The impact of carcinogenic infections on cancer-related mortality is unknown.
MethodsThe mortality due to cancers attributable to carcinogenic infections was estimated. The attributable fraction for the infectious agents classified as group 1 carcinogenic in human beings was applied to yearly data on causes of cancer mortality over the period 2013–2017 in Spain according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10).
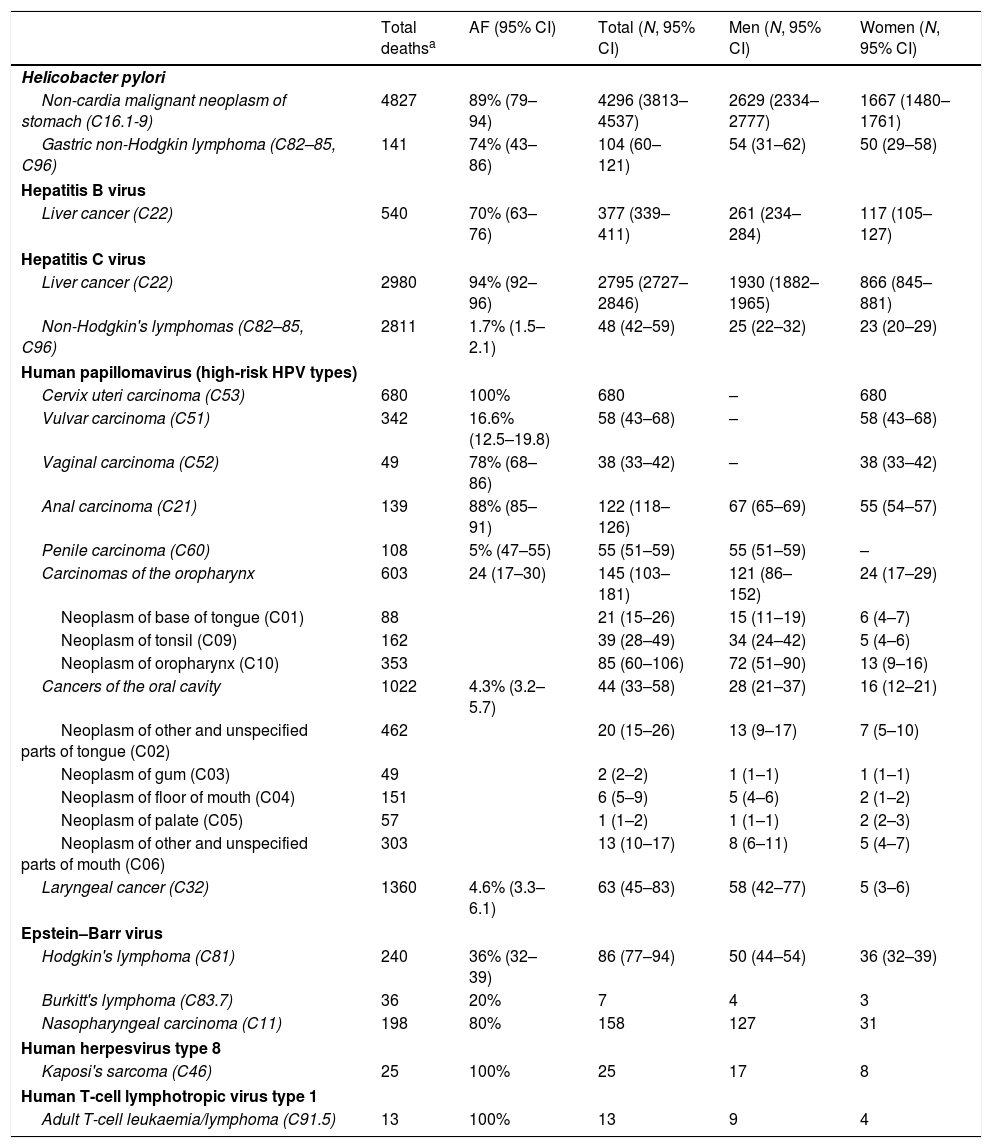
ResultsIt was estimated that 9115 deaths (over 110,287 cancer-related deaths, 8.3%) were attributable to infections caused by carcinogenic agents. The estimated number of deaths in men was 5434 (59.6%). The estimated mortality attributable to Helicobacter pylori infection accounted for 48.3% and four agents (H. pylori, HCV, HPV, and HBV) accounted for 96.8% of all cancer deaths attributable to carcinogenic infections. The burden of cancer-related mortality attributable to carcinogenic infections in Spain during the period 2013–2017 was approximately 8%.
ConclusionsIn Spain, one-twelfth of cancer deaths are attributable to carcinogenic infections. Public health measures aiming to reduce the impact of carcinogenic infections are essential.
El impacto de las infecciones carcinogénicas en la mortalidad por cáncer es desconocido.
MétodosSe estimó la mortalidad por cáncer atribuible a infecciones carcinogénicas en España. Se aplicó la fracción atribuible de los agentes infecciosos clasificados como carcinogénicos a los datos sobre causas de muerte por cáncer anuales del período 2013-2017 según la Clasificación Internacional de Enfermedades (CIE-10).
ResultadosDe 110.287 muertes por cáncer, se estimó que 9.115 (8,3%) fueron atribuibles a agentes infecciosos carcinogénicos en 2017. El número estimado de muertes en varones fue de 5.434 (59,6%). La mortalidad estimada por cáncer atribuible a infección por H. pylori representó el 48,3% y 4 agentes (H. pylori, VHC, VPH y VHB) registraron el 96,8% de todas las muertes por cáncer atribuible a infecciones carcinogénicas. La carga de mortalidad por cáncer atribuible a infecciones carcinogénicas en el período 2013-2017 en España fue del 8%, aproximadamente.
ConclusionesUna de cada 12 muertes por cáncer son atribuibles a infecciones carcinogénicas en España. Las medidas de salud pública son esenciales para reducir el impacto de las infecciones carcinogénicas.