There is growing evidence that vitamin D is related to the development of a variety of diseases. The current study was performed to investigate the status of serum vitamin D distribution among adult Chinese people and reveal the influence of gender, age, seasonality and residential regions on serum vitamin D levels.
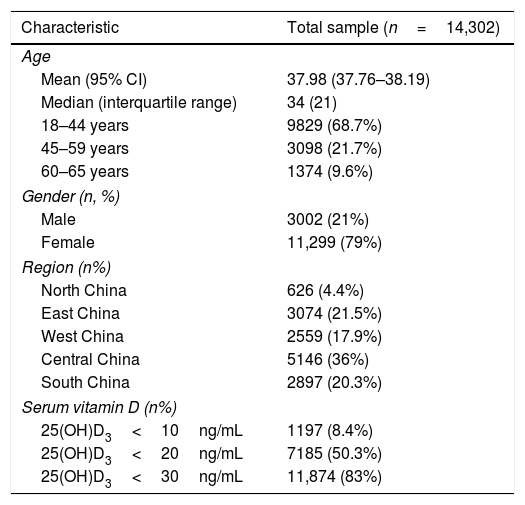
MethodThis cross-sectional study included 14,302 participants aged from 18 years old to 65 years old from six major cities in China. The basic demographic information and the levels of serum vitamin D (25(OH)D) and vitamin D3 (25(OH)D3) were collected from Jan 2, 2014 to Dec 25, 2017.
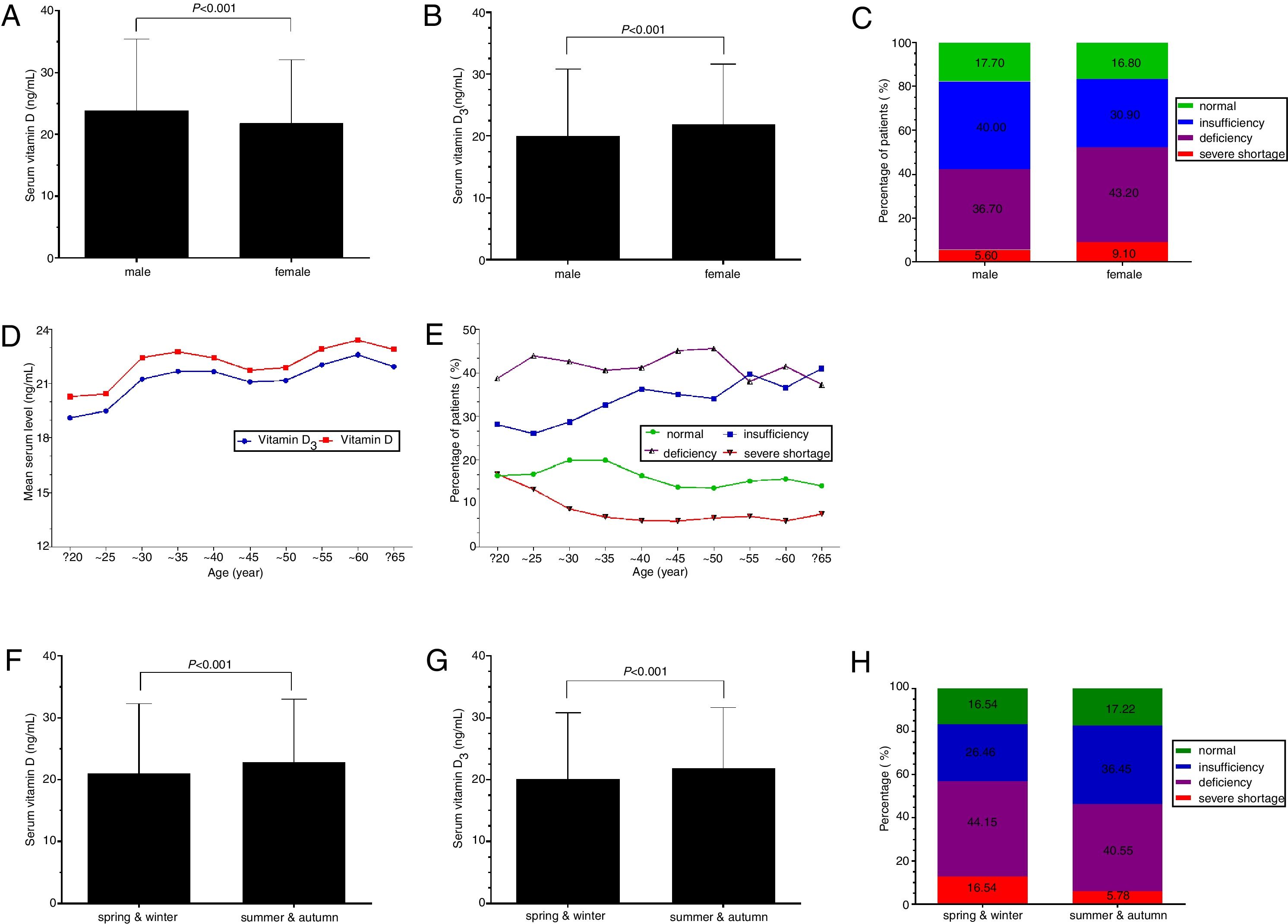
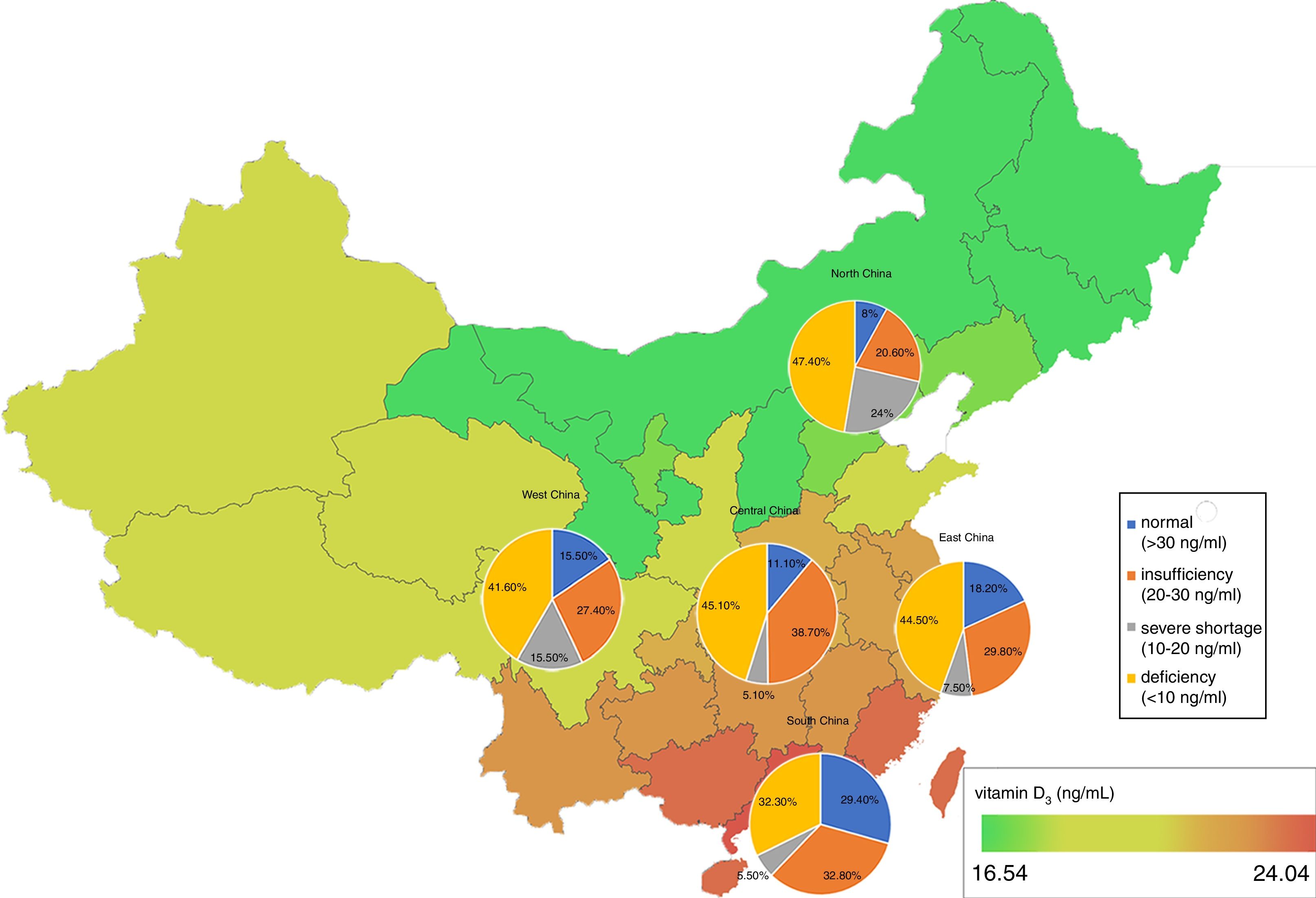
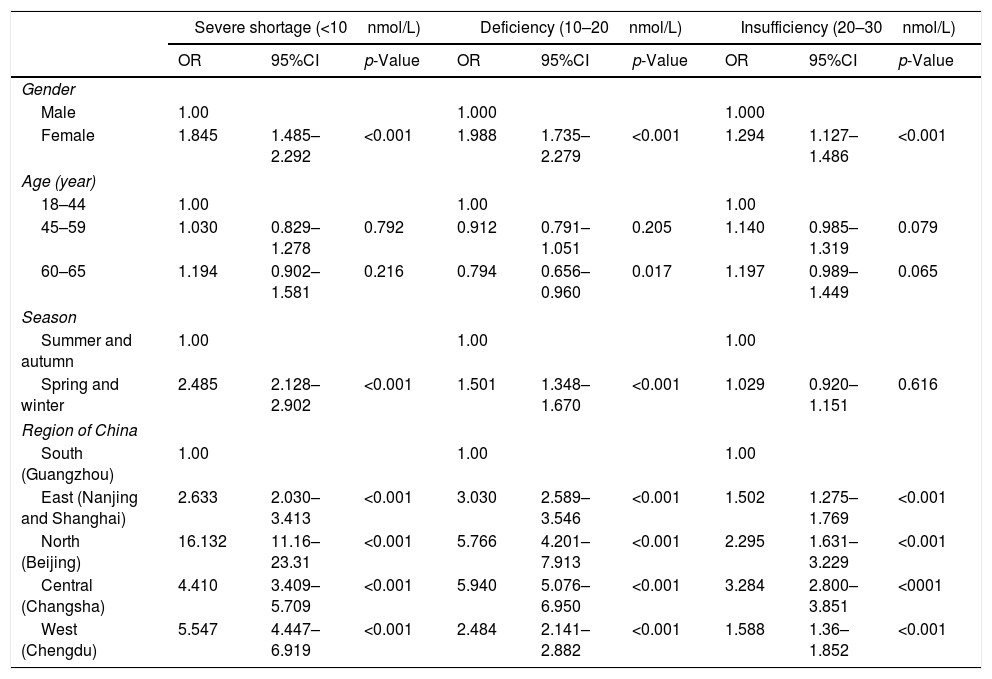
ResultThe prevalence of 25(OH)D3 concentration <30ng/mL reached up to 83%, in which the rate of vitamin D insufficiency (20–29ng/mL) was 32.7%, and vitamin D deficiency (10–19ng/mL) accounted for 41.9%, and vitamin D severe shortage (<10ng/mL) accounted for 8.4%. Women were more likely to have vitamin D3 deficiency and lower serum vitamin D3 concentration than men (both p<0.001). The mean concentration of serum 25(OH)D and 25(OH)D3 in summer and autumn were higher than that in spring and winter (p<0.001), and the mean concentration of serum 25(OH)D in people from Southern China was higher than that in people from other regions (p<0.001). Although the mean concentrations of serum 25(OH)D and 25(OH)D3 were both increased by age, the percentage of patients with serum 25(OH)D3 insufficiency was also increased.
ConclusionSerum vitamin D deficiency is very common in adults in China. The level of serum vitamin D may be associated with age, sex, seasonality and residential regions.
Una gran cantidad de investigaciones muestran que la vitamina D está relacionada con el desarrollo de una variedad de enfermedades. El presente estudio apunta a investigar el estado de la distribución de la vitamina D sérica entre los adultos chinos, y revelar la influencia del género, la edad, la estacionalidad y las regiones residenciales sobre los niveles séricos de vitamina D.
MetodologíaEl presente estudio transversal incluyó a 14.302 participantes con edades comprendidas entre de 18 y 65 años, provenientes de las 6 principales ciudades de China. Se recogió la información demográfica básica y se analizó la concentración sérica de vitamina D 25(OH)D y vitamina D3 25(OH)D3 del 2 de enero de 2014 al 25 de diciembre de 2017.
ResultadoLa prevalencia de concentración de 25(OH)D3Y3 y menor concentración sérica de vitamina D3 que los varones (pY3 en verano y otoño era mayor que en primavera e invierno (pY3 aumentaron levemente con la edad, el porcentaje de pacientes con insuficiencia sérica de vitamina D 25(OH)D3 también experimentó un incremento.
ConclusiónLa deficiencia sérica de vitamina D es muy común en adultos en China. Es probable que el nivel sérico de vitamina D esté asociado a la edad, el sexo, la estacionalidad y las regiones residenciales.