Early detection of sepsis is a critical step to improve patient's survival and cellular markers effective diagnosis tools. The aim of this work was to evaluate HLA-DR expression on peripheral T-lymphocytes (CD3+), a marker associate to T-cell activation, as an early sepsis detection tool.
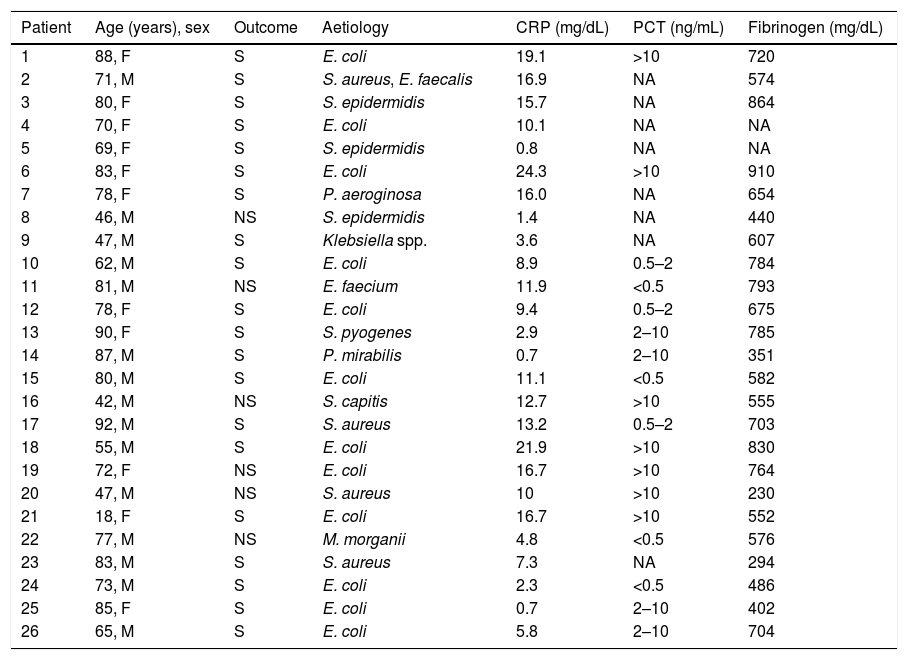
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional study was conducted in twenty-six patients with confirmed sepsis by blood culture, eighteen healthy individuals and four patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. The analysis of the HLA-DR expression was carried by flow cytometry.
ResultsThe patients with confirmed sepsis had significantly higher percentage of CD3+/HLA-DR+ lymphocytes compared with both, patients with SIRS (20.37±9.42 vs. 8.7±2.9; p<0.005) and healthy individuals (20.37±9.42 vs. 6.58±3.89; p<0.005). Moreover, the average amount of HLA-DR expressed was higher when caused by gram-positive than by gram-negative bacterias (216.61±131.35 vs. 135.05±31.82; p=0.041). A ROC curve analysis showed the utility of HLA-DR expression on T-cells to identify patients with sepsis.
DiscussionOur results suggest that surface expression of HLA-DR on T-lymphocytes could be an early marker for the presence of sepsis in non-surgical septic patients.
La detección temprana de la sepsis es un paso crítico para mejorar la supervivencia del paciente. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la expresión de HLA-DR en linfocitos T periféricos (CD3+), marcador asociado a la activación de células T, como herramienta de detección temprana de la sepsis.
Pacientes y métodosSe realizó un estudio en 26 pacientes con sepsis confirmada, 18 sanos y 4 con síndrome de respuesta inflamatoria sistémica(SIRS). La expresión de HLA-DR se midió por citometría de flujo.
ResultadosLos pacientes con sepsis tenían un porcentaje significativamente mayor de linfocitos CD3+/HLA-DR+ en comparación con los otros grupos, pacientes con SIRS (20,37±9,42 vs. 8,7±2,9; p<0,005) y sanos (20,37±9,42 vs. 6,58±3,89; p<0,005). La cantidad media de HLA-DR fue mayor cuando la sepsis estaba causada por bacterias gram-positivas que por gram-negativas (216,61±131,35 vs. 135,05±31,82; p=0,041). El análisis mediante curva ROC mostró la utilidad de la expresión de HLA-DR en células T para identificar pacientes con sepsis.
DiscusiónNuestros resultados sugieren que la expresión de HLA-DR en linfocitos T podría ser un marcador temprano de sepsis en pacientes sépticos no quirúrgicos.