The prevalence of non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) increases with the patient's age and is associated with high morbi-mortality rates. The main goal of this study was to describe the characteristics of hospitalized elderly patients with NVAF and to identify the clinical and functional factors which determine the use of different antithrombotic strategies.
Patients and methodsObservational, prospective, multicentre study carried out on patients with NVAF over the age of 75, who had been admitted for any medical condition to Internal Medicine departments.
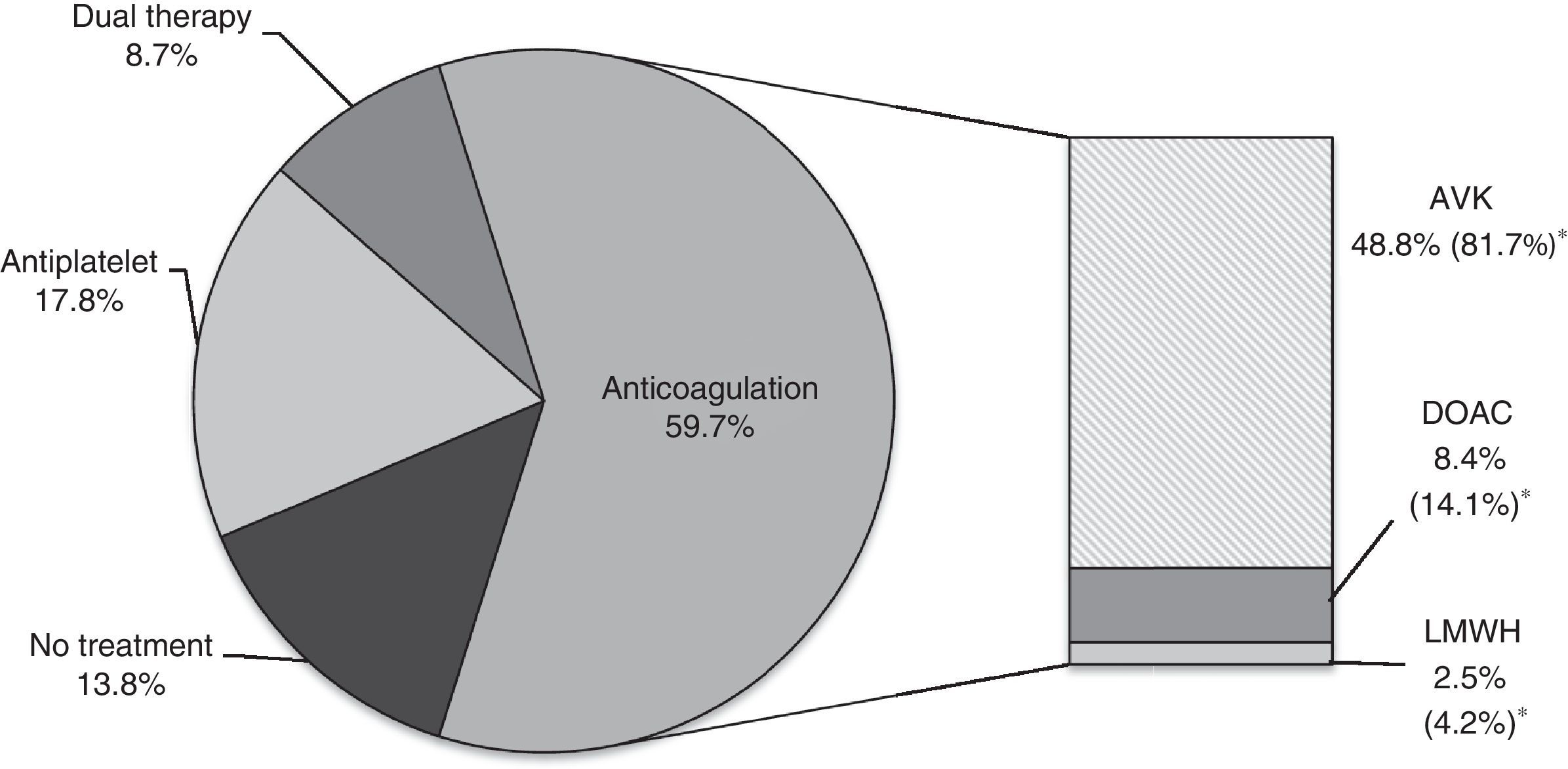
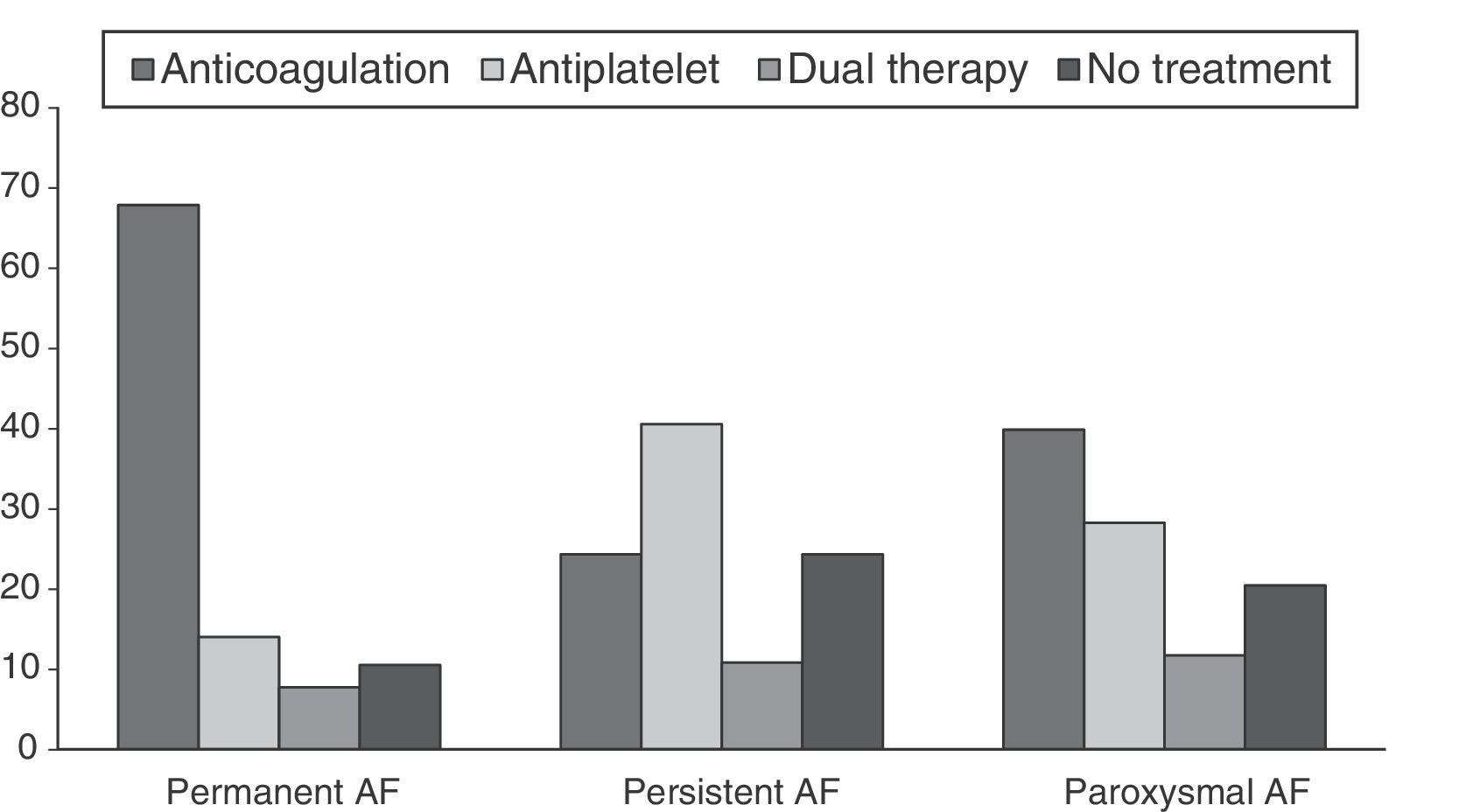
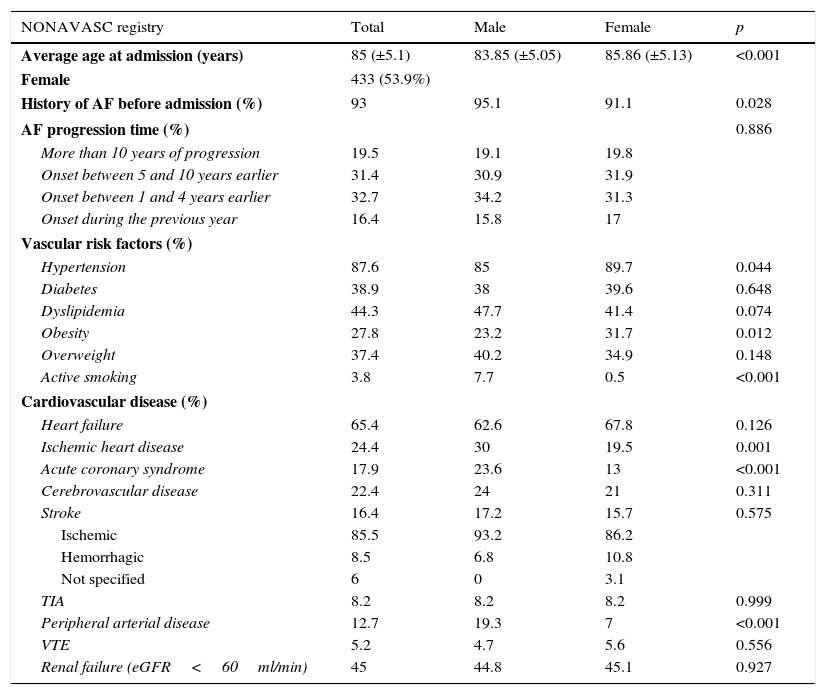
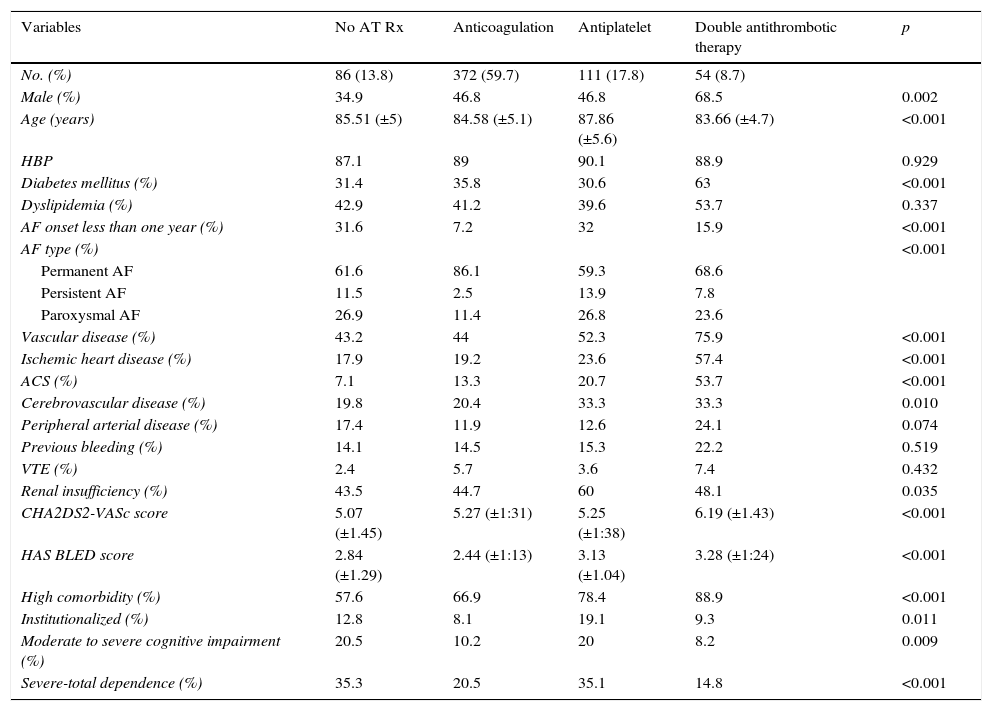
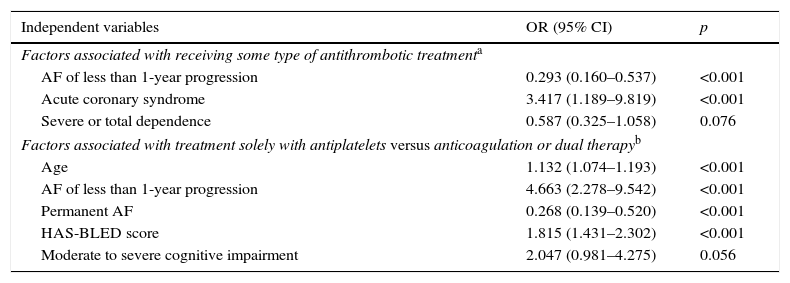
ResultsWe evaluated 804 patients with a mean age of 85 years (range 75–101), of which 53.9% were females. The prevalence of risk factors and cardiovascular