombóticas, particularmente el tromboembolismo venoso (TEV) y los accidentes cerebrovasculares, son las manifestaciones más frecuentes y las que más ponen en peligro la vida del síndrome antifosfolípido (SAF). El manejo del SAF precisa una adecuada valoración del perfil de anticuerpos antifosfolípido (aFL) y de la presencia concomitante de lupus eritematoso sistémico u otra enfermedad autoinmune sistémica, así como del riesgo cardiovascular y de hemorragia. La anticoagulación con antagonistas de la vitamina K (AVK) constituye la base del tratamiento del SAF trombótico. Dado que las plaquetas juegan un papel central en el SAF, el ácido acetilsalicílico a dosis bajas es la opción principal como tromboprofilaxis primaria y juega también un papel importante en terapias combinadas con AVK en trombosis arteriales. Los anticoagulantes orales directos pueden utilizarse en ciertas situaciones de bajo riesgo, pero no se recomiendan en pacientes con trombosis arteriales o aFL triple-positivos. Los tratamientos adyuvantes, como la hidroxicloroquina o las estatinas pueden ser útiles en situaciones complejas como trombosis recurrentes o alto riesgo de hemorragia. En este artículo, revisamos la evidencia y las recomendaciones de las guías para el tratamiento del SAF y ofrecemos un enfoque crítico y práctico de su manejo desde nuestra perspectiva clínica.