disease was high: hypertension (87.6%), heart failure (65.4%), ischemic cardiomyopathy (24.4%), cerebrovascular disease (22.4%) and chronic kidney disease (45%). Among those cases with previous diagnoses of NVAF, antithrombotic treatment was prescribed in 86.2% of patients: anticoagulants (59.7%), antiplatelet medication (17.8%) and double therapy (8.7%). The factors associated with the use of antithrombotic treatment were history of acute coronary syndrome and atrial fibrillation progression longer than one year. Older age, atrial fibrillation for less than one year, higher HAS-BLED scores and severe cognitive impairment were associated with the use of anti-platelet drugs. Permanent atrial fibrillation favored the use of anticoagulants.
ConclusionsHospitalized patients older than 75 years old with NVAF showed numerous comorbidities. The percentage of anticoagulation was small and 18% received only anti-platelet therapy. The patient's age, atrial fibrillation's progression time and the severity of the cognitive impairment influenced this therapy choice.
La prevalencia de fibrilación auricular no valvular (FANV) aumenta con la edad y se asocia a alta morbimortalidad. El objetivo principal fue conocer las características de los pacientes ancianos con FANV hospitalizados y los factores clínico-funcionales que determinan la estrategia antitrombótica utilizada.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, prospectivo, multicéntrico realizado en pacientes mayores de 75 años con FANV, hospitalizados por cualquier causa en Medicina Interna.
ResultadosSe evaluaron 804 pacientes con una edad media de 85 años (rango: 75–101); el 53,9% fueron mujeres. La prevalencia de factores de riesgo y enfermedades vasculares fue elevada: hipertensión (87,6%), insuficiencia cardíaca (65,4%), cardiopatía isquémica (24,4%), enfermedad cerebrovascular (22,4%) e insuficiencia renal (45%). Entre los pacientes con diagnóstico previo al ingreso de FANV el 86,2% recibía tratamiento antitrombótico: anticoagulantes (59,7%), antiagregantes (AAG) (17,8%) y doble terapia (8,7%). Los factores asociados con la utilización del mismo fueron el antecedente de síndrome coronario agudo y la FANV de más de un año de evolución. Se asociaron con el uso de antiagregación la edad avanzada, la FANV de menos de un año de evolución, las puntuaciones superiores de HAS-BLED y el deterioro cognitivo grave. La fibrilación auricular permanente favorecía la prescripción de anticoagulantes.
ConclusionesLos pacientes mayores de 75 años con FANV hospitalizados en Medicina Interna tienen numerosas comorbilidades. El porcentaje de anticoagulación es escaso y un 18% recibe solo antiagregación, influyendo en su selección la edad, el tiempo de evolución de la fibrilación auricular y la gravedad del deterioro cognitivo.